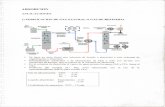
Sindrome de absorcion intestinal deficiente
-
Upload
jennifer-davila -
Category
Science
-
view
158 -
download
3
Transcript of Sindrome de absorcion intestinal deficiente

PEDIATRIA
DRA. SELENE I. LOPEZ CHANDOQUI
PRESENTADO POR:
JENNIFER XIOMARA HERNANDEZ DAVILA

DEFINICION
• Es todo aumento significativo de la frecuencia de evacuaciones (con o sin disminución de la
consistencia) con respecto a lo habitual del paciente.

DEFINICION Y CLASIFICACIÓN CON BASE A LA PRESENTACIÓN Y DURACIÓN
Diarrea aguda
Diarrea intratable
de la Infancia
Diarrea Prolongada
Diarrea Persistente.

CLASIFICACION FISIOPATOLÓGICA POR GRUPO Y EDAD:
• Conviene distinguir las diarreas secretoras de las diarreas osmóticas:
• DO: brecha osmolar >125 mOsm/l
• La DO sede con el reposo digestivo
• DS: brecha osmolar <50
• No sede al reposo digestivo.

0-30 días neonato
Abetalipoproteinemia
Alergia alimentaria
Diarrea sódica
enf. De hirsprung
Acrodermatitis enteropatica
Enteropatia autoinmune
Mala absorción congénita de sales biliares.
1 a 24 meses (lactante)
Enteropatia autoinmune
Fibrosis quística
Giardiasis
Sindrome pos entérico
Diarrea asociada a inmunodeficia
Diarrea fenotípica
2 años en adelante
Enfermedad celiaca
Sindrome pos entérico
Diarrea por desnutrición
Enfermedad de Crohn
Diarrea asociada a inmunodeficiencias
Sindrome de colon irritable

DIAREA SECRETORA
Diarrea por agentes infecciosos productores de enterotoxinas
Diarrea por síndrome paraneoplasico
Enteropatia autoinmune
DIARREA OSMOTICA
Mala absorción congénita de hidratos de carbono
Diarrea por mala absorción adquirida de hidratos de carbono
Diarrea por mala absorción adquirida de lípidos
Diarrea por malabsorción congénita de proteínas y aminoácidos
Enteropatías perdedora de proteína
Malabsorción por disminución de la suficiente absorción.

ABORDAJE DIAGNOSTICO
• En pacientes con diarrea prolongada que han recibido multiples antimicrobianos de amplio
espectro se favorece el sobrecrecimiento de clostridium difícile.
• Una DP en paciente eutrófico es sugestiva a la diarrea inespecífica del lactante con
evacuaciones liquidas o semilíquidas abundantes con restos alimentarios debido al transito
acelerado.

DESNUTRICIÓN ASOCIADA A DP:
• La Diarrea Prolongada Infecciosa (DPI):
1. Es mas frecuente
2. Etiología
3. Distintas manifestaciones
Bacteriana, parasitaria y viral.
Diarrea secretora o no, síndrome disenterico , síndrome de malabsorción
intestinal

“DIARREA SECRETORA”
Se asocia a agentes productores de entero toxinas que favorecen secreción intestinal como:
ETEC
aeromonas plesiomonas Vibrio colera Vibrio no colera
AL NO HABER DESTRUCCION DE MUCOSA NO HAY
SANGRE EN HECES

DIARREA SECRETORA + MOCO + SANGRE – SIN OTROS DATOS DEL SINDROME.
CAUSAS
INFECCIOSAS NO
INFECCIOSAS

1.1 CAUSAS INFECCIOSAS
SE PRESENTA CON: Fiebre Dolor abdominal Evacuaciones sin
sangre
Moco Leucocitos en heces
Elevacion de la velocidad de
sedimentación globular y proteína c
reactiva

Las bacterias son:
Salmonella (especies)
Shigella
Campilobacter
Yersina
Escherichia coliEntero invasiva
Giardia
Cryptosporidium
Isospora Belli
E. Histolytica

TUMOR UBICACION HORMONA CC TX
APUDOMAS
Vipoma Pancreas Peptido intestinal vasoactivo
DS, acloridria e hipokalemica
Somatostatina/ resección
Gastrioma Pancreas Gastrina Ulcera péptica y DS Somatostatina/ resección
Tumor carcinoide Celulas agentafinicasintestinales
Histamina y péptido intestinal vasoactivo
Dolor abdominal,eritrodermia, DS
Somatostatina
Mastocitoma Intestino, hígado, bazo,piel.
Histamina, VIP Prurito, eritema, diarrea
Bloqueadores H1 y H2, esteroides
Carcinoma medular Tiroides Calcitonina, VIP, prostaglandinas
DS Tiroidectomia
TUMORES NEUROGENICOS
Ganglioneurma, ganglioneuro,blastoma.
Suprarrenales y cavidad abdominal
Catecolaminas, VIP DS masiva acuosa Reseccion
Feocromocitoma Celulas cromafines Catecolaminas VIP Hipertension arterial,taquicardia, diaforesis, DS
Reseccion

1.2 CAUSAS NO INFECCIOSAS
Alergia alimentaria
Enfermedades inflamatorias intestinales

ALERGIA ALIMENTARIAS ASOCIADA A DIARREA PROLONGADA
• SE DEBEN DE DISTINGUIR REACCIONES MEDIADAS POR IGE DE LAS MEDIADAS POR
LIFONCITOS T.
IGE
REACCION ANAFILACTICA
SINDROME DE ALERGIA ORAL
ESOFAGITIS ALERGICA EOSINOFILICA
CELULAS
PROCTOCOLITIS INDUCIDA POR ALIMENTOS CON SANGRE MACROSCOPICA U OCULTA EN HECES
GASTROENTERITIS ALERGICA
ENFERMEDAD CELIACA

ALERGIA ALIMENTARIA:
DERMATITIS ATOPICA
ECZEMA URTICARIA RINITIS
ALERGICA ASMA

DIAGNOSTICO:
• PRUEBAS CUTANEAS
• PRUEBAS INMUNOLOGICAS
A) IGE TOTAL EN SUERO DEL PACIENTE
B) MEDICION DE IGE ESPECIFICAS
• PRUEBA D-XILOSA.

INTOLERANCIA A CARBOHIDRATOS
• EVACUACIONES LIQUIDAS Y EXPLOSITIVAS CON PH FECAL <5
• OBSERVAN: LESIONES PERIANALES SECUNDARIAS A LA ACIDEZ DE LAS HECES
• ES MUY RARA
• PUEDE SER SECUNDARIA A UN PROCESO INFECCIOSO

DIARREA POR DEFICIENTE DIGESTION INTRALUMINAL DE LIPIDOS
EVACUACIONES PASTOSAS
MAS BLANDAS QUE LIQUIDAS
HOMOGENEAS O GRASOSAS
PALIDAS “ COMO MASTIQUE”
ESTEATORREA AISALADA O ASOCIADA
PRESENCIA DE EDEMA
GENERALIZADO

SOSPECHA DE INSUFICIENCIA PANCREATICA:
PRIMERO SE DEBE DE DESCARTAR
FIBROSIS QUISTICA (PRUEBA DE
ELECTROLITOS EN SUDOR…
SINDROME DE SCHWACHMAN
SINDROME DE JOHANSON BLIZZARD
SINDROME DE PEARSON

SI NO HAY INSUFICIENCIA PANCREATICA S DEBE DE SOSPECHAR EN:
• FALTA DE REABSORCION DE LAS SALES BILIARES EN ILEON
• FALTA DE SECRECION DE BILIS A LA LUZ INTESTINAL
• DEFECTO CONGENITO EN LA SINTESIS DE SALES BILEARES.

DIARREA POR DIGESTION ALTERADA O MALABSORCION DE PROTEINAS
• LA SOSPECHA SE ESTABLECE POR EDEMA (FOCAL O GENERALIZADO) ASOCIADO A DP.
• SE PRESENTA HIPOALBUMINEMIA
• IGG BAJA
• IGA E IGM NORMALES O POCO AFECTADAS.

CAUSA DEL AUMENTO DE LA PERMEABILIDAD INTESTINAL A LAS PROTEINAS:
INFLAMACION INTESTINAL
POLIPOSIS INTESTINAL
LINFANGIECTASIAS PRIMARIAS
LINFANGIECTASIAS SECUNDARIAS ASOCIADAS A CIRUGIA DE
FONTAN
LINFANGIETASIAS SECUNDARIAS DE
OBSTRUCCION DEL FLUJO LINFATICO

LACTANTES CON ENFERMEDAD CELIACA:
• RETRASO PSICOMOTOR
• APATIA
• ANOREXIA
• DESNUTRICION
• DOLOR ABDOMINAL
• METEORISMO
• ANEMIA
ESCOLARES ESTREÑIMIENTO Y TALLA BAJA
LA INTOLERANCIA A LA LACTOSA ES FRECUENTE.

DIARREA PROLONGADA ASOCIADA A INMUNODEFICIENCIAS
SE DEBEN ANTE UNA HISTORIA DE INFECCIONES DE REPETICION.
PACIENTES CON SIDA:
CRYPTOSPORIDIUM
BLASTOMYCIS
COCCIDIA
MYCOBACTERUM AVIUM INTRACELULARE
ISOSPORA BELLI
CANDIDA ALBICANS

TRATAMIENTO DE DP:
1) TRATAMIENTO PARA LA DESIHIDRATACION:
PLAN A : Dar 1 taza (150 ml) después de cada evacuación en niños mayores de 1 año y media taza (75 ml) después de cada evacuación
en niños menores de 1 año Se ofrece a cucharaditas o sorbos
PLAN B (100 ML EN 4 HORAS/ 30 MIN/8 TOMAS)
PLAN C: Primera hora : 50 ml/kg/hora Segunda hora : 25 ml/Kg/hora Tercera hora : 25 ml/Kg/hora

SALMONELLA:
• LOS ANTIMICROBIANOS EN CASOS POCOS SEVEROS FAVORECEN EL ESTADO DEL
PORTADOR Y LA SELECCIÓN DE CEPAS MULTIRESISTENTES: POR LO QUE ESTOS SE
DEBEN DE INDICAR SOLO EN:
GASTROENTERITIS POR SALMONELLA EN MENORES DE 3
MESES
FIEBRE TIFOIDEABACTEREMIA POR
CEPAS NO TIFOIDICAS
DISEMINACION DE LA INFECCION
PACIENTES CON RESPUESTA
INMUNE DISMINUIDA.

SALMONELLA + SIDA
USAR UNA CEFALOSPORINA DE TERCERA GENERACION
O AMPICILINA (DEPENDIENDO EL
AGENTE)
EN CASOS DE BACTEREMIA SIN FOCO INFECCIOSO:
SE ADMINISTRA CEFTRIAXONA POR 14 DIAS
BACTEREMIA CON FOCO INFECCIOSO:
TRATAMIENTO SE EXTIENDE A 4 O 6
SEMANAS.

SALMONELLA + SIDA+ PATOLOGIA VESICULA BILIAR
SE ADMINISTRA CIPROFLOXACINA

CAMPYLOBACTER JEJUNI: • Indicación de antimicrobianos:
CUADROS SEVEROS CON:
FIEBRE ELEVADA
DIARREA SANGUINOLENTA O SEVERA
Farmaco de primera elección: ERITROMICINA
Cepas resistentes: CIPROFLOXACIONA
Farmaco alternativo: AZITROMICINA Y CLORANFENICOL
EN CASO DE AISARSE EL CAMPULOBACTER SE DELEGIRA GENTAMICINA O EL IMIPENEM

GIARDIASIS
• ESTE PROTOZOARIO ES SENSIBLE A METRONIDAZOL, FURAZOLIDONA Y PARAMOMICINA

CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE:
• CASOS POCOS SEVEROS:
SUSPENSIÓN DE LOS ANTIBIOTICOS Y MANEJO DE SOPORTE PARA EVITAR LA
DESIHIDRATACION
• FARMACO DE PRIMERA ELECCION:
METRONIDAZOL EN CASO DE RESISTENCIA USAR: VANCOMICINA

MANEJO NUTRICIONAL:
Diarreas sin impacto del crecimiento
Sindrome de colon irritable
Falsa diarrea del estreñido
Diarrea con impacto
nutricional
Diarreas crónico especificas del
lactante

MANEJO NUTRICIONAL
Casos específicos
Lactantes no ablactados
Pacientes ablactados

NUTRICION EN TRANSTORNOS ESPECÍFICOS ASOCIADOS A DP:
INTOLERANCIA CONGENITA A LA LACTOSA
INTOLERANCIA A LA GLUCOSA- GALACTOSA
INTOLERANCIA A LA GALACTOSA
ENFERMEDAD INFLAMATORIA INTESTINAL

INTOLERANCIA CONGENITA A LA LACTOSA
• FORMULA SIN LACTOSA Y ABLACTACION LIBRE DE LACTOSA
• SU TOLERANCIA AUMENTA CON LA EDAD
• LOS LACTEOS SE INTRODUCIRAN CUANDO YA NO PRESENTEN EL MAYOR APORTE
ENERGETICO.

INTOLERANCIA A LA GLUCOSA-GALACTOSA:
INTRODUCCION SUBSECUENTE DE NUTRICION ENTERAL EN FORMA A BASE DE FRUCTOSA.
LA TOLERANCIA MEJORA CON LA EDAD SIN NUNCA SER NORMAL.
ABLACTACION ENTRE LS 6 Y 12 MESES DE EDAD.
INTRODUCCION DE ALMIDONES PAULATINA.

INTOLERANCIA A LA GALACTOSA:
FORMULA LIBRE DE LACTOSA
DIETA: EXCLUYE LECHE Y
DERIVADOS PARA EVITAR COMPLICACIONES COMO LA
FORMACION DE CATARATAS Y DAÑO HEPATICO.
Excluir: Suero de leche, caseína, lactosa,
lactoglubulina y caseinato.

ENFERMEDAD INFLAMATORIA INTESTINAL:
• Cursan con deficiencias en folatos, vitaminas B12, A, D, E y K, calcio, zinc, y de hierro.

Diarreas secretoras no infecciosas
Alteraciones constitutivas de la mucosa intestinal
Entorpatiaautoinmune
DP por síndrome paraneoplasico
Enteropatiaperdedora de proteína
sin alteraciones del flujo linfático
EPP con alteraciones del flujo linfatico

DIARREA+ MOCO+ SANGRE:
• Signos y síntomas:
FIEBRE
DOLOR ABDOMINAL
EVACUACIONES CON SANGRE
MOCO
LEUCOCITOS EN HECES
SX INFLAMATORIO

• BACTERIAS:
SALMONELLA
SHIGELLA
CAMPILOBACTER
YERSINA
ESTERICHIA COLI ENTERO INVASIVA