SIckle Cell
-
Upload
kaila-wilson -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
description
Transcript of SIckle Cell

Sickle Cell Anemia
By: Kaila Wilson

What is Sickle Cell…• Sickle cell anemia is a condition where your blood
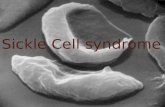
cells are abnormally shaped• Inherited disease• Body makes abnormal hemoglobin– Hemoglobin sticks together while transporting oxygen
to body tissues– The clumps are like liquid fibers which cause the RBCs
to become stiff and sickle shaped• Most common in: Africans, Central and South
Americans, Cubans, Indians, Saudi Arabians, Mediterraneans, and Hispanics.

History
• First appeared in African tribes• First case was formally reported in 1910


Signs and Symptoms• Fatigue• Shortness of breath• Dizziness• Headache• Coldness in hands and
feet• Pale skin• Chest pain• Delayed growth and
puberty
• Jaundice• Fever• Excessive thirst• Poor eyesight or
blindness• Leg ulcers• Rapid heart rate• Pain in abdominal area,
joints, and bones

Sickle Cell Crisis

Treatments

Prevention

Everyday Life

Point of View

Statistics
• 30% of Jamaican patients with sickle cell develop ulcers where as it’s only 1% for American ones.—It is estimated the up to 80,000 people in America have
Sickle Cell Disease—1/500 African Americans have Sickle Cell Disease—1/1000 -4000 Hispanics have Sickle Cell —1/12 African Americans are carriers for Sickle Cell —1/50 Asians are carriers for Sickle Cell—1/100 Greeks are carriers for Sickle Cell