Seventh Edition Elaine N. Marieb - Ms. Rickard's...
Transcript of Seventh Edition Elaine N. Marieb - Ms. Rickard's...

Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Slides 3.1 – 3.19
Seventh Edition Elaine N. Marieb
Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues
Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook

Cells and Tissues
Slide 3.1 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
• Cells are the building blocks of all living things
• Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and function

Anatomy of the Cell
Slide 3.2 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
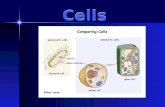
• Cells are not all the same • All cells share general structures • Cells are organized into three main
regions •Nucleus •Cytoplasm •Plasma membrane
Figure 3.1a

The Nucleus
Slide 3.3 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Control center of the cell •Contains genetic
material (DNA)
• Three regions •Nuclear
membrane
•Nucleolus
•Chromatin Figure 3.1b

Nuclear Membrane
Slide 3.4 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Barrier of nucleus
• Consists of a double phospholipid membrane
• Contain nuclear pores that allow for exchange of material with the rest of the cell

Nucleoli
Slide 3.5 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Nucleus contains one or more nucleoli
• Sites of ribosome production
• Ribosomes then migrate to the cytoplasm through nuclear pores

Chromatin
Slide 3.6 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Composed of DNA and protein
• Scattered throughout the nucleus
• Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes when the cell divides

Plasma Membrane
Slide 3.7a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Barrier for cell contents • Double phospholipid layer
•Hydrophilic heads •Hydrophobic tails
• Other materials in plasma membrane •Protein •Cholesterol •Glycoproteins

Plasma Membrane
Slide 3.7b Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.2

Plasma Membrane Specializations
Slide 3.8a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Microvilli •Finger-like
projections that increase surface area for absorption
Figure 3.3

Plasma Membrane Specializations
Slide 3.8b Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Membrane junctions •Tight junctions
•Desmosomes
•Gap junctions
Figure 3.3

Cytoplasm
Slide 3.9 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Material outside the nucleus and inside the plasma membrane •Cytosol •Fluid that suspends other elements
•Organelles •Metabolic machinery of the cell
• Inclusions •Non-functioning units

Cytoplasmic Organelles
Slide 3.10 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.4

Cytoplasmic Organelles
Slide 3.11 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Ribosomes •Made of protein and RNA •Sites of protein synthesis •Found at two locations •Free in the cytoplasm •Attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum

Cytoplasmic Organelles
Slide 3.12 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) • Fluid-filled tubules for carrying substances • Two types of ER •Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
• Studded with ribosomes • Site where building materials of cellular
membrane are formed •Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
• Functions in cholesterol synthesis and breakdown, fat metabolism, and detoxification of drugs

Cytoplasmic Organelles
Slide 3.13a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Golgi apparatus •Modifies and packages proteins •Produces different types of packages •Secretory vesicles •Cell membrane components •Lysosomes

Cytoplasmic Organelles
Slide 3.13b Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.5

Cytoplasmic Organelles
Slide 3.14 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Lysosomes •Contain enzymes that digest nonusable
materials within the cell • Peroxisomes
•Membranous sacs of oxidase enzymes •Detoxify harmful substances •Break down free radicals
(highly reactive chemicals) •Replicate by pinching in half

Cytoplasmic Organelles
Slide 3.15 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Mitochondria • “Powerhouses” of the cell
• Change shape continuously
• Carry out reactions where oxygen is used to break down food
• Provides ATP for cellular energy

Cytoplasmic Organelles
Slide 3.16a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Cytoskeleton •Network of protein structures that extend
throughout the cytoplasm
•Provides the cell with an internal framework

Cytoplasmic Organelles
Slide 3.16b Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Cytoskeleton •Three different types
• Microfilaments
• Intermediate filaments
• Microtubules
Figure 3.6

Cytoplasmic Organelles
Slide 3.17 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Centrioles •Rod-shaped bodies made of microtubules
•Direct formation of mitotic spindle during cell division

Cellular Projections
Slide 3.18 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Not found in all cells
• Used for movement •Cilia moves materials across the cell
surface
•Flagellum propels the cell

Cell Diversity
Slide 3.19a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.7; 1, 2

Cell Diversity
Slide 3.19b Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.7; 3

Cell Diversity
Slide 3.19c Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.7; 4, 5

Cell Diversity
Slide 3.19d Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.7; 6, 7

Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Slides 3.20 – 3.37
Seventh Edition Elaine N. Marieb
Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues
Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook

Cellular Physiology: Membrane Transport
Slide 3.20 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Membrane Transport – movement of substance into and out of the cell
• Transport is by two basic methods •Passive transport •No energy is required
•Active transport •The cell must provide metabolic energy

Solutions and Transport
Slide 3.21 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Solution – homogeneous mixture of two or more components •Solvent – dissolving medium •Solutes – components in smaller quantities
within a solution • Intracellular fluid – nucleoplasm and
cytosol • Interstitial fluid – fluid on the exterior of
the cell

Selective Permeability
Slide 3.22 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• The plasma membrane allows some materials to pass while excluding others
• This permeability includes movement into and out of the cell

Passive Transport Processes
Slide 3.23 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Diffusion •Particles tend to distribute themselves evenly
within a solution •Movement is
from high concentration to low concentration, or down a concentration gradient
Figure 3.8

Passive Transport Processes
Slide 3.24a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Types of diffusion •Simple diffusion
•Unassisted process
•Solutes are lipid-soluble materials or small enough to pass through membrane pores

Passive Transport Processes
Slide 3.24b Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Types of diffusion •Osmosis – simple diffusion of water
•Highly polar water easily crosses the plasma membrane
•Facilitated diffusion
•Substances require a protein carrier for passive transport

Diffusion through the Plasma Membrane
Slide 3.25 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.9

Passive Transport Processes
Slide 3.26 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Filtration •Water and solutes are forced through a
membrane by fluid, or hydrostatic pressure
•A pressure gradient must exist
•Solute-containing fluid is pushed from a high pressure area to a lower pressure area

Active Transport Processes
Slide 3.27 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Transport substances that are unable to pass by diffusion • They may be too large • They may not be able to dissolve in the fat core
of the membrane • They may have to move against a concentration
gradient • Two common forms of active transport
•Solute pumping •Bulk transport

Active Transport Processes
Slide 3.28a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Solute pumping •Amino acids, some sugars and ions are
transported by solute pumps
•ATP energizes protein carriers, and in most cases, moves substances against concentration gradients

Active Transport Processes
Slide 3.28b Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.10

Active Transport Processes
Slide 3.29a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Bulk transport •Exocytosis •Moves materials out of the cell •Material is carried in a membranous vesicle •Vesicle migrates to plasma membrane •Vesicle combines with plasma membrane •Material is emptied to the outside

Active Transport Processes
Slide 3.29b Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.11

Active Transport Processes
Slide 3.30a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Bulk transport •Endocytosis
•Extracellular substances are engulfed by being enclosed in a membranous vescicle
•Types of endocytosis
•Phagocytosis – cell eating
•Pinocytosis – cell drinking

Active Transport Processes
Slide 3.30b Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.12

Cell Life Cycle
Slide 3.31 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Cells have two major periods • Interphase
•Cell grows
•Cell carries on metabolic processes
•Cell division
•Cell replicates itself
•Function is to produce more cells for growth and repair processes

DNA Replication
Slide 3.32 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Genetic material duplicated and readies a cell for division into two cells
• Occurs toward the end of interphase
• DNA uncoils and each side serves as a template
Figure 3.13

Events of Cell Division
Slide 3.33 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Mitosis •Division of the nucleus •Results in the formation of two daughter
nuclei • Cytokinesis
•Division of the cytoplasm •Begins when mitosis is near completion •Results in the formation of two daughter
cells

Stages of Mitosis
Slide 3.34a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Interphase •No cell division occurs
•The cell carries out normal metabolic activity and growth
• Prophase •First part of cell division
•Centromeres migrate to the poles

Stages of Mitosis
Slide 3.34b Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Metaphase •Spindle from centromeres are attached to
chromosomes that are aligned in the center of the cell

Stages of Mitosis
Slide 3.35 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Anaphase •Daughter chromosomes are pulled toward
the poles
•The cell begins to elongate
• Telophase •Daughter nuclei begin forming
•A cleavage furrow (for cell division) begins to form

Stages of Mitosis
Slide 3.36a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.14; 1

Stages of Mitosis
Slide 3.36b Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.14; 2

Protein Synthesis
Slide 3.37 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Gene – DNA segment that carries a blueprint for building one protein
• Proteins have many functions •Building materials for cells
•Act as enzymes (biological catalysts)
• RNA is essential for protein synthesis

Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Slides 3.38 – 3.54
Seventh Edition Elaine N. Marieb
Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues
Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook

Protein Synthesis
Slide 3.37 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Gene – DNA segment that carries a blueprint for building one protein
• Proteins have many functions •Building materials for cells
•Act as enzymes (biological catalysts)
• RNA is essential for protein synthesis

Role of RNA
Slide 3.38 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Transfer RNA (tRNA) •Transfers appropriate amino acids to the
ribosome for building the protein • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
•Helps form the ribosomes where proteins are built
• Messanger RN •Carries the instructions for building a
protein from the nucleus to the ribosome

Transcription and Translation
Slide 3.39 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Transcription •Transfer of information from DNA’s base
sequence to the complimentary base sequence of mRNA
• Translation •Base sequence of nucleic acid is translated
to an amino acid sequence
•Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins

Protein Synthesis
Slide 3.40 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.15

Body Tissues
Slide 3.41 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Cells are specialized for particular functions • Tissues
•Groups of cells with similar structure and function
•Four primary types •Epithelium •Connective tissue •Nervous tissue •Muscle

Epithelial Tissues
Slide 3.42 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Found in different areas •Body coverings •Body linings •Glandular tissue
• Functions •Protection •Absorption •Filtration •Secretion

Epithelium Characteristics
Slide 3.43 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Cells fit closely together • Tissue layer always has one free
surface • The lower surface is bound by a
basement membrane • Avascular (have no blood supply) • Regenerate easily if well nourished

Classification of Epithelium
Slide 3.44a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Number of cell layers •Simple – one layer
•Stratified – more than one layer
Figure 3.16a

Classification of Epithelium
Slide 3.44b Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Shape of cells •Squamous – flattened
•Cuboidal – cube-shaped
•Columnar – column-like
Figure 3.16b

Simple Epithelium
Slide 3.45 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Simple squamous •Single layer of flat
cells •Usually forms
membranes •Lines body
cavities •Lines lungs and
capillaries Figure 3.17a

Simple Epithelium
Slide 3.46 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Simple cuboidal •Single layer of
cube-like cells •Common in
glands and their ducts
•Forms walls of kidney tubules
•Covers the ovaries Figure 3.17b

Simple Epithelium
Slide 3.47 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Simple columnar •Single layer of tall
cells
•Often includes goblet cells, which produce mucus
•Lines digestive tract
Figure 3.17c

Simple Epithelium
Slide 3.48 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Pseudostratified •Single layer, but
some cells are shorter than others
•Often looks like a double cell layer
•Sometimes ciliated, such as in the respiratory tract
•May function in absorption or secretion
Figure 3.17d

Stratified Epithelium
Slide 3.49 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Stratified squamous •Cells at the free edge
are flattened •Found as a protective
covering where friction is common
•Locations •Skin •Mouth •Esophagus Figure 3.17e

Stratified Epithelium
Slide 3.50 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Stratified cuboidal • Two layers of cuboidal cells
• Stratified columnar • Surface cells are columnar, cells
underneath vary in size and shape • Stratified cuboidal and columnar
• Rare in human body • Found mainly in ducts of large glands

Stratified Epithelium
Slide 3.51 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Transitional epithelium •Shape of cells
depends upon the amount of stretching
•Lines organs of the urinary system
Figure 3.17f

Glandular Epithelium
Slide 3.52 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Gland – one or more cells that secretes a particular product
• Two major gland types •Endocrine gland •Ductless •Secretions are hormones
•Exocrine gland •Empty through ducts to the epithelial surface • Include sweat and oil glands

Connective Tissue
Slide 3.53 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Found everywhere in the body
• Includes the most abundant and widely distributed tissues
• Functions •Binds body tissues together
•Supports the body
•Provides protection

Connective Tissue Characteristics
Slide 3.54 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Variations in blood supply •Some tissue types are well vascularized
•Some have poor blood supply or are avascular
• Extracellular matrix •Non-living material that surrounds living
cells

Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Slides 3.55 – 3.73
Seventh Edition Elaine N. Marieb
Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues
Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook

Extracellular Matrix
Slide 3.55 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Two main elements •Ground substance – mostly water along
with adhesion proteins and polysaccharide molecules
•Fibers •Produced by the cells •Three types
•Collagen fibers •Elastic fibers •Reticular fibers

Connective Tissue Types
Slide 3.56 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Bone (osseous tissue) •Composed of: •Bone cells in lacunae
(cavities) •Hard matrix of calcium
salts •Large numbers of
collagen fibers •Used to protect and
support the body Figure 3.18a

Connective Tissue Types
Slide 3.57 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Hyaline cartilage •Most common
cartilage •Composed of: •Abundant collagen
fibers •Rubbery matrix
•Entire fetal skeleton is hyaline cartilage Figure 3.18b

Connective Tissue Types
Slide 3.58a Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Elastic cartilage •Provides elasticity
•Example: supports the external ear

Connective Tissue Types
Slide 3.58b Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Fibrocartilage •Highly compressible
•Example: forms cushion-like discs between vertebrae
Figure 3.18c

Connective Tissue Types
Slide 3.59 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Dense connective tissue •Main matrix element
is collagen fibers •Cells are fibroblasts •Examples • Tendon – attach
muscle to bone • Ligaments – attach
bone to bone Figure 3.18d

Connective Tissue Types
Slide 3.60 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Areolar connective tissue •Most widely
distributed connective tissue
•Soft, pliable tissue •Contains all fiber
types •Can soak up excess
fluid Figure 3.18e

Connective Tissue Types
Slide 3.61 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Adipose tissue •Matrix is an areolar tissue in which fat
globules predominate •Many cells contain
large lipid deposits •Functions • Insulates the body • Protects some organs • Serves as a site of
fuel storage Figure 3.18f

Connective Tissue Types
Slide 3.62 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Reticular connective tissue •Delicate network of
interwoven fibers • Forms stroma
(internal supporting network) of lymphoid organs • Lymph nodes •Spleen •Bone marrow
Figure 3.18g

Connective Tissue Types
Slide 3.63 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Blood •Blood cells
surrounded by fluid matrix
•Fibers are visible during clotting
•Functions as the transport vehicle for materials
Figure 3.18h

Muscle Tissue
Slide 3.64 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Function is to produce movement • Three types
•Skeletal muscle •Cardiac muscle •Smooth muscle

Muscle Tissue Types
Slide 3.65 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Skeletal muscle •Can be controlled
voluntarily •Cells attach to
connective tissue •Cells are striated •Cells have more than
one nucleus Figure 3.19b

Muscle Tissue Types
Slide 3.66 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Cardiac muscle • Found only in the
heart • Function is to pump
blood (involuntary) •Cells attached to
other cardiac muscle cells at intercalated disks
•Cells are striated •One nucleus per cell Figure 3.19c

Muscle Tissue Types
Slide 3.67 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Smooth muscle • Involuntary muscle •Surrounds hollow
organs •Attached to other
smooth muscle cells •No visible striations •One nucleus per cell
Figure 3.19a

Nervous Tissue
Slide 3.68 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Neurons and nerve support cells
• Function is to send impulses to other areas of the body • Irritability
•Conductivity Figure 3.20

Tissue Repair
Slide 3.69 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Regeneration •Replacement of destroyed tissue by the
same kind of cells • Fibrosis
•Repair by dense fibrous connective tissue (scar tissue)
• Determination of method •Type of tissue damaged •Severity of the injury

Events in Tissue Repair
Slide 3.70 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Capillaries become very permeable • Introduce clotting proteins •Wall off injured area
• Formation of granulation tissue • Regeneration of surface epithelium

Regeneration of Tissues
Slide 3.71 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Tissues that regenerate easily •Epithelial tissue • Fibrous connective tissue and bone
• Tissues that regenerate poorly •Skeletal muscle
• Tissues that are replaced largely with scar tissue •Cardiac muscle •Nervous tissue within the brain and spinal cord

Developmental Aspects of Tissue
Slide 3.72 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
• Epithelial tissue arises from all three primary germ layers
• Muscle and connective tissue arise from the mesoderm
• Nervous tissue arises from the ectoderm
• With old age there is a decrease in mass and viabililty in most tissues