SAP Variant configuration
-
Upload
kumbum-ramesh -
Category
Technology
-
view
1.945 -
download
136
description
Transcript of SAP Variant configuration

VARIANT CONFIGURATION
Prepared by : Ramesh Kumbum

Training Agenda
Target Audience
Overview of Variant configuration
Cross module integration
Process steps
Master Data
Characteristic and Class
Configuration profile
Configuration stimulation
Object dependencies
Training Manuals
Q&A

Target Audience
Primary: SAP SD Consultants SAP PP Consultants SAP Solution Architects
Secondary Other SAP Consultants Delivery Team

OVERVIEWOVERVIEW

VARIANT CONFIGURATION OVERVIEW
Variant configuration is useful if you have large number of
combination of parts that go into a product. It means
different permutations and combinations of the parts of
the same material
Example:
A Customer ordering a computer can choose
different
combinations of monitor ,CPU, keyboard.
A customer ordering a car can choose different
combinations of accessories and colors.

VARIANT CONFIGURATION-OVERVIEW
Variant Configuration is a tool which improves information
exchange between sales,engineering and production.
Variant configuration helps sales person to put together
specification for the product, so that product can be
produced from these specifications.
Variant configuration is for manufacturing complex product
which contains various characteristics and variants

What is Configurable Product???
VARIANT CONFIGURATION-OVERVIEW

Wrist
• Wrist IW 49 II
• Wrist IW 90 II
Enhancements
• YES
• NO
Arm Type
• Arm type 30-K/1
• Arm type 60-K/1
• Arm type 60L45-K/1
Type of Intermediate Plate
• Intermediate plate with pin
• Intermediate plate w/o pin
Power Supply
• 160 V
• 230 V
• 430 V
No. of Employees to be Trained
• 3• 5• 15
EXAMPLE FOR VARIANT CONFIGURATION

EXAMPLE FOR VARIANT CONFIGURATION

VARIANT CONFIGURATION INDUSTRIES
new industries - new requirements...
Aircrafts
Automotive
Elevators
Gear units
Telecommunication
High-Tech
Food
Steel Chemicals

CROSS MODULE INTEGRATION

MASTER DATA FOR VC
Super BOM
Super Routing
Characteristic and Values
Classification
Object Dependency
Configurable Profile
Configuration stimulation
SD Condition Records

MODELING VARIANT CONFIGURATION

KMAT VS FERT?
FERT KMAT
Non-Variant Parts
Non-Variant Parts
Variant Parts

PROCESS STEPS
Process steps
1 Creating Sales Order
2 Checking Requirements using MRP
3 Requirements Planning
4 Converting the planed order into a Production order
5 Confirming the production order
6 Checking the production order settlement
7 Creating the delivery
8 Creating the billing document

CONFIGURATION OF VC
Create a Material - KMAT type with Item category (002)
Create characteristics
Assign Characteristics to class
Assign the class to material master
Creating a configuration profile
Configuration stimulation
Assign object dependences

Master data settings:
Basic data 2 : Set Material is Configurable indicator
To determine item category TAC in sales order, maintain the
suitable item category such as 0002
MRP 2 View: set Procurement type E
MRP 3 View :Set strategy group 25: Make to order for
configuration
MRP3 :set Availability check 02 ;Individual Requirement
Class view ; Attach the variant class
Master data settings for VC

Master data settings:
Master data settings for VC

Master data settings:
Master data settings for VC

Master data settings:
Master data settings for VC

Master data settings for VC

Master data settings for VC

Master data settings for VC

Master data settings for VC

Master data settings for VC

Master data settings for VC

Master data settings for VC

T.Code :CS01
Bill of Material

CHARACTERISTIC AND VALUES
Characteristics describe the properties of objects.
The values of a characteristic specify these properties.
Example Material - PC
Chracteristic ValuesRAM 256 MB,512 MB,
1 GB Hard Disk 80 GB,120 GB,160 GB
Chracteristic Value can be Numeric ,Characters,Date and Time and Currency format.
It can be single or multi value or restrict value.

Screens for maintaining the characteristic

Reference characteristics are characteristics that refers to tables &fields
Tables and structures whose fields values can be changed by
dependencies
SDCOM-Communication between the SD and Variant configuration
VCSD_UPDATE: Table for updating sales documents from the
configuration
Reference Characteristics

Create the Characteristic and values
T.code:CT04

T.code:CT04
Create the Characteristic and values

Create the Variant pricing Characteristic

T.code:CT04
Create the Variant pricing Characteristic
Table SDCOM, Field VKOND

CLASS AND CLASS TYPE
A Class is used to hold the characteristics that describe
about configurable material.
Class type used to determines which object types can be
classified.
Class types 200 and 300 are defined for material which are
used in variant configuration/Classification .

Create classes type 300 assign characteristics

Create classes type 300 assign characteristics

Screens for maintaining the classes

Assign class to material
T.codeCL24N

Assign class to material

CONFIGURATION PROFILE
Configurable Profile is used for assigning one or more variant classes to configurable material.
A configurable material has several profiles.Profile is selected during configuration or according to priority.
It also possible to define central settings for Configurable Object.

CONFIGURATION PROFILE CONTD..

Create Configuration profile
T.Code .
T.Code :cu41

T.Code .
T.Code :cu41
Create Configuration profile

Create Configuration profile

Create Configuration profile

Create Configuration profile

Tcode:CU41
Create Configuration profile

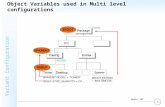
ASSIGN DEPENDENCIES

CONFIGURATION SIMULATION
Configuration simulation to check configuration model.
In the configuration simulation, one can test whether it has
created the objects correctly and whether dependencies
work.

CONFIGURATION SIMULATION
Tcode:CU50

CONFIGURATION SIMULATION

CONFIGURATION SIMULATION

CONFIGURATION SIMULATION

1. Select Characteristic Value
2. Press ' Assign Variant Condition' button.
3. Enter Variant Key
4. Save
CONFIGURATION SIMULATION

,
T.Code .
T.Code :VK30
Create Variant Keys with any Name and Description

T.Code .
T.Code :VK11
Create Variant Condition with Variant Price

T.Code .
T.Code :VK11
Create Variant Condition with Variant Price

Material Variant in sales order
Tcode:VA01

Material Variant in sales order

SECOND DAY

DEPENDENCIES
Super BOM contains all the required and Variable items. From the variable items required items will be selected which are Matching the characteristic value.

DEPENDENCIES TYPE
The following types of dependencies are available in VC
Preconditions
Selection conditions
Actions
Procedures

DEPENDENCY - PRECONDITION
Preconditions are used to hide characteristics and characteristic values that are not allowed.
Example: Material Bicycle ( Configurable Material)
Characteristic Value Precondition
Model RacingStandard
MountainGears 10
1217
model eq ‘racing’

DEPENDENCY - PRECONDITION

DEPENDENCY - PRECONDITION

DEPENDENCY - PRECONDITION

DEPENDENCY - PRECONDITION

DEPENDENCY - PRECONDITION

DEPENDENCY - PRECONDITION

DEPENDENCY- SELECTION CONDITIONS
Selection conditions can be allocated to the following objects:
Characteristics
BOM items
Operations in task lists
Sub-operations
Sequences of operations (Alternative or Parallel)
Production resources/tools (PRTs)
A selection conditions describe which BOM components or Routing Operations has to be copied during configurations.
Example: Material Personal Computer 1 PCComponent Quantity
selection condition RAM-256 1RAM-512 1RAM 1 GB 1
Hard_disk GE 80GB

DEPENDENCY- SELECTION CONDITIONS

DEPENDENCY- SELECTION CONDITIONS

DEPENDENCY - PROCEDURE
Procedures can be assigned to the following objects:
The characteristic value
The characteristic
The configuration profile
BOM items – to change the component quantity
Operations in task lists – to change the standard values
Example Bicycle - Configurable material
BOM Components Qty. ProcedureBrake 2 Quantity = 3 if
Backpedal
When Backpedal option is selected by customer system automatically propose 3 qty of brake instead of 2.
Syntax: $SELF.QUANTITY = 3 if BACKPEDAL = 'Yes’

DEPENDENCY - PROCEDURE
Characteristic Values Condition
Characteristic Values Weight calculation
WEIGHT -
(3 figures, 1 decimal place)
FRAME Aluminum 10 kg
Steel 14 kg
EXTRAS (multiple-value) Mudguard 0.5 kg
Luggage rack 1.0 kg

DEPENDENCY - PROCEDURE
1. Create a procedure for the weight of the BIKE, depending on the frame. This procedure has the following source code:
$SELF. WEIGHT = 10 if FRAME = ‘Aluminum’,
$SELF. WEIGHT = 14 if FRAME = ‘Steel’.
3. Allocate the procedure to the configuration profile of material

DEPENDENCY - ACTION
The following Objects can assign to action:· The characteristic value that triggers the action · The characteristic that triggers the action · The configuration profile of the configurable object· Configuration profile· BOM items – to change the quantity· Operations in task lists – to change the standard values
Since Action is lead to serious system performance problems, it
replaced by Procedure and Constraint.
Actions are used to infer characteristic values. An action is processed
as soon as the characteristic to which it is assigned has a value.
It is not possible to overwrite the characteristic values that are set by
an action.

DEPENDENCY - ACTION
Characteristic Values Action
MODEL Racing SADDLE = ‘Leather’
Standard
Mountain
SADDLE Plastic
Leather

If the value ‘Racing’ is set for MODEL, the value ‘Leather’ is automatically set for SADDLE, because racing bikes are always supplied with a leather saddle.
Procedure
1. Create an action.
2. Enter the following source code in the dependency editor:
$SELF.SADDLE = ‘Leather’ if MODEL = ‘Racing’
3. Allocate the action to the configuration profile of material BIKE.
Result
If the value ‘Racing’ is set for MODEL when you configure the BIKE, the value ‘Leather’ is automatically set for SADDLE.
Dependency - Action

Questions

TRAINING MANUALSTRAINING MANUALS

TRAINING MANUALS
User Manual: It contains•Overview•Step by Step guide – Transactional•Material Master creation•BOM Creation
Configuration Manual: It contains step by step guide for Variant configuration
Microsoft Word Document
Microsoft Excel Worksheet

THANKS