Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
-
Upload
iamsanwar019170 -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
0
Transcript of Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
1/34
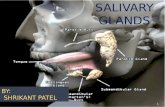
Salivary Gland Tumours
MOHAMMED SANWAR
HUSSAIN
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
2/34
Risk Factors
nutritional deficiency exposure to ionizing radiation UV exposure genetic predisposition EBV
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
3/34
Epidemiology
Salivary tumors 7% of ead and neck tumors!arotid tumors "#x more common ten
su$mandi$ular and "##x more common ten lingual
!arotid #% $enign &pleomorpic adenoma'Su$mandi$ular (#% malignantSu$lingual ma)ority &*(+%' are malignantE,ual incidence $et-een sexes
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
4/34
Staging system for major
salivary gland cancer • Tx Primary tumor cannot be assessed• T0 No evidence of primary tumor • T1 Tumor < 2cm in greatest dimension• T2 Tumor 2-4 cm in greatest dimension• T3 Tumor 4-6 cm in greatest dimension
• T4 Tumor > 6 cm in greatest dimension
• ll categories are subdivided! "a# no local e$tension% "b# locale$tension&
• 'ocal e$tension is clinical or macroscopic invasion of s(in) soft tissue)bone) or nerve&
•
*icroscopic evidence alone is not a local e$tension for classificationpurposes&• T+e merican ,oint ommission on ancer &see also +andouts&
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
5/34
Staging
." / 0cm and no extraparencymal extension
.0 1 0cm $ut not 12cm -itout extraparencymalextension
.3 12cm and or extraparencymal extension.2a invades skin4 mandi$le4 ear canal and5or facial
nerve
.2$ invades skull $ase and or pterygoid plates andor encases carotid artery
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
6/34
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
7/34
Structural elements of t+e
salivary gland unit&• pleomorp+ic adenomas originate from t+eintercalated duct cellsand myoepit+elial cells
• oncocytic tumors
originate from t+estriated duct cells
• acinous cell tumors originate from t+e acinarcells)
• *ucoepidermoidtumors and s.uamouscell carcinomas developin t+e e$cretory ductcells&
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
8/34
Pathology
/ Benign Tumors
0 PleomorphicAdenomas
/ Malignanttumors 0 Parotid –
mucopidermoidmost common– low grade,slow growingcured bysurgery alone
Submandibularand minorsalivary –adenoid cysticmost common.
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
9/34
Pleomorp+ic denoma
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
10/34
Pleomorp+ic denoma
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
11/34
Pleomorphic Adenoma
• pleomorp+ic
adenoma contains
bot+ epit+elial "1#
and stromal "S#components&
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
12/34
Pleomorphic Adenoma
• 1pit+elial omponents – Tubular and cord-li(e arrangements
– ells contain a moderate amount of cytoplasm
–*itoses are rare
• Stromal or mesenc+ymal3 omponents – an be .uite variable
– ttributable to t+e myoepit+elial cells –
*ost tumors s+o c+ondroid "cartilaginous#differentiation
– 5sseous metaplasia not uncommon
– elatively +ypocellular and composed of pale blueto slig+tly eosinop+ilic tissue&
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
13/34
Pleomorphic Adenoma
• T+e diverse microscopic patternof t+is lesion is one of its mostc+aracteristic features&
• 7slands of cuboidal cellsarranged in ductli(e structuresis a common finding&
• 'oose c+ondromy$oid stroma)+yalini8ed connective tissue)cartilage"arros# and evenosseous tissue are observed&
• T+is neoplasm is typicallyencapsulated) alt+oug+ tumorislands may be found it+in t+e
fibrous capsule&
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
14/34
Warthin's Tumor
• 9art+in:s tumor "benignpapillary cystadenomalymp+omatosum#
• t+e second most
common benign tumorof t+e parotid gland
• 7t accounts for 2-;= ofall parotid gland tumors
•
ilateral in ;= of t+ecases• may contain mucoid
bron fluid
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
15/34
Warthin’s Tumor
• Mid Power
• T+oug+t to arise
from salivary gland
inclusions it+inlymp+ nodes&
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
16/34
Warthin’s Tumor
• Epithelial omponent – onsists of papillary fronds +ic+
demonstrate 2 layers of oncocytic epit+eilal
cells – ytoplasm stains deep pin( and s+os
granularity b?c of an abundance ofmitoc+ondria
– 5ccasionally undergoes s.uamousmetaplasia "may mista(enly diagnoseSa #
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
17/34
Warthin’s Tumor
• !"mphoid omponent – n abundance of t+is is present
– 5ccasional germinal centres ill be seen
– 'ymp+oid tissue forms t+e core or papillary
structures
• ot+ l"mphoid and oncoc"tic
epithelial elements must be present todiagnose 9art+in@s
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
18/34
Warthin’s Tumor
• #i$h Power
• 'ymp+ocytc
infilterates&
• ilayer of epit+ilium&
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
19/34
9art+in@s Tumor
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
20/34
Warthin’s Tumor
• 1lectron microscopy s+os atremendous number ofmitoc+ondria in t+e epit+elialcells) +ic+ are responsible forits granular eosinop+ilicappearance&
• *itoc+ondria-ric+ oncocytes arefound in 9art+in@s tumors &
• 5ncocytes selectivelyincorporate tec+netium Tc AAmand appear as +ot spots on aradionucleotide scan&
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
21/34
Monomorphic Adenoma
• Similar to Pleomorp+ic denoma e$cept nomesenc+ymal stromal component – Predominantly an epit+elial component
• *ore common in minor salivary glands "upper lip#
• ;2= bilateral• are malignant potential• Types!
– asal ell denoma – anicular denoma
– *yoepit+elioma denoma – lear ell denoma – *embranous denoma – Blycogen-ic+ denoma
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
22/34
%asal ell
Adenoma• monomorp+ic adenoma• 7t is composed of uniform
&asaloid epithelial cells it+ amonomorp+ous pattern&
• T+e arrangement of tumor cells
may be trabecular) tubular orsolid&
• Cistologically) t+ese tumors aredistinguis+ed from pleomorp+icadenomas by t+eir absence ofc+ondromy$oid stroma and t+epresence of a uniform epit+elial
pattern&
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
23/34
Mali$nant ali(ar" )land
Tumors
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
24/34
Mucoepidermoid
arcinoma • *1s contain to
major elements!• mucin-producing cells
and epit+elial cells oft+e epidermoid variety
• "1pidermoid and*ucinous
components#&• *1 is divided intolo-grade "elldifferentiated#&
• Cig+-grade "poorly
differentiated#&
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
25/34
*ucoepidermoid arcinoma
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
26/34
Mucoepidermoid arcinoma
• *ucoepidermoid carcinoma "*1# is t+emost common malignant tumor of t+e parotidgland and t+e second-most common
malignancy "adenoid cystic carcinoma ismore common# of t+e submandibular andminor salivary glands&
• Stained Dve by musicarmine&
•*1s constitute appro$imately EF= ofsalivary gland malignancy) and G= to A=of *1s occur in t+e parotid gland&
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
27/34
Adenoid "stic arcinoma
• denoid cysticcarcinoma it+ wisscheese pattern&
• 7t is t+e second-most
common malignanttumor of t+e salivaryglands&
• is t+e mostcommon malignanttumor found in t+esubmandibular)sublingual) and minorsalivary glands&
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
28/34
Adenoid "stic arcinoma
• Nerve "N# invaded
by adenoid cystic
carcinoma
"t+e blue areasurrounding t+e
nerve#&
• Spread may occur
by emboli along t+e
nerve lymp+atics
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
29/34
denoid ystic arcinoma
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
30/34
Acinic ell
arcinoma • The acinic cell adenocarcinomaoccurs mainl" in the parotid$land* also +nown as &lue dottumor ,
• lassic multic"stic pattern,• tained &" PA,
• ells hea(il" stained,
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
31/34
cinic ell arcinoma
• T+is lesion is c+aracteri8ed by a benign+istomorp+ologic picture but by occasionalmalignant be+avior&
• T+ese lesions are treated by surgical e$cision
• ilateral involvement occurs in E= ofpatients) ma(ing acinic cell carcinoma t+esecond-most common neoplasm) after
9art+in@s tumor) to e$+ibit bilateralpresentation&
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
32/34
#od$+in's !"mphoma
• Codg(in:s disease
involving t+e parotid
gland&
• Note t+e eed-
Sternberg cell& "Hine
needle aspiration) Pap)
6E$#
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
33/34
ali(ar" )land Tumors
•
-
8/8/2019 Salivary Gland Carcinoma Presentation
34/34