Advertising Budget And Sales Paths Under The Dynamics Of ...
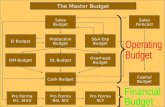
Sales Budget
Transcript of Sales Budget

Sales Budgeting
Estimating future levels of revenue, selling expenses, and profit contributions of the sales function.

Budget
• A budget is simply a tool, a financial plan, that an administrator uses to plan for profits by anticipating revenues and expenditure.
• Sales budget is a detailed blue print of who is going to sell how much of what during operating period and to which class of customers.
• It consists of estimates of an operating period’s probable rupee and unit sales and likely selling expense.

What is a Sales Budget?• It includes estimates of sales volume and selling
expenses• Sales volume budget is derived from the company
sales forecast –generally slightly lower than the company sales forecast, to avoid excessive risks
• Selling expenses budget consists of personal selling expenses budget and sales administration expenses budget
• • Sales budget gives a detailed break-down of estimates of sales revenue and selling expenditure
• Purposes of the Sales Budget• Planning• Coordination• Control

Purpose of Sales Budget:-
1. Planning :-• The company formulates marketing and sales objectives;
the budget determines how these objectives will be met through a detailed breakdown of the sales budget among products, territories and customers.
2. Co-ordination:-• The budget establishes what the cost of various heads be
thereby maintaining a desired relationship between expenditure and revenues. The budget enables sales executives to coordinate expenses with sales. It also restricts the sales executives form spending more that their share of the funds helping to prevent expenses from getting out of control.
3. Evaluation:-• Sales department budgets become tools to evaluate the
department’s performance. By meeting the sales & cost goals set forth in the budget, a sales manager may prove himself to be a successful executive. Sales budget can be determined on the basis of following categories:

Types of BudgetFinancial statement that outlines firms intended actions and the resulting cash flow consequences. Most sales budgets covers a period of one year, but they are often broken down into quarterly or even monthly targets.
• Sales budget – projection of revenue computed from forecast unit sales and average prices.
• Selling expenses budget – approved amount that the department will spend to obtain the revenues projected in the sales budget.
• Profit budget – merged sales budget and the selling expense budget to determine gross profit.



Basis of Selling Expense Budgets
• Affordable methods – management determines what to spend on selling after accounting for the cost of good sold and the desired profit level.
• Percentage of sales method – the funding level is found by multiplying the sales revenue by a given percentage. Budgeting is based on anticipated rather then historical revenue.
• Competitive parity method – sales budgeting method based on the competitive practices in an industry. They refer to either a specific competitor or the industry average.

• Objective and task method – budget allocation is based on the objective of the firm, tasks necessary to achieve those objectives, and the expenses related to those tasks. It is known as zero-based budgeting.
• Bidding system – in this the sales function competes with other functions for limited funds available on the basis of payoffs.
• Return on investment (ROI) – some sales managers have begun to use this financial management concept to chose between alternative courses of action. ROI is determined by dividing net income by total assets employed to earn the income.


Sales Budgeting Procedures
1. Situational Analysis – sales managers have to look at the magnitude of past differences between budgeted and actual figures and the reasons for these differences.
2. Identification of Problems and Opportunities the actual potential threat and challenges has to be assessed and addressed to determine the probabilities of occurrence their impact.
3. Development of Sales Forecast – manager is equipped to forecast sales, using one of the various methods. Projections are made about the anticipated levels of sales by territory, product or type of account. It is expressed both in units and dollars.
4. Formulation of Sales Objectives – once the forecast has been developed, sales force has to be told what sales target to strive and what objectives to pursue.
5. Determination of Sales Tasks – sales manager and sales force have to carry a broad array of sales activities, ranging from recruitment to evaluation, and from prospecting to after sales service.

6. Specification of Resource Requirement – the resources that will be required to implement the specified activities and achieve the objectives.
7. Completion of Projections – here all the input and requests from various units of the sales function are assembled and tied into a comprehensive package.
8. Presentations and Review –present and defend its sales budget proposal to the management.
9. Modification and revision – sales managers have to engage in a series of compromise sessions. Here the sales targets and budgets might be adjusted by the higher management, reflecting both to the needs of the corporation and the true potential of the marketplace.
10. Budget approval – final levels are eventually approved and authorized for both the sales and the selling expense budgets. Here onwards budgets are reviewed periodically looking at the on going market conditions and other external forces.