Root locus
-
Upload
sahed-dewan -
Category
Engineering
-
view
10 -
download
1
Transcript of Root locus

GREEN UNIVERSITY OF BANGLADESH
Department: EEE (Eve)
Prepared For:
Md. Joynal AbedinLecturer, GUB
Prepared By:
Shahida AkterID# 143010003
Course Title: Control System

Root Locus

DefinitionIn control theory and stability theory,
Root Locus analysis is a graphical method for examining how the roots of a system change with variation of a certain system parameter, commonly a gain within a feedback system.

The root locus is the path of the roots of the characteristic equation traced out in the s-plane as a system parameter (K) is changed.(0<K<∞) It can be used to describe qualitatively the performance of a system as various parameters are changed It gives graphic representation of a system’s transient response and also stability We can see the range of stability, instability, and the conditions that cause a system to break into oscillation
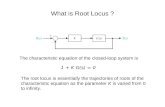
What is Root Locus

Root Locus Concept…T(s) = 1 + K G(s) H(s)
K G(s)
Character eqn,
1 + K G(s) H(s) = 0K G(s) H(s) = -1= 1 180̊= 1 (2K + 1) 180̊
<<

Pole Angle: θ1 = Given Point – PoleZero Angle: θ2 = Given Point – Zero
Root Locus Concept…
Angle Contribution = Pole Angle – Zero Angle [if Angle Contribution is odd multiplication of 180̊, Point lies on Root Locus; else not]
Π Pole LengthΠ Zero Length
Corresponding Gain: K =

Defining the Root Locus
Test whether point P = -5 + j5 lies on root locus and also calculate gain.
R(s) C(s)s (s + 10) K
+-

T(s) = s + 10s + K
K
2 P = -5 + j5
б-10 0
θ1
θ2
θ1 = (-5 + j5) – 0 = 5√2 135̊θ2 = (-5 + j5) – (-10) = 5√2 45̊
<<
jω
Given point P = -5 + j5
Angle Contribution = θ1 + θ2 = 135̊ + 45̊ = 180̊Since, Angle Contribution is odd multiple of 180̊, point P lies on Root Locus.
Corresponding Gain: K =
= (5√2 + 5√2) / 1 = 50
Π Pole Length
Π Zero Length
R(s) C(s)s (s + 10)
K +
-