Risk Benefit Ratio of PPI - c.ymcdn.com · PDF fileRisk Benefit Ratio of Proton Pump...
Transcript of Risk Benefit Ratio of PPI - c.ymcdn.com · PDF fileRisk Benefit Ratio of Proton Pump...

3/22/2017
1
Understanding the Risk Benefit Ratio of Proton Pump InhibitorsRICHARD P SHAUGHNESSY DOARIZONA OSTEOPATHIC MEDICAL ASSOCIATION95TH ANNUAL CONVENTION
History of Proton Pump Inhibitors
PPIs were first released in 1989 Omeprazole followed by lansoprazole, rabeprazole, esomeprazole,
pantoprazole and dexlansoprazole
OCT use was first approved in 2003 Prilosec, Prevacid, Nexium
Class demonstrated substantial efficacy over H2 receptor antagonists, excellent tolerability, minimal short term side effects and minimal drug interactions
Current use One of the most commonly prescribed medications in primary care
Commonly used without physician advise or prescription Vanderhott BT, Tahoub RM. Proton pump inhibitors: an update. Am Fam Physician.
2003;66(2):274-280Department of Health and Human Services. Prilosec OTC Approval Letter. NDA 21-229. June 2003

3/22/2017
2
Pharmacology
Parietal Cells Located in the gastric glands in the
body and fundus of the stomach
Activated by stimuli Acetylcholine
Histamine
Gastrin
Acid production Acid released at the Hydrogen
Potassium ATPase pump
Parietal Cell
Source of Graphic : Treatment and Replenishment of G.I. Tract with Combined Regimen Therapy (CRT) of Allopathic (PPIs) and Ayurvedic (Aloe Vera) Medicine in Peptic Ulcer Disease to Counteract RelapseJ Gastrointest Dig Syst 5: 272. 5:2, (2015)http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2161-069X.1000272
Pharmacology
Supports dosing 30 minutes before meals
PPIs are absorbed in the proximal small bowel Short half life of 1-2 hours Lipophilic weak base crosses
membrane of the parietal cell Passes into the parietal cell
canaliculus
In Acidic environment of canaliculus Molecule become protonated Activated sulphenamide form of
drug Binds covalently with the H+/K+
ATPase enzymes Irreversible inhibition of the proton
pump Cell can activate other proton
pumps or build new ones
Parietal Cell
Source of Graphic : Treatment and Replenishment of G.I. Tract with Combined Regimen Therapy (CRT) of Allopathic (PPIs) and Ayurvedic (Aloe Vera) Medicine in Peptic Ulcer Disease to Counteract RelapseJ Gastrointest Dig Syst 5: 272. 5:2, (2015)http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2161-069X.1000272

3/22/2017
3
Efficacy and Benefit
Healing of reflux is superior to H2RA (omeprazole vs ranitidine) Decreased risk of relapse in maintenance of GERD Effective in patients with reflux which is refractory to H2RA Superior healing of erosive esophagitis, both efficacy and rate of
healing Superior healing for gastric and duodenal ulcers Significantly reduce the risk of re-bleeding or surgery in patients with
peptic ulcer bleeding Bardahan KD. The role of proton pump inhibitors in the treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1995; 9 (suppl 1): 15-25. 5. Chiba N, De Gara CJ, Wilkinson JM, et al. Speed of healing an symptom relief in grade II to IV gastroesophageal reflux disease: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology, 1997;112(6):1789-1810Eriksson S, Langstrom G, Rikner L, et al. Omeprazole and H2-receptor antagonists in the actuetreatment of duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer and reflux oesophagitis: a meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1995;7(5):467-475.Leontiadis GI, Sreedharan A, Dorward S et al. Systematic reviews of the clinical effectiveness and const effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors in acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
Health Technol Assess. 2007 Dec;11(51)iii-iv, 1-164.
FDA Indications
Healing of erosive esophagitis
Maintenance of healed erosive esophagitis
Treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease
Risk reduction of gastric ulcer associated with NSAID use
Helicobacter pylori eradication to reduce the risk of duodena ulcer recurrence
Pathological hypersecretory conditions (ZE syndrome)
Short term treatment or maintenance of duodenal and gastric ulcers Dose and duration are different based on indications
GERD 14 days repeat at four month intervals
ZE life long
Centers for Medicare & Medicade Services. Proton Pump Inhibitors: use in adults October 2015

3/22/2017
4
Trends….where are we going?
Population study in Finland 1987-1999 Elective surgery and parietal cell vagotomy have become nearly obsolete Increase in emergency surgery from 5.2 to 7.0 operations per 10(5) Hospital admission rate increased by 79% and mortality rate increased 31%
Changes driven by bleeding gastric ulcers in elderly women
Population study in England (1989-1999) Decreased admissions for peptic ulcer disease in younger patients
H. pylori treatment
Substantial increase in admissions for both men and women age >75 Medication exposure
ASA 75mg increased 460%
Oral anticoagulants increased by 200%
NSAIDS increased by 13%
Paimela H, Oksala NK, Kivilaakso e. Surgery for peptic ulcer today. A study on the incidence, methods and mortality in surgery for peptic ulcer in Finland between 1987 and 1999. Dig surg. 2004;21(3);185-91Paimela H, Paimela L, Myllykangas-Luosujarvi R, et al. Current features of peptic ulcer disease in Finland: incidence of surgery hospital admission and mortality for the disease during the past twenty-five years. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2002 Apr;37(4):399-403Higham J, Kang Y-K, Majeed A. Recent trends in admission and mortality due to peptic ulcer in England: increasing frequency of haemorrhage among older subjects. Gut 2002;50:460-464
Challenges for the Clinician
Epidemiological studies suggest increasing disease burden of acid peptic disease Demographic shift for older age
Polypharmacy (NSAIDS, anticoagulants, ASA, SSRI)
Co-morbid conditions (obesity, OSA, renal failure, COPD)
Wide availability in the OTC market
Observational studies have demonstrated positive associations Osteoporosis
Vitamin and mineral deficiency
Chronic kidney disease
Myocardial infarction
Stroke
Dementia
Greater scrutiny of the drug class Reluctance of clinicians to prescribe and patients to consume the medication

3/22/2017
5
Challenges for the Clinician
Observational studies have demonstrated positive associations Osteoporosis
Vitamin and mineral deficiency
Chronic kidney disease
Myocardial infarction
Stroke
Dementia
Greater scrutiny of the drug class Reluctance of clinicians to prescribe and patients to consume the
medication
Achlorhydria and Hypergastrinemia
Animal studies in mice with high dose omeprazole Profound achlorhydria
Sustained hormonal stimulation with gastrin
Development of carcinoid tumors of enterochromaffin-like cells
Never seen in humans Review of 10,000 patients on long term omeprazole showed no
carcinoid tumors
Level of achlorhydria is NOT complete and is similar to that of selective proximal vagotomy
Havu N. Enterochromaffin-like cell carcinoids of gastric mucosa in rats after life-long inhibition of gastric secretion. Digestion 1986;35 Suppl 1:42-55Arnold R, Koop H. Omeprazole, long-term safety. Digestion 1989;44 Suppl 1:77-86

3/22/2017
6
Achlorhydria and Hypergastrinemia Changes seen in humans
Rise in mean serum gastrin levels (110 to 200.2 ng/L)
Moderate initial increase in the enterochromaffin-like cell density over the first there years
Development of fundic gland polyps Parietal cell hyperplasia with parietal cel protrusion
Due to acid suppression and resulting elevated gastrin levels
Associated with duration of use (>5 years OR 3.8, 95% CI 2.2-6.7)
Dysplasia and cancer risk determined to be negligible
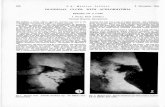
Multiple fundic gland polyps in a 77 year old woman on PPI therapy. Image courtesy of Atlanta South Gastroenterology www.endoatlas.com
Jalving M, Koornstra JJ, Wesseling J et al. Increased risk of fundic gland polyps during long-term proton pump inhibitor therapy. Alimentary Pharm and Therap 2006 Nov;24(9) 1341-1348
Calcium
2010/2011 FDA released a letter warning of increased fracture risk for patients on high dose or long term PPI use
Mechanism of calcium depletion (unproven) An acidic environment may aid in the dissociation of calcium from the
food bolus
Decreased absorption may cause increased bone resorption
Review of 14 observational studies (1980-Feb 2011) Eight studies showed association with hip fracture
Five studies showed association with spine fracture
Three studies showed reduction in fracture risk after discontinuation of PPI Insonga, K The effect of proton pump inhibiting drugs on
mineral metabolism. Am J Gastroenterol 104 (Suppl. 2) S2-S4Lau YT, Ahmet NN. Fracture risk and bone mineral density reduction associated with proton pump inhibitors. Pharmacotherapy. 2012 Jan;32(1):67-97

3/22/2017
7
CalciumCause of Fracture Risk
Bone Mineral Density (BMD) Decreased BMD in osteoporosis is associated with fracture risk
Canadian population study of 8,340 patients Decreased BMD in the PPI group on presentation
NO evidence of accelerated bone loss in the PPI group over 10 years
Previous study with same group using a different Canadian data base showed no difference in BMD at baseline or follow up.
Bone structure and strength Evaluation for unknown factor in PPI exposed patients
three dimensional quantitative computer tomography
Buckling ratio
In 104 patients there was no difference in bone structure or strengthTargownik LE, Leslie WD, Davison KS, et al. The relationship between proton pump inhibitor use and longitudinal change in bone mineral density: a population-based study from the Canadian MulticentreOsteoporosis study (CaMos). Am J Gastroenterol. 2012 Sept; 107(9):1361-9Targowinik LE, Lix LM, Leung S. Proton-pump inhibitor use is not associated with osteoporosis or
accelerated bone mineral density loss. Gastroenterology. 2010 Mar; 138(3):896-904Targownik LE, Goertzen AL, Luo Y et al. Long-term proton pump inhibitor use is not associated with changes in bone strength and structure. Am J Gastroneterol. 2017 Jan; 112(1) 95-101
CalciumRecommendations
Currently there are no guidelines for screening, monitoring, or supplementation of calcium in patients on long term PPI therapy
FDA reconfirmed the safety of OTC PPIs when used as directed

3/22/2017
8
Vitamin B12
Essential nutrient acquired form animal derived food (meat, eggs, diary)
Absorption Pepsin is activated from pepsinogen in an acidic environment
Pepsin cleaves vitamin B12 from the food source
In an achlorhydric environment B12 may not be cleaved from the food source to bind R protein and would thus be degraded by pancreatic enzymes
Data Limited research in the form of case reports and cross sectional observational
trials
Vitamin B12Recommendations
There is insufficient data to recommend screening or supplementation in patients who are on long term PPIs
Monitoring or screening may be reasonable in high risk groups Elderly
Nursing home residents
Malnourished
People on a strict vegan diet

3/22/2017
9
Vitamin C
Water soluble molecule not synthesized by the body PPI therapy decreases vitamin C concentrations
Decreases biologically active compound, ascorbic acid
Possible clinical significance Ascorbic acid prevents conversion of nitrate to N-nitroso compounds
Currently there are no guidelines for monitoring or replacement
Iron
Dietary iron is present in two forms Nonheme (66%) Heme (32%)
Acidic environment of stomach and proximal duodenum Results in dissociation of nonheme iron from food Dissociated nonheme becomes soluble iron salts Forms complexes with sugars and amines to facilitate absorption
Data Case reports: impaired absorption in patients on PPI who fail to respond to replacement Retrospective cohort of 98 patients demonstrated an OR of 5.03 (95% CI 1.71-14.78) for
decrease in hemoglobin by 1 gram in patients on PPI
Guidelines No guidelines to monitoring or replacement Index or suspicion is reasonable in high risk patients

3/22/2017
10
Hypomagnesemia
Rare with unknown mechanism Presentation
Concomitant hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, severe ataxia, paresthesia, seizures and confusion
Requires hospitalization Median age 70 Associated with long term use
5 years 61%
10 years 29%
25% do not respond to magnesium therapy PPI MUST be discontinued
Switching to another PPI will result in recurrent symptoms
Screening Patients presenting with or history of arrhythmia on PPI therapy
Enteric infections
Role of gastric acid Highly acidic environment is effective at eliminating most potential
enteric pathogens
Common enteric pathogens Salmonella, E. coli, Shigella, Campylobacter
Clostridium difficile Spore forming bacterium
Typically more resistant to environmental insults including heat, cold, desiccation, and acid

3/22/2017
11
Common enteric pathogensSalmonella, E coli, Shigella, Campylobacter
Systematic review Six papers with total of 11,280 patients with enteric infections
Any acid suppression OR 2.55 (95% CI 1.53-4.26) H2RA OR 2.03 (95% CI 1.05-3.92) PPI therapy OR 3.33 (955 CI 1.84-6.02)
Risk of H2RA vs PPI trended for increased safety but was not statistically significant
Special attention for high risk populations Those traveling to high risk areas Antibiotic exposure Malnourished Elderly Immunosuppression Leonard J, Marshall J, Moayyedi P et al. Systematic
review of the risk of enteric infection in patients taking acid suppression. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102: 2047-2056
Infection with C. difficile
Analysis of 12 papers involving 2,984 patients with initial C. difficile infection
Risk on any acid suppression OR 1.94 (95% CI 1.37-2.75)
Risk on H2RA OR 1.40 (95% CI 0.85-2.29)
Risk on PPI OR 1.96 (95% CI 1.28-3.00)
Leonard J, Marshall J, Moayyedi P et al. Systematic review of the risk of enteric infection in patients taking acid suppression. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102: 2047-2056

3/22/2017
12
Infection with C. difficile
Recurrent C. difficile infection occurs in 20% of infection Significant cost ($11,000) with high risk of morbidity, mortality, and subsequent
infection
Cohort study of 754 patients with recurrent C difficile Risk factors for recurrence
Age >75, continuous PPI use, length of hospital stay, vancomycin as initial treatment regimen
OR for recurrent antibiotic exposure 1.30 (95% CI 0.9-1.7)
OR for continuous PPI use 1.5 (95% CI 1.1-2.0)
Less than half of the patients studies had an evidence based indication for continuous PPI use
Only three were taken off of therapy with the goal of reducing recurrent C difficile infection risk
McDonald E , Miligan J, Frenette C et al. Continuous proton pump therapy and the associated risk of recurrent clostridium difficile infection. JAMA Intern Med. 2015; 175 (5): 784-791
Kidney Disease
Scope of disease Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects approximately 13.6% of the US
population
High costs
Increased risk of cardiac events and death
Prevalence of CKD is increasing Diabetes/Hypertension
Polypharmacy and medication exposure may be a risk as well
No proposed mechanism to explain association of PPI with risk of CKD

3/22/2017
13
Incident and Progression of CKD
VA cohort study of patients followed over 5 years 173,321 new PPI prescriptions
20,270 new H2RA prescriptions Risk of new CKD diagnosis was OR 1.28 (95% CI 1.23-1.34) for PPI vs H2RA
Risk of doubling of creatinine was OR 1.53 (95% CI 1.42-1.65)
Graded association based on duration of exposure
Xie Y Bowe B, Li T et al. Proton pump inhibitors and the risk of incident CKS and progression to ESRD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Oct;27(10):3153-3163
Incident and Progression of CKD
Atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) database of 10,482 patients
Patients on PPI were more likely to be white, obese, and hypertensive Incident CKD was 14.2/1000 person years for PPI group vs 10.7/1000 person years for
non-PPI
OR for CKD was 1.5 (95% CI 1.14-1.96) in PPI group
10 year absolute risk was 15.6% in the PPI group vs 13.9 in the non-PPI group
Absolute risk difference of 1.7
No increased risk of CKD was seen in the H2RA groupLazarus B, Chen Y, Wilson F et al. Proton pump inhibitor use and the risk of chronic kidney disease. JAMA Intern Med. 2016 Feb 1; 176(2): 238-246

3/22/2017
14
Dementia
Progressive cognitive decline resulting in loss of functional independence Incidence expected to increase from 35 million to 84 million by 2040
Global cost of dementia estimated at 604 Billion
Prevention is essential
Proposed mechanisms of association B12 deficiency
Increased beta amyloid in the brain (mice studies)
Modulation of beta amyloid degradation by PPIs (mice studies)
Dementia
73,679 patients analyzed from a German insurance data base Patients all >75 years old at enrollment
Regular PPI use was associated with dementia OR 1.44 (95% CI 1.36-1.52)
Dementia is a multifactorial disease Other factors identified: depression, stroke, female, diabetes, polypharmacy
Anticholinergic drugs were and independent risk factor OR 1.8 (95% CI 1.65-1.96)
Study did no differentiate different etiologies of dementia
Patients with intermittent PPI use had an OR of 1.16 (95% CI 1.13-1.19) Suggests basis for dose reduction
Gomm W, von Holt K, Thome F et al. Association of proton pump inhibitors with risk of dementia a pharmacoepidemiological claims data analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2016;73(4):410-416

3/22/2017
15
Myocardial Infarction
Multiple observational studies have associated MI with both GERD and PPI use Mechanism of association is unknown
Reflux patients have greater number of comorbidities Hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, alcohol related illness, stroke, obesity,
COPD, asthma, depression, and anxiety
PPI directly result in endothelial dysfunction Mouse study
PPIs inhibit enzymatic activity of dimethylarginine dimethylaminhydrolasewhich is responsible for the clearance of asymmetric dimethylarginine which is an endogenous molecule known to inhibit the activity of nitric oxide synthase
Impairment of NOS can increase vascular resistance and promote inflammation and thrombosis Sehested TS, Fosbol EL, Charlot MG et al. Proton pump inhibitor use
increased the associated risk of first-time ischemic stroke. A nationwide cohort study. Circulation. 2016;134:A18462Chen C, Lin C, Kao C. Association between gastroesophageal reflux disease and coronary heart disease. A nationwide population-based analysis. Medicine. 2016 95:27
Cardiac EventsLong-term PPI use
Large population based Chinese study GERD patients were at increased risk for CAD OR 1.49 (95% CI 1.34-1.66) PPI less than one year risk of CAD OR 1.56 (95% CI 1.39-1.74) PPI greater than one year risk of CAD OR 1.67 (95% CI 1.34-2.08)
Demonstrates GERD to be an independent risk factor Results confirmed in other large cohort study
Determined a number needed to harm NNH of 4,357
Stanford study used data mining to review 16M clinical documents from 2.9M individuals PPI use associated with an OR of 1.16 (95% CI 1.09-1.24 No increased risk seen with H2RA Researchers hypothesized that if data mining were available in 2000,
association could be found “pharmacovigilance algorithms”Shah N, LePendu P, Bauer-Mehern A et al. Proton pump inhibitor usage and the risk of myocardial infarction in the general population. PLoS ONE 10(6): e0124653Shih CJ, Chen YT, Ou SM, et al. Proton pump inhibitor use represents an independent risk factor for myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2014 Nov 15;177(1):292-7

3/22/2017
16
Cardiac EventsShort-term PPI use
Canadian population based study Identified 5,550 hospital admissions for acute MI
Patients had been started on PPI within 12 weeks of admission Increased risk of MI with PPI exposure 1.8 (95% CI 1.7-1.9)
Study also showed increased risk with H2RA as well as benzodiazepines both of which have previously been considered not to be a risk for AMI
Swedish study evaluated patients admitted with AMI Started on PPI within three months
OR was 1.36 (95% CI 0.82-2.25) Results not significant
Authors suggest that observed increased risk may be result of cardiac symptiomsmisdiagnosed as dyspepsia
Recent PPI administration appears poorly associated with AMIJuurlink DN, Dormuth CR, Huang A et al. Proton pump inhibitors and the risk of adverse cardiac events. PLoS ONE 8(12): e84890Turkiewicz A, Vicente RP, Ohlsson H et al. Revising the link between
proton pump inhibitors and risk of acute myocardial infarction a case crossover analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;71(1):125-9
Ischemic Stroke
Endothelial dysfunction suggested in patients with acute MI by also increase the risk of ischemic stroke
Presented in abstract form American Heart Association meeting 11/2016 Nationwide Danish health registry
Identified 244,679 patients underwent gastroscopy and age >30
Forty percent of patients had filled a prescription for a PPI
PPI patients were older and had an increased risk of atrial fibrillation
Risk of first time ischemic stroke was 1.21 (95% CI 1.16-1.27)
No increased risk was seen with H2RA
No increased risk for: omeprazole 20mg, lansoprazole 15mg, esomeprazole 20mg
Risk was associated with higher dose formulations Sehested TS, Fosbol EL, Charlot MG et al. Proton pump inhibitor use increased the associated risk of first-time ischemic stroke. A nationwide cohort study. Circulation. 2016;134:A18462

3/22/2017
17
“Popular heartburn medications linked to higher risk of stroke”“Most serious warning yet” Immediately following oral presentation of abstract CNN released
article with the above headline
The article has not been published in a peer reviewed journal
Population based cohort studies do not demonstrate causality
Results have not been replicated in other studies
Author is not a physician or hold a degree in statistics
Is this responsible?
Is this #FakeNews? Ben Tinker is a supervising producer for CNN Health. He primarily works with CNN Chief Medical Correspondent, Dr. Sanjay
Gupta, telling the most compelling and newsworthy health and wellness stories. Tinker produced CNN's weekly health and wellness show, Sanjay Gupta MD, providing consumer-driven news and advice for living a longer, happier, healthier life. Prior to joining CNN Health, Tinker worked in New York for CNNMoney, where he produced Your Bottom Line, the network's weekly personal finance program. He holds dual degrees in journalism and psychology from New York University.
Media Based Sensationalism
Role of the physician Understand the risk, benefits, alternatives of proposed treatment or
therapy
Understand the strength and weakness of current research and data
Advocate for patient safety
Engage in shared decision making with our patients with the goal of good outcomes
The discussion should be shaped and guided by physicians advocating for the best interest of their patients, not the media

3/22/2017
18
Mitigation of RiskPracticing Evidence Based Medicine and Limiting Exposure
Risk stratify patients based on pre-existing comorbidities Elderly, frail, malnourished
Hospitalized, antibiotic exposed, renal failure
Diabetic, hypertensive
Over half of all patients on PPIs do not have an evidence based indication for the drug Review medications lists frequently especially at transition of care such
as hospital discharge
Consider trial of H2RA or antacids
Discontinue PPI whenever possible
Mitigation of RiskPracticing Evidence Based Medicine and Limiting Exposure
Some patients are on a PPI for correct indication or do not tolerate discontinuation Dose reduction has been shown to decrease risk of multiple disease
associations
Intermittent dosing is tolerated in some patients
High dose PPI not responding to therapy Consider other diagnosis
Hypersensitive esophagus or functional heartburn

3/22/2017
19
Lifestyle Modification
The most common indication for PPIs is GERD GERD symptoms are often driven by lifestyle issues
Dietary modification
Smoking cessation
Weigh loss
Dietary modification is free and low risk Compliance has been shown to be low even for severely symptomatic
patients
Requires frequent re-education and encouragement
Kubo A, Block G, Quesenberry C et al. Dietary guideline adherence for gastroesophageal reflux disease BMC Gastroenterol. 2014; 14: 144
Smoking and Exercise
Swedish study monitored patients with multiple gastrointestinal symptoms over an 18 year period The OR was 3.5 for improvement of reflux with exercise
The OR was 3.45 for improvement of reflux with decreased smoking
These interventions are free, no risk and will also reduce other comorbid diseases discussed in this talk
Stake-Nilsson K, Hultcrantz R, Unge P et al. Changes in symptoms and lifestyle factors in patients seeking healthcare for gastrointestinal symptoms: an 18 year follow up study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Dec;25(12):1470-7

3/22/2017
20
Obesity
The incidence of obesity continues to increase in the US In a study of patients on double dose PPI obesity was associated with
persistent acid opposed to another diagnosis such as hypersensitive esophagus
A clear association with increased reflux episodes and increased BMI was demonstrated using impedance pH monitoring
These studies demonstrate a clear association between obesity and reflux disease
Western diet high in meat and processed foods is fueling an epidemic of disease which fosters a dependence on pharmacology (opinion)
Viazi N, Karamanolis GP, Anastasiou J et al. Refractory GERD: increased body mass index is associated with persisting acid exposure but not hypersensitive esophagus or functional heartburn. Eur J GastroenterolHepatol. 2013 Dec;25(12):1450-538. Hajar N, Castell DO, Ghomrawi H et al. Impedance pH confirms the relationship between GERD and BMI. Dig Dis Sci 2012 Jul;57(7): 1875-9
Weight loss
Study evaluating the effect of weight loss on 101 patients with GERD symptoms Group A: personalized supervised hypocaloric diet and aerobic exercise program Group B: given a standard of care diet Both groups were placed on a PPI at enrollment
Results Group A
BMI decreased from 30.3 to 25.7
PPI was discontinued in 27/50
PPI was halved in 16/50
PPI continued at full dose in 7/50
Group B No weight loss was seen
PPI was halved in 22/51
PPI was continued at full dose in 29/51
NO patients discontinued PPI therapy
De Bortoli N, Guidi G, Marinucci et al Voluntary and controlled weight loss can reduce symptoms and proton pump inhibitor use and dosage in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: a comparative study. Dis Esophagus. 2016 Feb-Mar;29(2):197-204

3/22/2017
21
Physical Medicine/OMT
Study of 38 patients randomized to OMT of the diaphragmatic muscle vs sham technique
Esophageal manometry evaluated before and after treatment
Some parameters of the lower esophageal sphincter pressure improved after treatment
Study on a single patient demonstrated improved GERD symptoms score over a series of four treatments
da Silva RC, D Sa CC, Pascual-Vaca AO. Lincrase of lower esophageal sphincter pressure after osteopathic intervention on the diaphragm in patients with gastroesophageal reflux. Dis Esophagus 2013 Jul;26(5):451-6Dinz LR, Nesi J, Curi AC. Qualitative evaluation of osteopathic manipulative therapy in a patient with gastroesophageal reflux disease: a brief report. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2014 Mar:114(3):180-8
Physical Medicine/OMT
Abdominal breathing exercise Prospective randomized controlled study
At nine months patients who were taught breathing exercises Sustained results
Improved quality of life scores
Decreased PPI use
While it may be difficult in a busy clinical practice, a holistic approach to reflux management would include physical medicine with the goal of reducing pharmacological therapy
Eherer AJ, Netolitzki F, Hogenauer C. Positive effect of abdominal breathing exercise on gastroesophageal reflux disease: a randomized, controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012 Mar;107(3):372-8

3/22/2017
22
Final Thought
Proton pump inhibitors when used correctly are highly efficacious medications for the management of multiple acid peptic disorders
The art and science of osteopathic medicine requires that we Recognize patients at high risk for serious side effects of PPIs
Recognize that some patients benefit greatly from PPIs
Practice evidence based guidelines and eliminate superfluous medications
Reduce dosing amount and frequency whenever possible
Use lifestyle modifications to eliminate medication dependency
Thank-you for your attention