Right Angle Trigonometry - Rochester Institute of … opposite angle A. II. Right Triangle Facts and...
Transcript of Right Angle Trigonometry - Rochester Institute of … opposite angle A. II. Right Triangle Facts and...

www.rit.edu/asc Page 1 of 12
I. Basic Facts and Definitions 1. Right angle – angle measuring 90
2. Straight angle – angle measuring 180
3. Acute angle – angle measuring between 0 and 90
4. Complementary angles – two angles whose sum is 90
5. Supplementary angles – two angles whose sum is 180
6. Right triangle – triangle with a right angle
7. Isosceles triangle – a triangle with exactly two sides equal
8. Equilateral triangle – a triangle with all three sides equal
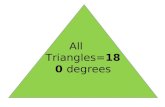
9. The sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 .
10. In general, capital letters refer to angles while small letters refer
to the sides of a triangle. For example, side a is opposite angle A
.
II. Right Triangle Facts and Examples
1. Hypotenuse – the side opposite the right angle, side c .
2. Pythagorean Theorem - 222 cba
3. A and B are complementary.
Right Angle Trigonometry

www.rit.edu/asc Page 2 of 12
III. Examples: 1. In a right triangle, the hypotenuse is 10 inches and one side is 8
inches. What is the length of the other side?
Solution: 222 cba
222 108 b
10064 2 b
362 b
6b
2. In a right triangle ABC , if 23A , what is the measure of B ?
Solution: The two acute angles in a right triangle are
complementary. 90BA
9023 B
67B
IV. Similar Triangles: a. Two triangles are similar if the angles of one triangle are equal to
the corresponding angles of the other. In similar triangles, ratios of corresponding sides are equal.
B
A C
8a
?b
10c
C
B
A
Conditions for Similar Triangles (EGFABC ~ )
1. Corresponding angles in similar triangles are equal:
EA FB GC
2. Ratios of corresponding sides are equal:
FG
BC
EF
AB
EG
AC

www.rit.edu/asc Page 3 of 12
Example 1:
Example 2:
B C
A
F E
22
50
50
50AE meters 22EF m and 100AB m
Find the length of side BC .
Notice that ABC and AEF are similar since corresponding angles are equal. (There
is a right angle at both F and C , A is the
same in both triangles and B equals the acute angle at E .)
Solution: BC
EF
AB
AE so
BC
22
100
50
By cross multiplying we get:
)100(22)(50 BC
Therefore 44BC meters.
50AE meters 22EF m and 100AB m
Find the length of side BC .
All 904545 triangles are similar to one another. Two sides are of equal length and the
hypotenuse is 2 times the length of each of the equal sides.
All 906030 triangles are similar to one another. The shortest side of length a is opposite
the smallest angle ( 30 ). The hypotenuse is twice the length of the shortest side. The side opposite
the 60 has a length 3 times the shorter leg.

www.rit.edu/asc Page 4 of 12
Problem: Find the lengths of the legs of a 906030 triangle if the hypotenuse is 8 meters.
Solution: 1) If 82 a , then 4a meters and 2) 34)4(33 a meters.
V. The Six Trigonometric Ratios for Acute Angles TRIG TRICK: A good way to remember the trig ratios is to use the mnemonic SOH CAH TOA!
sine Ac
a
hypotenuse
oppositeA sin cosecant A
a
c
opposite
hypotenuse
AA
sin
1csc
cosine Ac
b
hypotenuse
adjacentA cos secant A
b
c
adjacent
hypotenuse
AA
cos
1sec
tangent Ab
a
adjacent
oppositeA tan cotangent A
a
b
opposite
adjacent
AA
tan
1cot
c
a
b A
B
C
SOH CAH TOA ine
pposite
ypotenuse
osine
djacent
ypotenuse
angent
pposite
djacent

www.rit.edu/asc Page 5 of 12
Example 1:
Find the six trigonometric ratios for the acute angle B . Solution:
c
b
hypotenuse
oppositeB sin . Using the above definitions, the rest are:
c
aB cos ,
a
bB tan ,
b
cB csc ,
a
cB sec ,
b
aB cot
Example 2:
In the right ABC , 1a and 3b . Determine the six trigonometric ratios for
B . Solution: Use Pythagorean Theorem:
222 bac 222 31 c
22 10c
10c
(Since length is positive, we will only use 10c .)
10
103
10
3sin
hyp
oppB
10
10
10
1cos
hyp
adjB 3
1
3tan
adj
oppB
3
10csc
opp
hypB 10
1
10sec
adj
hypB
3
1cot
opp
adjB

www.rit.edu/asc Page 6 of 12
VI. Special Cases
a. Trigonometric values of 30 and 60 (Use the 906030 triangle from pg. 3.)
b. Trigonometric values of 45 (Use the 904545 triangle from pg. 3.)
1b
2c 3a
60
30 2
130sin
2
360sin
2
330cos
2
160cos
3
3
3
130tan 3
1
360tan
21
230csc
3
32
3
260csc
3
32
3
230sec 2
1
260sec
31
330cot
3
3
3
160cot
1b
1a 2c
45
45
30
60
2
2
2
145sin 2
1
245csc
2
2
2
145cos 2
1
245sec
11
145tan 1
1
145cot

www.rit.edu/asc Page 7 of 12
VII. Converting Minutes and Seconds to Decimal Form
(Necessary for most calculator use in evaluating trig values) 1. To convert from seconds to a decimal part of a minute, divide the
number of seconds by 60. 2. To convert from minutes to a decimal part of a degree, divide the
number of minutes by 60.
Example 1: Convert 7464 to degrees using decimals.
Solution:
60
47647464
783.64783.647464
Example 2: Convert 012115 to degrees using decimals.
Solution: 012115012115
60
102115012115
716.1215012115
60
167.1215012115
203.15203.15012115
VIII. Right Triangle Trigonometry Problems
To Solve Right Triangle Problems: There are six parts to any triangle; 3 sides and 3 angles. Each trig formula (ex: sin A = a/c) contains three parts; one acute angle and two sides. If you know values for two of the three parts then you can solve for the third unknown part using the following method:
1. Draw a right triangle. Label the known parts with the given values and indicate the unknown part(s) with letters.
2. To find an unknown part, choose a trig formula which involves the unknown part and the two known parts.

www.rit.edu/asc Page 8 of 12
Example 1: A right triangle has 38a and 61B . Find the length of side b .
Solution: (Always check your answer by comparing size of angle and length of side; the longer side is always opposite the larger angle.)
IX. Angles of Elevation and Depression
Example: From a point 124 feet from the foot of a tower and on the same level, the angle of
elevation of the tower is 0236 . Find the height of the tower. Solution:
Angle of elevation
61
b
38a B
A
C
Which trig formulas involve an acute angle (B) and the side opposite (b) and the side adjacent (a) to the angle? Since both tangent and cotangent do, either could be used to solve this problem. We will use tangent.
a
b
adj
oppB tan so,
3861tan
b or
388040.1
b .
Therefore 6.68b .
Angle of depression
h
124 ft.
0236
)333.36tan(0236tan24
h
)7355.0(124h
2.91h ft.

www.rit.edu/asc Page 9 of 12
Practice Problems:
1. In right triangle ABC , if 39c inches and 36b inches, find a .
2. Find the length of side AC . Note: This problem and diagram corresponds to finding the height of a street light pole ( AC ) if a 6 ft. man ( EF ) casts a shadow ( BF ) of 15 ft. and the pole casts a shadow ( BC ) of 45 ft.
3. Evaluate:
a) sin E = _____________ b) tan E = _____________
c) cos F = _____________ d) sec F = _____________
4. Evaluate: (Draw reference 906030 and 904545 triangles)
a) sin 30 = _____________ b) tan 60 = _____________
c) sec 60 = _____________ d) tan 45 = _____________
e) csc 45 = _____________ f) cot 30 = _____________
B C
A
E
F
6
15 30
F
G E
13 12
5

www.rit.edu/asc Page 10 of 12
5. Evaluate:
a) tan A = _____________ b) csc B = _____________
c) cot A = _____________ d) sec B = _____________
6. Convert to decimal notation using a calculator:
a) 6076
b) 317245 Evaluate, using a calculator:
c) 8452sin
d) 2439cot
7. Label the sides and remaining angles of right triangle ABC , using A , B ,
a , b and c . If 43a and 37A , find the values of the remaining parts.
B
C A
10 8
C

www.rit.edu/asc Page 11 of 12
8. Given right triangle ABC with 622.0b and 0451 A , find c . Draw a diagram.
9. From a cliff 140 feet above the shore line, an observer notes that the angle
of depression of a ship is 0321 . Find the distance from the ship to a point on the shore directly below the observer.
cliff ship

www.rit.edu/asc Page 12 of 12
Answers to Right Triangle Trigonometry: 1. 15a inches (use Pythagorean Theorem)
2. BF
BC
EF
AC
15
6
45
AC 18AC
3. a) 13
12sin E b)
5
12tan E c)
13
12cos F d)
12
13sec F
4. (see part E of the handout)=
a) 2
130sin b) 360tan c) 260sec
d) 145tan e) 245csc f) 330cot
5. 6b (use Pythagorean Theorem)
a) 3
4
6
8tan A b)
3
5csc B c)
4
3cot A d)
4
5sec B
6. a) 1.76 b) 454.45 c) 7965. d) 2045.1 7. 53B 06.57b 45.71c
8. 1c (Use c
bA cos or
b
cA sec to solve for unknown c )
9. x
1400321tan
41.355x ft.
C
B
A b
a c
cliff ship
(Angle of depression)