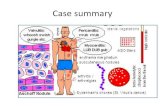
Rheumatic fever clinical features and diagnosis
-
Upload
sujit-sahu -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
2.332 -
download
3
description
Transcript of Rheumatic fever clinical features and diagnosis

RHEUMATIC FEVERRHEUMATIC FEVERClinical features Clinical features
and and diagnosisdiagnosis
DR . SUJIT SAHUDR . SUJIT SAHU
http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION HISTORICAL BACKROUND HISTORICAL BACKROUND EPIDEMIOLOGYEPIDEMIOLOGYPATHOGENESISPATHOGENESISPATHOLOGY PATHOLOGY CLINICAL FEATURESCLINICAL FEATURESDIAGNOSISDIAGNOSIS

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
INTRODUCTIONINTRODUCTION
Clinical syndrome Clinical syndrome
Acute , non-suppurative inflammatory Acute , non-suppurative inflammatory disease disease
following Group A Beta Hemolytic following Group A Beta Hemolytic Streptococcal sore throatStreptococcal sore throat
Classified as Connective tissue disease or Classified as Connective tissue disease or collagen vascular diseasecollagen vascular disease
affecting the Joints, heart , brain , skin and affecting the Joints, heart , brain , skin and subcutaneous tissuesubcutaneous tissue

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
HISTORICAL HISTORICAL BACKROUNDBACKROUND
1604 –1604 – Guilleaume (France)Guilleaume (France)
Thomas Syndenham (Eng)Thomas Syndenham (Eng)
--PolyarthritisPolyarthritis1605 -1605 - SydenhamSydenham - - St. Vitus Dance St. Vitus Dance 1761 -1761 - Morgani Morgani (Italy) – (Italy) – Heart valvesHeart valves1813 -1813 - W.C.wells W.C.wells – – Subcutaneous Subcutaneous
NodulesNodules 1818 -1818 - LaennecLaennec - - RHD (clinical)RHD (clinical)

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
HISTORICAL HISTORICAL BACKROUNDBACKROUND
1886 -1886 - CheadleCheadle - - Full syndromeFull syndrome 1904 -1904 - Aschoff Aschoff - - Aschoff NoduleAschoff Nodule1931 -1931 - Coburn Coburn - - Streptococcal Streptococcal
assocassoc..1944 -1944 - Jones Jones - - Criteria Criteria 1951 -1951 - WannamakerWannamaker (penicillin (penicillin
prophylaxis)prophylaxis)

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
EPIDEMIOLOGYEPIDEMIOLOGY

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
EPIDEMIOLOGYEPIDEMIOLOGY

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
IndiaIndiaS PadmavatiS Padmavati
Director, National Heart Institute, New Director, National Heart Institute, New Delhi, IndiaDelhi, India
In 2000, in a school survey involving In 2000, in a school survey involving 3963 children from the district of 3963 children from the district of Kanpur, the prevalence of RHD was Kanpur, the prevalence of RHD was 4.54 per 1000 4.54 per 1000 (Urban 2.56 and Rural (Urban 2.56 and Rural 7.42). 7.42).
The prevalence of RF was 0.75 per The prevalence of RF was 0.75 per 1000 1000 (Rural 1.20, Urban 0.42) (Rural 1.20, Urban 0.42)

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
EPIDEMIOLOGYEPIDEMIOLOGY2000 - 20042000 - 2004
HOSPITAL BASED SURVEYSHOSPITAL BASED SURVEYS : : Agarwal et al (varanasi) : Decreasing Agarwal et al (varanasi) : Decreasing
(8.4% - RHD & 1.1% RF) (8.4% - RHD & 1.1% RF)
Despande et al (Mumbai): No changeDespande et al (Mumbai): No change
Mishra et al (cuttack) : No changeMishra et al (cuttack) : No change

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
EPIDEMIOLOGYEPIDEMIOLOGY
PREVELANCE :PREVELANCE :
2 million at present2 million at present
INCIDENCE :INCIDENCE :
50 000 new cases every year 50 000 new cases every year

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
PATHOGENESISPATHOGENESIS

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
STRUCTURE OF Group –A STRUCTURE OF Group –A Beta Hemolytic Beta Hemolytic StreptococcusStreptococcus

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
Group - A StreptococcusGroup - A Streptococcus Two highly conserved epitopes within M Two highly conserved epitopes within M
protein divide GAS protein divide GAS immunologically into immunologically into
Class I (throat) Class II (skin) strains.Class I (throat) Class II (skin) strains. All RF strains fall clearly into Class I throat All RF strains fall clearly into Class I throat
strains strains The site of infection must be pharyngealThe site of infection must be pharyngeal. .
Regardless of how virulent an invasive strain may be, Regardless of how virulent an invasive strain may be, ARF does not result when it is introduced extra-ARF does not result when it is introduced extra-pharyngeally, e.g. through skin lesions or wound pharyngeally, e.g. through skin lesions or wound infections infections

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
CROSS REACTIVITYCROSS REACTIVITY

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
CO-PATHOGENSCO-PATHOGENS
Burch et al & Pongpanich et al :Burch et al & Pongpanich et al :
(1970) (1976)(1970) (1976)
Serological evidence of Cox B Serological evidence of Cox B viruses in patients with rheumatic viruses in patients with rheumatic fever fever

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
GENETIC GENETIC PREDISPOSITIONPREDISPOSITION
Specific B - cell alloantigen Specific B - cell alloantigen HLA DR 3 - Indians HLA DR 3 - Indians Moari races in New Zealand & Moari races in New Zealand &
Samoans in Hawaii Samoans in Hawaii High concordance in twins High concordance in twins Increased risk in families with H/O Increased risk in families with H/O
RFRF

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
ENVIRONMENTENVIRONMENT Low socio-economic groupLow socio-economic group
Urban slumsUrban slums Poor accesibility to health carePoor accesibility to health care Over crowdingOver crowding Unclean environment Unclean environment
Mostly seen in developing Mostly seen in developing countriescountries

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
INTERACTIONINTERACTION

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
PATHOLOGYPATHOLOGY

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
INFLAMMATORY RESPONSEINFLAMMATORY RESPONSE
Edematous changeEdematous change
Cellular infiltrateCellular infiltrate
Fibrinoid necrosisFibrinoid necrosis
Aschoff body Aschoff body (seen only in heart)(seen only in heart)

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
Joints : Joints : serositisserositis
PericardiumPericardium
Skin (S/C nodule) : Skin (S/C nodule) : Fibrinoid Fibrinoid
Heart Heart degenerationdegeneration
Erythema Marginatum : Erythema Marginatum : VasculitisVasculitis
Chorea : Chorea : VasculitisVasculitis

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
GranulomaGranulomaCentral Central
fibrinoid fibrinoid necrosisnecrosis
Surrounded by Surrounded by lymphocytes, lymphocytes, Antischkow Antischkow cells and cells and Plasma cellsPlasma cells
ASCHOFF BODYASCHOFF BODY

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/

Initial edemaInitial edema
Hyaline degenerationHyaline degeneration
Verrucae formation at the edge of leafletsVerrucae formation at the edge of leaflets
Prevents approximation Prevents approximation RegurgitationRegurgitation
Fibrosis & calcification Fibrosis & calcification StenosisStenosis

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
ORDER OF VALVE ORDER OF VALVE INVOLVEMENTINVOLVEMENT
MitralMitral
AorticAortic
Tricuspid Tricuspid
PulmonaryPulmonary

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
INTERNATIONAL SERIES BY INTERNATIONAL SERIES BY BONOWBONOW
PURE MS : PURE MS : 25 %25 %
PURE MR : PURE MR : 10 %10 %
MS / MR : MS / MR : 25 %25 %
AORTIC : AORTIC : 8 %8 %
ALL VALVES : ALL VALVES : 7 %7 %

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
CLINICAL FEATURESCLINICAL FEATURES

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
PERCENTAGE PERCENTAGE INVLOVEMENTINVLOVEMENT
(Indian Scenario)(Indian Scenario)ARTHRITISARTHRITIS : : 70 %70 %
ARTHALGIAARTHALGIA : : 90 %90 %CARDITISCARDITIS : : 70 %70 %CHOREACHOREA : : 08 %08 %S/C NODULES/C NODULE : : 02 %02 %ERYHTEMA MARGINATUMERYHTEMA MARGINATUM : : 01 % 01 %

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
LATENCYLATENCY
From onset of sore throat to onset From onset of sore throat to onset of initial attack of rheumatic fever of initial attack of rheumatic fever isis
1 – 5 weeks1 – 5 weeks
for recurrent attacksfor recurrent attacks
Median of 19 days & shorterMedian of 19 days & shorter

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
LATENCYLATENCY
Joint manifestations are Joint manifestations are firstfirst to occur to occur - heralding onset of disease- heralding onset of disease Carditis occurs within Carditis occurs within 2 weeks2 weeks - is apparent when patient is first seen- is apparent when patient is first seen Subcutaneous nodules appear Subcutaneous nodules appear 4 weeks4 weeks or or
more after onset of symptomsmore after onset of symptoms Chorea may appear Chorea may appear 2 to 6 months2 to 6 months later later
Erythema marginatum occurs both early & Erythema marginatum occurs both early & later later

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
MODE OF ONSETMODE OF ONSET
VariableVariable Abrupt onsetAbrupt onset with fever & acute polyarthritiswith fever & acute polyarthritis Insidious or sub clinical Insidious or sub clinical in mild indolent carditisin mild indolent carditis May present with CCFMay present with CCF
May present atypically with acute abdomen May present atypically with acute abdomen due to peritoneal inflammationdue to peritoneal inflammation

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
POLYARTHRITISPOLYARTHRITIS
Most common & Least specificMost common & Least specificsevere in adultssevere in adultsLarge joints ; asymetricalLarge joints ; asymetricalFlitting - Flitting - involves joints after jointsinvolves joints after jointsFleeting - Fleeting - Lasting for short timeLasting for short time3 days - 1 week 3 days - 1 week No residual damage No residual damage

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
POLYARTHRITISPOLYARTHRITIS
Responds dramatically to aspirinResponds dramatically to aspirin Severity inversely related to carditisSeverity inversely related to carditis
(Feinstein & Spagnuola et al – 1962)(Feinstein & Spagnuola et al – 1962)
JACCOUDS ARTHRITISJACCOUDS ARTHRITIS :: Small joints Small joints Produces residual damage Produces residual damage Seems to be related to RFSeems to be related to RF

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
PANCARDITISPANCARDITIS More severe in the youngMore severe in the young
Sub clinical to fulminant Sub clinical to fulminant
ENDOCARDITIS :ENDOCARDITIS : ARAR : 20 %: 20 %
MRMR : 75 %: 75 %
: due to - Valvulitis: due to - Valvulitis - MVP (anterior - MVP (anterior
leaflet)leaflet) - Annular - Annular
dysfunctiondysfunction

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
ENDOCARDITISENDOCARDITIS
Clinical Evidence of Clinical Evidence of Endocaritis :Endocaritis :
Apical holosystolic murmur Apical holosystolic murmur Carey coomb’s murmurCarey coomb’s murmur Early diastolic murmurEarly diastolic murmur

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
MYOCARDITISMYOCARDITIS
Clinical evidence of Myocarditis :Clinical evidence of Myocarditis :
Cardiomegaly Cardiomegaly
Clinical features of CHFClinical features of CHF
Gallop rhythm Gallop rhythm

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
PERICARDITISPERICARDITIS
Clinical evidence of Pericarditis :Clinical evidence of Pericarditis :Pericardial rubPericardial rub
Associated with endocarditisAssociated with endocarditis Indicates severe carditisIndicates severe carditis (High rheumatic activity)(High rheumatic activity)
No residual constriction No residual constriction

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
CHOREA CHOREA
Occurs 3 months later than other RF Occurs 3 months later than other RF features features - spontaneous resolution- spontaneous resolution
Duration : variable Duration : variable ( upto 6 months) ( upto 6 months) Often in prepuberal girlsOften in prepuberal girls Neuropsychiatric disorderNeuropsychiatric disorder Seen in 5 - 15 % casesSeen in 5 - 15 % cases

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
CHOREACHOREA
ST. VITUS DANCE ST. VITUS DANCE
25 - 30 % develop RHD particularly 25 - 30 % develop RHD particularly MSMS (Bland et al – 20 years follow up)(Bland et al – 20 years follow up)
Multiple purposeless movements of legs Multiple purposeless movements of legs and hands and hands
(also involves face)(also involves face)
on exertion & absent during sleepon exertion & absent during sleep

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
DD FOR CHOREADD FOR CHOREA
HABITUAL SPASMSHABITUAL SPASMS
WILSONS DISEASEWILSONS DISEASE
POST ENCEPHALITISPOST ENCEPHALITIS
HYSTERESIS HYSTERESIS

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
SUBCUTANEOUS SUBCUTANEOUS NODULENODULE
FIRM FIRM PAINLESS PAINLESS 0.5 – 3 cm IN SIZE 0.5 – 3 cm IN SIZE IN CROPS ( OVER EXTENSORS)IN CROPS ( OVER EXTENSORS)DISAPPEAR IN 12 WEEKS DISAPPEAR IN 12 WEEKS
ALWAYS ASSOCIATED WITH CARDITISALWAYS ASSOCIATED WITH CARDITIS

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
SUBCUTANEOUS SUBCUTANEOUS NODULENODULE

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
SUBCUTANEOUS SUBCUTANEOUS NODULENODULE

ERYTHEMA ERYTHEMA MARGINATUMMARGINATUM
Rare (< 1 %)Rare (< 1 %)
Bikini distributionBikini distribution
EvanescentEvanescent vanishingvanishing
Non pruritic Non pruritic

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
OTHER MANIFESTATIONSOTHER MANIFESTATIONS
EPISTAXISEPISTAXIS ABDOMINAL PAINABDOMINAL PAIN
- - Occurs in 5% cases Occurs in 5% cases
- Clinical importance - Clinical importance
Often appear hours or days before major Often appear hours or days before major manifestationsmanifestations
Acute abdomen [ appendicitis ] to be excluded Acute abdomen [ appendicitis ] to be excluded

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
FEVERFEVER
Relatively common But nonspecificRelatively common But nonspecific
Low grade; subside without treatment in 1-Low grade; subside without treatment in 1-2wk2wk
Associated with constitutional symptoms Associated with constitutional symptoms
Lab indices are high even after fever subsidesLab indices are high even after fever subsides Remission does not exclude rheumatic activityRemission does not exclude rheumatic activity

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
ECG CHANGESECG CHANGES
Seen in 2/5Seen in 2/5thth patients patients
[ Disciascio(1980)][ Disciascio(1980)]
PR interval ; PR interval ;
QT interval ;QT interval ;
AV blocksAV blocks
Does not correlate with organic murmurs, Does not correlate with organic murmurs,
prognosis or residual heart diseaseprognosis or residual heart disease
Nonspecific & occur in many other Nonspecific & occur in many other
infectioninfection

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
LAB INVESTIGATIONSLAB INVESTIGATIONS
Monitoring the Detecting the Monitoring the Detecting the antecedentantecedent
inflammatory activity infection with inflammatory activity infection with streptococcusstreptococcus
There is no single diagnostic testThere is no single diagnostic test

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
EVIDENCE OF STREPTOCOCAL EVIDENCE OF STREPTOCOCAL INFECTIONINFECTION
TH ROAT SWAB CULTURETH ROAT SWAB CULTURE : :
Only in Minority of casesOnly in Minority of cases
ASO TITREASO TITRE : : elevated from 7 - 10 days elevated from 7 - 10 days rise and fall rapidlyrise and fall rapidly >240 todd units (adults)>240 todd units (adults) >330 todd units (children)>330 todd units (children) Antibiotics/steroids/liver Antibiotics/steroids/liver
disease affect the titredisease affect the titre

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
EVIDENCE OF STREPTOCOCAL EVIDENCE OF STREPTOCOCAL INFECTIONINFECTION
ANTI-DNAase B TESTANTI-DNAase B TEST : :
## > 120 todd units (adults)> 120 todd units (adults)
# > 240 todd units (children) # > 240 todd units (children)
# used when ASO titre is not # used when ASO titre is not conclusive conclusive
# remains elevated for long time # remains elevated for long time
STREPTOZYME TESTSTREPTOZYME TEST : :
Detects antibodies against streptococcal Detects antibodies against streptococcal antigen antigen

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
RHEUMATIC ACTIVITY RHEUMATIC ACTIVITY DETECTIONDETECTION
Activity considered ended only when both Activity considered ended only when both ESR & CRP become normal ESR & CRP become normal
and remain so for 2 weeks after stopping and remain so for 2 weeks after stopping drugsdrugs
Fever & tachycardia subside long before Fever & tachycardia subside long before lab reactants declinelab reactants decline
Joint symptoms & active carditis do not Joint symptoms & active carditis do not occur after ESR & CRP declineoccur after ESR & CRP decline

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
RHEUMATIC ACTIVITY RHEUMATIC ACTIVITY DETECTIONDETECTION
CRP more specific than ESRCRP more specific than ESR
Usually lasts for 3 monthsUsually lasts for 3 months
Longer in patients with valvular Longer in patients with valvular involvementinvolvement
In 5% cases rheumatic activity persist In 5% cases rheumatic activity persist longer than longer than 6 months6 months
termed CHRONIC RHEUMATIC FEVERtermed CHRONIC RHEUMATIC FEVER

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
ECHOCARDIOGRAMECHOCARDIOGRAM
Abernathy et al : Abernathy et al :
echo allowed earlier diagnosis of echo allowed earlier diagnosis of carditiscarditis
Veasy et al :Veasy et al :
echo increased the sensitivity of echo increased the sensitivity of detecting carditis from 72% to 91% detecting carditis from 72% to 91%

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
ECHOCARDIOGRAMECHOCARDIOGRAM
Differentiates between innocent Differentiates between innocent murmur and Rheumatic MRmurmur and Rheumatic MR
Detects MVP due to Rheumatic feverDetects MVP due to Rheumatic fever
(Wu et al – JACC 1994)(Wu et al – JACC 1994)
- AML- AML
- Elongated chordae- Elongated chordae
- No myxomatous thickening- No myxomatous thickening

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
ECHOCARDIOGRAMECHOCARDIOGRAM
Cost effectiveness and the Cost effectiveness and the additional workload have to be additional workload have to be validatedvalidated
Vasan et al (Circ . 1994 ):Vasan et al (Circ . 1994 ): showed showed
no additional detection of carditis no additional detection of carditis by echo than by clinical detection by echo than by clinical detection

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
OTHER INVESTIGTIONSOTHER INVESTIGTIONS
Endomyocardial biopsyEndomyocardial biopsy – to establish – to establish the myocarditisthe myocarditis
not likely to provide additional not likely to provide additional informationsinformations
Radionuclide imaging- Radionuclide imaging- - - Gallium-67 imaging has better diagnostic Gallium-67 imaging has better diagnostic
characteristics than antimyosin scintigraphycharacteristics than antimyosin scintigraphy
- the results confirm that rheumatic carditis is - the results confirm that rheumatic carditis is infiltrative rather than degenerative in natureinfiltrative rather than degenerative in nature
- not suitable for routine investigation- not suitable for routine investigation

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
DUCKETT JONES DUCKETT JONES CRITERIACRITERIA
ORIGINAL (JAMA 1944)ORIGINAL (JAMA 1944)
MAJORMAJOR MINOR MINOR
Carditis Carditis erythema mariginatum erythema mariginatum ChoreaChorea fever / epistaxis / fever / epistaxis / ArthralgiaArthralgia abdominal pain abdominal pain S/C NoduleS/C Nodule WBC / ESR / CRP WBC / ESR / CRP Preexisting RFPreexisting RF

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
DUCKETT JONES DUCKETT JONES CRITERIACRITERIA
MODIFIEDMODIFIED :1956 - AHA :1956 - AHA Arthritis : Included as – major Arthritis : Included as – major
criteriacriteria Erythema marginatum: Included as – major criteriaErythema marginatum: Included as – major criteria
REVISEDREVISED : 1965 /84 - AHA : 1965 /84 - AHA Recent streptococcal infection is included as essential Recent streptococcal infection is included as essential
criteriacriteria
WHO : 1988 WHO : 1988
UPDATEDUPDATED : 1992 - AHA : 1992 - AHA WHO CRITERIA : 2003WHO CRITERIA : 2003

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
DUCKETT JONES DUCKETT JONES CRITERIACRITERIA
WHO CRITERIA FOR RF AND RHD- 2003WHO CRITERIA FOR RF AND RHD- 2003
MAJORMAJOR MINOR MINOR
CarditisCarditis ClinicalClinical Polyarthritis - FeverPolyarthritis - Fever ChoreaChorea - Arthralgia - Arthralgia S/C NodulesS/C Nodules LaboratoryLaboratory Ery. MarginatumEry. Marginatum - Leucocytosis - Leucocytosis
- Elevated : ESR /CRP- Elevated : ESR /CRP ECGECG - Increased PR - Increased PR
intervalinterval

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
DUCKETT JONES DUCKETT JONES CRITERIACRITERIA
Supporting evidence of antecedent Supporting evidence of antecedent streptococcal infection Within the streptococcal infection Within the last 45 dayslast 45 days - - positive Throat culture positive Throat culture
- Rapid streptococcal antigen test- Rapid streptococcal antigen test - Elevated or Rising ASO Titer- Elevated or Rising ASO Titer - Recent scarlet fever- Recent scarlet fever

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
Diagnostic categories: WHO Diagnostic categories: WHO 20032003
PRIMARY RF :PRIMARY RF : 2 major or 1 major and 2 minor + evidence of preceding 2 major or 1 major and 2 minor + evidence of preceding
Gr-A streptococcal infectionGr-A streptococcal infection
RECURRENT ATTACK OF RF WITHOUT RECURRENT ATTACK OF RF WITHOUT ESTABLISHED RHD ESTABLISHED RHD
2 major or 1 major and 2 minor + evidence of preceding 2 major or 1 major and 2 minor + evidence of preceding Gr-A streptococcal infectionGr-A streptococcal infection
RECURRENT ATTACK OF RF WITHRECURRENT ATTACK OF RF WITH ESTABLISHED RHDESTABLISHED RHD 2 minor + evidence of preceding Gr-A streptococcal 2 minor + evidence of preceding Gr-A streptococcal
infectioninfection

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
Diagnostic categories: WHO Diagnostic categories: WHO 20032003
Rheumatic chorea Rheumatic chorea Insidious onset rheumatic carditisInsidious onset rheumatic carditis
Other major manifestations or evidence of Other major manifestations or evidence of Group-A streptococcal infection not Group-A streptococcal infection not requiredrequired

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
Diagnostic categories: WHO Diagnostic categories: WHO 20032003
Chronic valve lesions of RHDChronic valve lesions of RHD
Patients presenting first time with Patients presenting first time with pure MS or mixed mitral valve pure MS or mixed mitral valve disease and /or aortic valve diseasedisease and /or aortic valve disease
Do not require any other criteria Do not require any other criteria for diagnosis as having RHDfor diagnosis as having RHD

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
DUCKETT JONES DUCKETT JONES CRITERIACRITERIA
Specificity – 97 %Specificity – 97 %
Sensitivity – 77 %Sensitivity – 77 %

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
BEYOND JONES CRITERIABEYOND JONES CRITERIA
Not a substitute for clinical judgmentNot a substitute for clinical judgmentNot meant to predict course or Not meant to predict course or
severityseverityUseful for initial diagnosis onlyUseful for initial diagnosis onlyExceptions : Exceptions :
- Chorea- Chorea
- Isolated indolent carditis- Isolated indolent carditis
- Recurrence with RHD- Recurrence with RHD

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
APPLYING JONES CRITERIAAPPLYING JONES CRITERIA
2 major criteria is stronger than 2 major criteria is stronger than One major and 2 minor One major and 2 minor
Arthalgia cannot be used as minor criteria Arthalgia cannot be used as minor criteria when arthritis is presentwhen arthritis is present
Prolonged PR cannot be used as a minor Prolonged PR cannot be used as a minor criteria when clinical carditis is present criteria when clinical carditis is present

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
APPLYING JONES CRITERIAAPPLYING JONES CRITERIA
Absence of evidence of an antecedent Absence of evidence of an antecedent Group-A Beta-hemolyticus Streptococci Group-A Beta-hemolyticus Streptococci is a warning that RF is unlikelyis a warning that RF is unlikely
Possibility of early suppression of full Possibility of early suppression of full clinical manifestations by drugs should clinical manifestations by drugs should be sought during history taking be sought during history taking

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
RECURRENCERECURRENCE
Cardiac status deteriorates with each new Cardiac status deteriorates with each new attackattack
Younger the patient - higher recurrence rateYounger the patient - higher recurrence rate
Recurrence decreases with passage of time – Recurrence decreases with passage of time – . . - - 50% within first year 50% within first year
- only 10% after 5 years- only 10% after 5 years Recurrence more in those with valvular lesionRecurrence more in those with valvular lesion
Increase antibody response associated with Increase antibody response associated with high recurrence ratehigh recurrence rate

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
RECURRENCERECURRENCE
Clinical manifestations in recurrence Clinical manifestations in recurrence tend to mimic those in preceding attacktend to mimic those in preceding attack
Recurrence distinguished from rebound Recurrence distinguished from rebound or exacerbation if interval of 3 months or exacerbation if interval of 3 months freedom of rheumatic activityfreedom of rheumatic activity
Valve stenosis at diagnosis indicates Valve stenosis at diagnosis indicates recurrencerecurrence

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
RHEUMATIC FEVERRHEUMATIC FEVER
Licks the Joint and Bites the Heart Licks the Joint and Bites the Heart

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.incardiologysearch.blogspot.in//

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
THANK YOUTHANK YOU

http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/
Kindly send your suggestions to Kindly send your suggestions to improve this site improve this site
Visit us regularly for updatesVisit us regularly for updates
Send your articles/ ppt/pdf to Send your articles/ ppt/pdf to publish in this site . publish in this site .
http://http://cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/cardiologysearch.blogspot.in/