Review Week1
description
Transcript of Review Week1

Review Week1
FZR Rev1.0 1UPM ECC3105 S1-12/13

Week2 Outline
• Basic Architecture – BUS
FZR Rev1.0 2UPM ECC3105 S1-12/13

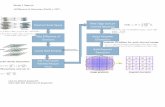
Basic Architecture: Personal Computer
Memory bus
VESA PCI EISAISABusUSB
FZR Rev1.0 3UPM ECC3105 S1-12/13

Basic Architecture: Personal Computer (cont.)
FZR Rev1.0 UPM ECC3105 S1-12/13 4
Microprocessor
Northbridge
Southbridge
Memory
USB
PCI/PCIe
Memory
IDE/Parallel ATA
Graphic Card
Ethernet Serial ATA
Figure 2

Basic Architecture: Bus
Note that Pentium system bus architecture is more complex that this.
FZR Rev1.0 5UPM ECC3105 S1-12/13

Basic Architecture: Bus (cont.)
• Address:– If I/O, a value between 0000H and FFFFH is issued.
– If memory, it depends on the architecture:• 20-bits (8086/8088)• 24-bits (80286/80386SX)• 25-bits (80386SL/SLC/EX)• 32-bits (80386DX/80486/Pentium)• 36-bits (Pentium Pro/II/III)
• Data:• 8-bits (8088)• 16-bits (8086/80286/80386SX/SL/SLC/EX)• 32-bits (80386DX/80486/Pentium)• 64-bits (Pentium/Pro/II/III)
• Control:• Most systems have at least 4 control bus connections (active low).• MRDC (Memory Read Control), MWRC, IORC (I/O Read Control), IOWC
FZR Rev1.0 6UPM ECC3105 S1-12/13

Basic Architecture: Bus Standards
• ISA (Industry Standard Architecture): 8 MHz• 8-bit (8086/8088)• 16-bit (80286-Pentium)
• EISA: 8 MHz• 32-bit (older 386 and 486 machines).
• PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect): 33 MHz• 32-bit or 64-bit (Pentiums)• New: PCI Express and PCI-X 533 MTS
• VESA (Video Electronic Standards Association): Runs at processor speed.
• 32-bit or 64-bit (Pentiums) • Only disk and video. Competes with the PCI but is not popular
FZR Rev1.0 7UPM ECC3105 S1-12/13

Basic Architecture: Bus Standard (cont.)
• USB (Universal Serial Bus): 1.5 Mbps,12 Mbps, 480 Mbps and now 5Gbps.
• Newest systems.• Serial connection to microprocessor.• For keyboards, the mouse, modems and sound cards.• To reduce system cost through fewer wires.
• AGP (Advanced Graphics Port): 66MHz• Newest systems.• Fast parallel connection: Across 64-bits for 533MB/sec.• For video cards.• To accommodate the new DVD (Digital Versatile Disk) players.• Latest AGP 3.0 with peak bandwidth of 2.1GB/s.
FZR Rev1.0 8UPM ECC3105 S1-12/13

Inside your iPhone…

ECC3105 Assignment 1 (Deadline: 26/09/2012, 0900hr)
• Task:1. Based on the given picture, please label the
components appropriately.
2. Give the definition of Moore’s Law and its relation to our course.
3. Some says Moore’s Law will get to an end. Name the reasons why Moore’s Law will end?
4. Please give at least 3 answers for each question:1. Why do we need to learn about microprocessors.
2. What do you aspect to learn from microprocessor course.
FZR Rev1.0 10UPM ECC3105 S1-12/13

PC platform
A. Connector for peripherals
B. CPUC. Northbridge (w/ heat
sink)D. 20-pin ATX power
connectorE. RAM memory slotF. FDD connectorG. AGP SlotH. CMOS battery
backupI. IDE connector (2x)J. BIOS chipK. SouthbridgeL. PCI slot M. PCI-express slot
FZR Rev1.0 UPM ECC3105 S1-12/13 11
Figure 1