The NERVOUS SYSTEM __________________ & __________________ Nervous System.
Question Bank Nervous System - Testlabz · Question Bank Nervous System 1. ... The part of the...
Transcript of Question Bank Nervous System - Testlabz · Question Bank Nervous System 1. ... The part of the...

Class-X Question Bank 1
Question Bank
Nervous System
1. Name the following :
(i) The cells of retina sensitive to colour.
(ii) The part of the brain which controls the activities of the internal organs.
(iii) The part of the autonomic nervous system which prepares the body for
violent action against abnormal conditions.
(iv) The part of the human eye which controls the light entering it.
(v) The number of spinal nerves in the human body.
(vi) The part of the brain concerned with memory.
(vii) The middle coat of the eye which is soft, vascular and thin.
(viii) The eye defect caused due to the shortening of the eyeball from front to back.
Ans. (i) Cones (ii) Medulla oblongata
(iii) Sympathetic nervous system
(iv) Iris (v) 31 pairs
(vi) Cerebrum (vii) Choroid
(viii) Hypermetropia or Long-sightedness.

Class-X Question Bank 2
2. Fill in the blanks:
(i) The part of the eye responsible for change in the size of the pupil is the
__________ . [Iris / Ciliary muscle / Retina].
(ii) The connective tissue membrane which closely adheres to and covers the
brain and spinal cord is known as _____________ [Duramater / Piamater /
Meninges].
(iii) Calcium carbonate particles present in endolymph are called _________
[Otocenia / Ampullae / Cochlea].
(iv) Our tongue can perceive _______________ basic tastes. [Two / Three
/ Four].
(v) The role of accessory structures such as the bones of the middle ear, in a
sense organ is to _________ [Integrate the response / Amplify the stimulus
/ Amplify the response].
(vi) A molecule cannot be tasted or smelled until it has been _____________.
[Converted into a protein / Converted into a neurotransmitter / Dissolved
in a liquid].
(vii) Most of what we taste in food is actually __________________ [Imagined
by our cerebral cortex / A memory from childhood when we had more
taste receptors / Odour].
(viii) Receptor cells for balance and equilibrium in man are the ___________.
[Malleus, Incus and stapes / Hair cells / Statoliths].

Class-X Question Bank 3
Ans. (i) Iris (ii) Meninges
(iii) Otocenia (iv) Four
(v) Amplify the stimulus (vi) Dissolved in a liquid
(vii) Odour (viii) Hair cells
3. State whether the following statements are True or false. If false, rewrite the
sentence by changing the word printed in bold type only.
(i) Spinal nerves and cranial nerves constitute the central nervous system.
(ii) Reflex action involves brain.
(iii) Hypermetropia is a defect of the eye caused due to the eyeball being
elongated.
(iv) Two meninges cover the brain and the spinal cord.
(v) Rods enable us to see three primary colours.
(vi) Cones are photoreceptor cells that are sensitive to dim light.
Ans.(i) False (Peripheral) (ii) False (Spinal cord)
(iii) False (Myopia) (iv) False (Cone)
(v) False (Cones)
(vi) False. (Rods are photoreceptors cells that are sensitive to dim light.)
4. Match the following structures of the vertebrate eye with their respective
functions.
(a) Cornea 1. Provides opening for light to enter.
(b) Fovea 2. Transduces blue, green and red light.
(c) Iris 3. Transduces all waves of light.

Class-X Question Bank 4
(d) Lens 4. Controls the amount of light that enters the eye.
(e) Optic nerve 5. Alters the shape of the lens.
(f) Pupil 6. Transmits information to the cones.
(g) Periphery of retina 7. Focuses light directly on retina.
(h) Ciliary muscles 8. Bends light and protects the inner eye
Ans. a–8; b–2; c–4; d–7; e–6; f–1; g–3; h–5
5. (i) Label the diagram of brain given alongside.
(ii) Name the coverings of brain and spinal cord.
(iii) Name the fluid present between the meninges and mention its function.
(iv) What is the difference in the location of grey matter in brain and spinal cord ?
(v) Name the fibres which join two cerebral hemispheres.
(vi) What is the importance of convolutions in the grey matter?
(vii) Name the part of the brain which performs the following functions :
(a) Secretion of cerebro-spinal fluid
(b) Control of reflex action
(c) Intelligence/judgement
(d) Balance of the body
(e) Control of the body temperature and blood pressure
(f) Co-ordination of muscle movements on the two sides of the body.
(g) Control of heartbeat.

Class-X Question Bank 5
(viii) Give two functions of the spinal cord
(ix) Draw a T.S of spinal cord.
Ans. (i) 1. Hypothalamus; 2. Optic chiasma; 3. Pituitary gland, 4. Spinal cord;
5. Medulla oblongata; 6. Pons; 7. Cerebellum; 8. Mid brain; 9. Pineal body;
10. Cerebrum; 11. Corpus callosum; 12. Thalamus.
(ii) Piamater, Arachnoid and Duramater
(iii) Cerebro-spinal fluid. Its functions are :
(a) Protects the brain and the spinal cord against mechanical injury and shock.
(b) Helps in exchange of food, respiratory gases and waste products.
(c) Maintains a constant pressure inside the cranium inspite of fluctuation
in the pressure of blood in the cranial vessels.
(iv) In brain, grey matter is situated on the outside and white matter is located
on the inside whereas in spinal cord white matter forms an outer layer
surrounding the grey matter.
(v) Corpus callosum.

Class-X Question Bank 6
(vi) Convolutions in the cerebrum increases the surface area of cortex for
accomodating more nerve cells. The number of convolutions are believed
to be associated with the degree of intelligence.
(vii) (a) Medulla oblongata
(b) Medulla oblongata
(c) Cerebrum
(d) Cerebellum
(e) Hypothalamus
(f) Pons
(g) Medulla oblongata
(viii) (a) Acts as a main centre of reflex action.
(b) Acts as a link between spinal nerves and brain. It participates in
conscious action.
(ix)

Class-X Question Bank 7
6. (i) The V.S. of the human eye is given alongside. Label all the parts from
1 to 14.
Start labelling in anticlockwise direction with conjunctiva as
1 and vitreous chamber as 14.
(ii) The human eye is different from a camera in the sense that it can adjust
its focal point. Explain how. What is accommodation?
(iii) Enlist the major changes that occur when the eyes are trying to adapt in
the dark or in light.
(iv) Where is the vision least in the eye? Why is it called the blind spot?
(v) Where is the vision best in the eye? Why is it so?
Ans. (i) 1. Conjunctiva 2. Cornea; 3. Pupil; 4. Iris; 5. Suspensory ligament;
6. Blind spot 7. Optic nerve; 8. Yellow spot; 9. Retina 10. Choroid
11. Sclerotic layer 12. Lens 13. Ciliary muscles 14. Vitreous Chamber.

Class-X Question Bank 8
(ii) The human eye is able to change its focal point by changing the shape of
the lens in accordance with how far the object being viewed is from the eye.
The lens is connected via suspensory ligaments to ciliary muscles that
contract to flatten the lens and relax to make the lens more convex.
When the eye is to view a distant object, the ciliary muscles contract to
give the lens a flatter shape. When the object to be viewed is closer, the
ciliary muscles relax and the lens returns, by its own elastic recoil, to its
natural convex shape.
Accommodation : Adjustment of the eye for a clear vision of objects at
different distances is called accommodation.
(iii) Major changes occurring in the eye during adaptation are as follows :
Dark adaptation
1.The pupils dilate to allow more light to enter the eye.
2.The pigment of the rods, visual purple, is regenerated.

Class-X Question Bank 9
Light adaptation
1.The pupils constrict to prevent entry of light into the eye.
2. The visual purple is bleached.
(iv) Blind Spot — The area of no vision.
Just below the yellow spot is the blind spot. There are no sensory cells
here, and therefore, this is the point of no vision. This is the point at which
the nerve fibres from all the sensitive cells of the retina converge and
bundle together to leave the eyeball in the form of the optic nerve.
(v) Yellow spot — The area of best vision.
The distribution of rods and cones is not uniform. A particular spot called
the macula or yellow spot (or fovea centralis) lies at the back of the eye,
almost at the centre at the horizontal axis of the eyeball. This spot contains
the maximum number of sensory cells, particularly the cones. As a result,
this is the region of the brightest vision and also of the colour vision.
The rest of the retina has fewer cones and more rods.
Yellow spot is the place of best vision of the normal eye. This is the reason
why you move your eyes from word to word as you read a line through a
printed page.
7. (i) Draw a labelled diagram to show a reflex arc.
(ii) Define reflex action.
(iii) How is presbyopia different from myopia?

Class-X Question Bank 10
Ans. (i)
(ii) It is an action which is instantaneous and not under control of the will, for
example the instantaneous withdrawal of the hand when it accidentally
touches a hot object.
(iii) Presbyopia: It is a condition affecting older people due to which they
cannot see nearby objects clearly. The lens loses its flexibility resulting
in a kind of far-sightedness. This is corrected by using convex lens.
Myopia : It is a condition in which the near objects can be seen clearly
while the distant objects appear blurred, as the image is formed in front
of the retina. This is corrected by using concave lenses.
8. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
(i) What handicaps would result from damage to part 3 and damage to part 4?
(ii) Name the brain membranes.
(iii) What is meningitis?

Class-X Question Bank 11
Ans. (i) Damage to 3 : It would lead to vision impairment.
Damage to 4 : The coordination of muscular activity and body
equillibrium would be disturbed.
(ii) Brain membranes :
(a) Inner piamater
(b) Middle arachnoid
(c) Outer duramater.
(iii) Meningitis: This is a disease caused due to the inflammation of the brain
membranes and results in the clear cerebrospinal fluid turning turbid.
The patient suffers from severe headache.
9. The diagram below represents the parts of the human ear:
(i) Name the parts labelled ‘1’ to ‘8’.
(ii) What is the function of the parts marked ‘2’ and ‘3’?
(iii) Why is it harmful to use a pin or any sharp object to remove wax from
the ear?

Class-X Question Bank 12
Ans. (i) 1. Stirrup or stapes
2. Semicircular canals
3. Auditory nerve
4. Cochlea
5. Eustachian tube
6. Malleus or Hammer
7. Tympanum
8. Pinna
(ii) 2. Maintaining body balance
3. Transmit action potential to the auditory cortex.
(iii) It may rupture the eardrum and thus impair hearing.
10. The diagram given below represents the reflex arc. Name the parts (1 to 7).
Ans. 1. Afferent (sensory) fibre
2. Cell body of sensory neuron
3. Dorsal root of spinal nerve
4. Adjustor neuron
5. Central canal
6. Grey matter
7. Spinal nerve

Class-X Question Bank 13
11. The taste buds responsible for the various tastes are located on certain areas
of the tongue. Fill the table keeping in mind the following:
Taste buds Location on the tongue 1. Salt 2. Sweet 3. 4.
rear side and back
Ans.
Taste buds Location on the tongue 1. Salt 2. Sweet 3. 4.
tip and sides front of tongue rear side and back
12. Draw a neuron and label all its parts.
Ans.

Class-X Question Bank 14
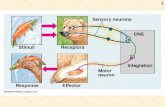
13. Nervous system performs three major functions. What are they?
Ans. The major functions of the nervous system are :
(i) To control and coordinate the various body activities, both voluntary and
involuntary.
(ii) To react to the environment through sense organs.
(iii) To regulate the internal environment of the body.
14. Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary actions.
Ans. Differences between Voluntary Action and Involuntary Action
Voluntary Action Involuntary Action 1. The actions are under the will. Actions not under one’s control or will. 2. They may or may not involve information from receptors or sense organs.
These are in response to information received from receptors or sense organs.
3. Impulse originates in the brain.
Impulse originates in receptors or sense organs.
4. They involve brain, motor nerve fibres and effector organs.
Involve receptors, sensory nerves, interneuron, motor nerve fibres and effector organs.
15. Give one point of difference between the following pairs on the basis of what
is indicated in brackets : Medulla oblongata and Cerebellum (function).
Ans. Medulla oblongata : Posterior medulla controls the activities of the internal
organs. It has reflex centres such as cardiac centre, respiratory centre and
vasomotor centre. It also has reflex centres for swallowing, coughing, sneezing
and vomiting.
Cerebellum : It is concerned with coordinating movements of skeletal muscles.
It maintains posture, equilibrium and muscular toning.

Class-X Question Bank 15
16. Name the 3rd, 5th, 10th and 12th cranial nerves.
Ans. 3rd— Occulomotor, 5th— Trigeminal, 10th — Vagus,
12th — Hypoglossal
17. Match the following structures of the ear with their respective functions.
Column A Column B
(a) Auditory canal 1. Channels pressure
waves of air into the middle ear.
(b) Auditory 2. Collects pressure waves
(eustachian tube) of air.
(c) Auditory nerve 3. Converts pressure
waves of air into vibrations of bones.
(d) Incus 4. Dissipates sound waves.
(e) Malleus 5. Equalises pressure
between the middle ear
and the atmosphere.
(f) Oval window 6. Provides information
about the spatial
orientation of the head.
(g) Pinna 7. Transfers vibrations
from a bone to a fluid.
(h) Round window 8. Transfers vibrations
from a bone to a membrane.

Class-X Question Bank 16
(i) Semicircular canals 9. Transfer vibrations
from a bone to a bone.
(j) Stapes 10. Transfers vibrations
from a membrane to a bone.
(k) Tympanic membrane 11. Transmits action potential to the
auditory cortex.
Ans. (a) (1) (b) (5) (c) (11)
(d) (9) (e) (10) (f) (7)
(g) (2) (h) (4) (i) (6)
(j) (8) (k) (3).
18. (i) What is meant by ‘Power of accommodation’ of the eye? Name the
muscles of the eye responsible for the same.
Ans. ‘Power of accommodation’ of the eye :
Adjustment of the eye for a clear vision of objects at varying distances is
called accommodation. This is mainly brought about by a change in the
curvature of the elastic lens, making it more convex or concave, with the aid
of ciliary body and suspensory ligaments. This is called power of
accommodation.The muscle responsible for the accommodation of the eye
are called the ciliary muscles.
(iii) Draw a labelled diagram of the inner ear. Name the part of the inner ear
that is responsible for static balances in human beings.

Class-X Question Bank 17
Ans. The parts of the inner ear that is responsible for static balance in human being
are the semi-circular canals.
19. Give the exact location and one function of Pinna.
Ans. Location : External ear
Function : Collects the sound waves and directs them into the ear canal.
20. What is the difference between Choroid and Sclerotic layers of the eye
(Function)?
Ans. Choroid layer : Choroid layer contains a black pigment which prevents light
rays from reflecting and scattering inside the eye.
Sclerotic layer : It is a protective layer of the eye.
21. The diagram given below is the external view of the human brain. Study the
same and answer the questions that follow :
(i) Name the parts labelled 1, 2 and 3.

Class-X Question Bank 18
Ans. 1 — Cerebrum/cerebral hemisphere
2 — Cerebellum
3 — Spinal cord
(ii) State the main functions of the parts labelled 1 and 2.
Ans. Cerebrum : Seat of consciousness, thinking, memory, reasoning, perception
and stimulus interpretation.
Cerebellum : It maintains posture, equillibrium and muscular toning.
(iii) How are the brain cells arranged in the part labelled ‘1’?
Ans. Cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is divided into right and left
halves called cerebral hemispheres. These are connected together by a sheet
of nerve fibres called corpus callosum. The wall of cerebrum has two regions.
The outer region is called the cortex and contains cells bodies of the neurons
and is thus greyish in colour. So it is also called the grey matter. The grey
matter is highly convoluted with ridges and grooves.
(iv) What is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system?
Ans. Structural and functional unit of the nervous system is neuron.
(v) Name the fluid that surrounds the brain. State its function.
Ans. CSF or cerebro-spinal fluid surrounds the brain. It protects the brain from
jerks and jolts.

Class-X Question Bank 19
22. On entering a poorly lit room, one feels blinded for a short while. Why?
Ans. This is due to the fact that it takes some time for the regeneration of the
visual purple or rhodopsin and dilation of the pupil permitting more light
into the eyes.
23. The following diagram represents the human brain as seen in an external
view. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow :
(i) Name the parts labelled 1, 2, 3 and 4.
(ii) Mention the difference in the arrangement of the nerve cells in the parts
marked ‘1’ and ‘4’.
(iii) What is the main function of the parts marked ‘3’ and ‘4’?
(iv) Name the sheet of nerve fibres that connect the two halves of the part
labelled ‘1’.
Ans. (i) 1. Cerebrum 2. Cerebellum
3. Medulla oblongata 4. Spinal cord.
(ii) 1. Grey matter is outside and white matter is inside.
4. White matter is outside and Grey matter is inside.

Class-X Question Bank 20
(iii) 3. Medulla oblongata controls all involuntary movements of internal
organs e.g., breathing movements of lungs, beating of heart,
vasodilation, vasoconstriction, blood pressure, gland secretion etc.
4. The spinal cord has two main functions—
(1) Provide pathway to sensory impulses towards brain & motor
impulses away from brain.
(2) Performs reflex action below neck without the involvement of brain.
(iv) Corpus callosum.
24. (i) What is a Lacrimal gland?
(ii) In what two ways is yellow spot different from blind spot?
(iii) Name an old-age eye defect. Why is it caused?
Ans. (i) Lacrimal gland : It is a secretory gland present in top right part of the eye.
Its secretion is called tears which lubricates the eye and it contains
lysozyme which protects the eye from infection of microbes.
(ii) Yellow Spot Blind Spot 1. It is the area of best vision. It is the area of no vision. 2. It contains maximum number of cone cells.
There are no cone and rod cells in this area.
(iii) Presbyopia : It is an old age defect, in which lens looses its flexibility.
25. The diagram given below shows the internal structure of the spinal cord,
depicting a simple reflex. Study the same and then answer the questions that
follows.
(i) Name the parts numbered 1 to 5.

Class-X Question Bank 21
(ii) Using the letters of the alphabet shown in the figure, indicate the direction in
which an impulse enters and leaves the spinal cord.
(iii) What is the term given to the point of contact between two nerve cells?
(iv) What is meant by “simple reflex”? Give two examples of simple reflexes
and name the stimuli too.
Ans. (i) 1. Sensory neuron 2. Cell body of sensory neuron
3. White matter 4. Cell body of motor neuron
5. Spinal nerve
(ii) B C A
(iii) Synapse.
(iv) Simple reflex : A simple reflex or natural reflex is a response to stimulus,
performed without conscious control or it is a quiet involuntary response
to a stimulus that passes through a reflex arc. Naturally, the necessary
response automatically and suddenly occurs almost as soon as stimulus is
received. Functionally, these are the basic units of nervous co-ordination.
e.g. moving away of hand when pricked by a pin, watering of mouth
by sight of sweets, blinking of eyes due to sudden appearance of some
object in front of eyes.

Class-X Question Bank 22
26. (i) Draw a labelled diagram of a myelinated neuron.
(ii) Explain the difference between sensory nerve and motor nerve.
Ans. (i)

Class-X Question Bank 23
(ii)
Afferent (Sensory) Nerve Efferent (Motor) nerve
It conducts nerve impulse from
receptors to the central nervous
system.
It conducts nerve impulse from
central nervous system (C.N.S.) to
the effectors (muscles and glands) of
the body.
It is generally made up of pseudounipolar neurons.
It is generally made up of multipolar neurons.
Its dendrites are comparativelylonger than the axon.
Its axon is comparatively longer than dendrites.
Its axon enters into the C.N.S. Its axon emerges out from C.N.S.
27. Given below is the diagram of a part of the human ear. Study the same and
then answer the questions that follow:
(i) Give the biological term for Malleus, Incus and Stapes.
(ii) Name the parts labelled A, B and C in the diagram.
(iii) State the functions of the parts labelled ‘A’ and ‘B’.
(iv) Name the audio receptor region present in the part labelled ‘A’.

Class-X Question Bank 24
Ans. (i) Hammer, anvil and stirrup. (Ear ossicles)
(ii) A = Cochlea, B = Semicircular Canals, C = Ampullae/utriculus, sacculus.
(iii) A = Concerned with sense of hearing, B = Sense of dynamic balance.
(iv) Organ of corti
28. The given diagram refers to the ear of a mammal.
(i) Label the parts 1 to 10 to which the guidelines point.
(ii) Which structure
(1) Converts sound waves into mechanical vibrations?
(2) Converts vibrations into nerve impulses?
(3) Responds to change in position?
(4) Transmits impulses to the brain?
(5) Equalizes atmospheric pressure and pressure in the ear?
Ans. (i)
(1) Cochlea (2) Auditory nerve
(3) Semi-circular canals (4) Ear ossicles

Class-X Question Bank 25
(5) Auditory canal (6) Pinna
(7) Ear drum (8) Round window
(9) Eustachian tube (10) Oval window
(ii)
(1) Ear drum (2) Cochlea
(3) Semi-circular canals (4) Auditory nerve
(5) Eustachian tube
29. Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye.
Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
(i) Name the defect shown in the diagram.
(ii) Give two possible reasons for this defect of the eye in human beings.
(iii) Name the parts labelled 1 to 4.
(iv) Name the type of lens used to correct this eye defect.
(v) Draw a labelled diagram to show how the above mentioned defect is
rectified using the lens named above.

Class-X Question Bank 26
Ans. (i) Myopia, (Short-sightedness).
(ii) The possible reasons for this defect may be:
1. The eye ball is lengthened from front to back.
2. The lens is too curved.
(iii) 1. Vitreous humour
2. Fovea centralis (yellow spot)
3. Lens
4. Pupil
(iv) This defect can be corrected by suitable concave lens.
(v) See along side the figure.
30. Enumerate the common defects of visions, their causes and the possible
methods of correcting them.
Ans.
Defect Cause Corrective measure Myopia Hypermetropia Astigmation Presbyopia Cataract Night blindness Colour blindness Squint
(i) Lens is too curved (ii) Eyeball is lengthened (i) Lens is too flat (ii) Shorting of the eyeball Uneven curvature of cornea Losses in flexibility of lens Lens turns opaque Non-formation of visual purple pigment Genetic defect Weak eye muscles
Concave lenses Convex lenses Cylindrical lenses Convex lenses Surgery Vitamin A No cure Surgery

Class-X Question Bank 27
31. The figures below compares a part of our eye with a part of a photographic
camera.
(a) Name the corresponding parts of the eye and the camera shown here that are
comparable in function.
(b) Explain the mode of working and the functions of the parts of the eye
mentioned above.
Ans. Eye Camera 1. Eyeball 2. Lens 3. Eyelids 4. Iris 5. Pupil 6. Lens muscles 7. Pigmented lining of the wall 8. Light-sensitive retina
Camera-box Lens Lens cap Diaphragm Aperture (lens opening) Focusing device Black lining of the box Light sensitive film or plate
1. Lens – Focussing for near and distant vision. 2. Eyelids – Prevent foreign material from entering the eye.
3. Iris – Widens and constricts the pupil.
4. Pupil – Regulate the amount of light entering the eye.
5. Lens muscles – Control the curvature of the lens.
6. Pigment lining – To prevent light rays from scattering of the wall inside
the eye.
7. Light sensitive – Image is formed here on retina.

Class-X Question Bank 28
32. Name the three ear ossicles. How do they contribute to the mechanism of
hearing?
Ans. Incus, Malleus and stapes. They magnify and transmit the vibrations from
the outer to inner ear.
33. By closing the eyes and gently pressing them with your palms, you may see
some specks of brilliant light. How do you get this sensation while there is
no light entering your eyes?
Ans. When the eyes are pressed, the retina is physically stimulated causing the
sensation of light.