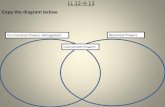
Q: What are enumerated powers? A: Powers expressly written in the Constitution.
-
Upload
rosanna-tamsin-townsend -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Q: What are enumerated powers? A: Powers expressly written in the Constitution.

Q: What are enumerated
powers?
A: Powers expressly written in the Constitution

Q: How does the election of the President differ from a Prime
Minister? A: Legislative branch chooses Prime Minister, while President elected by people

Q: What is bureaucracy?
A: Governmental departments and agencies and their staffs, principally civil service members and political appointees.

Q: What does a Writ of Certiorari
do?
A: Requires the lower courts to send records of a case to the Supreme Court.

Q: Describe how a Bill becomes a law
A: 1. Committee Assignments- Subcommittees give bills rigorous
scrutiny2. Hearings- Public hearings are scheduled to gather information3. Deliberations- “Mark Up Sessions” called to make changes 4. Report- A written report is given to members of the house on a bill to be considered5. Floor Vote- Bill is placed on the calendar for debate and vote in the full house6. Referral to the other chamber- When a bill passes in one house, it then goes to the other house where the entire process is repeated7. Conference Committee- Members from both houses that worked on the bill will meet to reach a compromise. If they can reach an agreement, the bill is sent back to both houses for an up or down vote8. Referral to the president- The president has 3 options with a bill. Veto, Pocket veto, and signing the bill.

Q: Identify one way Parliament
differs from Congress
A:
Representation (houses represent classes)Separation of Powers (Parliament is intertwined withother branches)
Length of terms (Elections are not fixed in Parliament)Federalism (power delegated to local governments by federal in GB)

Q: What is a filibuster?
A: The practice of refusing to surrender the floor during a debate to prevent the Senate from voting on a proposal.

Q: What is original jurisdiction?
A: In some cases, such as those in which a state is the party, the Supreme Court has the right to consider the facts and the law in a case without it having first been passed on by the lower court.

Q: Identify a power denied to Congress.
A:
Cannot stop importation of slave for 20 yearsCannot suspend Habeas CorpusNo Bill of Attainder or Ex Post Facto lawsNo Direct TaxNo Taxation on Exports from statesNo money from treasury without appropriation made by lawNo titles of nobility

Q: What are the 4 methods of
Constitutional interpretation?
A: Textualism, Original Intent, Fundamental Principles, Modernism

Q: What is lobbying?
A: The practice of attempting to affect legislation by influencing legislators

Q: Identify 2 checks placed on
the Supreme Court.
A:
Self imposed limits (refuse to hear political, no advisory)Presidential appointments to the CourtExecutive Enforcement (refuse to enforce rulings)Congressional Powers (budget, Amendments)Federalism (states enforce rulings)

Q: Describe the committee system
of Congress.
A: Groups in Congress that have jurisdiction over particular subjects and work on proposed legislation

Q: What is patronage?
A: Support, often financial, given by a person or institution to a person, group, or institution in need. ex: Rewarding supporters by giving them permanent government jobs.

Q: Define Cabinet.
A: The group of advisors to the president composed of the heads of the departments of the executive branch and certain other officials. Cabinet advice to U.S. presidents

Q: How has the Presidency evolved?
A: Presidency changes based on who is in office. Powerful presidents expanded the power of the president to create change they thought necessary to best serve the United States.

Q: What is impeachment?
A: Charging a public official with a crime while in office and bringing him or her to trial. Convicted officials are removed from office.

Q: What is the Rule of Four?
A: Upon review, if 4 out of 9 Supreme Court Justices believe the case has merit, they agree to hear the case.

Q: What are the 3 categories of
Executive Agencies?
A:1. Executive departments2. Executive Office of the President (EOP)3. Independent Agencies

Q: How are states “testing grounds”?
A: States can choose to try new and innovative programs. Initiative, referendum, recallEx. Environmental protection and health care

Q: Representation in the House of
Representatives is based on what?
A: Population

Q: Define seniority.
A: Length of service. In the House of Representatives of the Senate, certain powers and responsibilities of congressional members, such as committee chairmanships, are granted on the basis of their time in office.

Q: Name one role of the President in
foreign policy.
A:
Commanding the Armed ForcesMaking treatiesAppointing ambassadorsReceiving ambassadors

Q: Identify one Constitutional
power given to the Supreme Court.
A: Article III created Supreme Court
Life tenure for justicesFederal courts have specific jurisdiction regarding national laws and people from more than one stateTrial by jury

Q: Identify one place where ideas
for bills come from.
A:
The executive branchConstituentsInterest GroupsLobbyists

Q: Give an example of
federalism today.
A: Ex. gay marriage, marijuana, etc.

Q: What is a dissenting opinion?
A: A Supreme Court Justice on the minority side of a decision can write a dissenting opinion. This states their reasons for disagreeing with the decision using legal reasons.

Q: What is a veto?
A: The right of a branch of government to reject a proposed law that has been passed by another branch in an effort to delay or prevent its enactment.

Q: Identify a Constitutional
power given to the President.
A:
Commander in ChiefHead of the Executive BranchGranting reprieves and pardonsMaking treatiesNominating ambassadorsRecommend legislationReceive legislation passed by CongressReceive ambassadors and other diplomats

Q: What is the Civil Service?
A: Employment in federal, state, or provincial, and local governmental agencies. The civil service was formed in an effort to reduce political patronage and promote professionalism in government.

Q: Under the Articles of
Confederation, who had the most
power?
A: The states

Q: How are Presidential
powers limited?A:Rejecting the President’s legislative agenda (Congress)Asserting its Constitutional authority (Congress)Refusing to ratify treaties (Congress)Refusing to confirm Presidential appointments (Congress)Refusing to fund the President’s programs (Congress)Removing the president from office (Congress)Judicial branch can also limit, by declaring acts of the President unconstitutional.

Q: What is the power of judicial
review?
A: The power of the courts to declare laws and actions of the local and state governments or national government invalid if they are found to contradict the U.S. Constitution.

Q: What is appellate
jurisdiction?
A: The legal authority of a court to hear appeals from a lower court.

Q: What is gerrymandering?
A: Drawing the boundaries of an electoral district to favor a political party.

Q: What is a bill?
A: A proposed law placed before a legislature for approval.

Q: Name one Executive
Department. A: Department of:AgricultureCommerceDefenseEducationEnergyHealth and Human ServicesHomeland SecurityHousing and Urban DevelopmentJusticeStateInteriorTreasuryTransportationVeteran Affairs