Pu ZPIC Zone 4 Decision Tree Modeling - Sitemason ZPIC Zone 4 Decision Tree Modeling.pdfDecision...
Transcript of Pu ZPIC Zone 4 Decision Tree Modeling - Sitemason ZPIC Zone 4 Decision Tree Modeling.pdfDecision...

1
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Zone Program Integrity Contractor Zone 4Decision Tree Modeling
Holly Pu, M.S.
Chief Statistician
October 14, 2009
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Data Project
Home Health
– Overview
– Fraud Indicators
– Decision Trees
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Overview

2
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Home Health Rules and Regulations
• 42 CFR (Code of Federal Regulations)
– Sections 409.40‐409.50 – Home Health Services
– Section 424.22 – Requirements for Home Health Services
– Section 484 – Home Health Conditions of Participation
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Home Health Rules and Regulations
•• Publications 100Publications 100‐‐XXXXPublication 100‐01, Medicare General Information, Eligibility and Entitlement Manual , Chapter 1, Section 10.2, Home Health Services and Chapter 4, Section 30, Physician Certification
Publication 100‐02, Medicare Benefit Policy Manual, Chapter 7, Home Health Services
Publication 100‐04, Medicare Claims Processing Manual, Chapter 10, Home Health Agency Billing
Publication 100‐08, Program Integrity Manual (PIM)
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Home Health Eligibility
• To qualify for Medicare coverage of home health services, the patient must meet each of the following:
– Services billed from a Medicare participating Home Health Agency
– Be confined to the home (homebound)
– Be under the care of a physician
– Be in need of skilled services
– Be under a Plan of Care

3
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
State County Summary
12,11653,140$29,497,595SAN JUAN NM
15,007125,816$38,260,750DONA ANA NM
24,8791511,774$63,050,653BERNALILLO NM
11,106126,727$29,105,530EL PASO CO
25,3661615,896$71,196,049ARAPAHOE CO
28,6432617,413$76,212,907DENVER CO
39,21656,408$81,676,418PUSHMATAHA OK
68,7862822,482$167,193,549TULSA OK
102,4665431,000$256,388,647OKLAHOMA OK
150,30211749,424$444,553,066BEXAR TX
169,15410350,356$483,479,760TARRANT TX
329,49111654,175$866,242,700HIDALGO TX
329,05236775,354$1,011,769,175DALLAS TX
376,68346293,954$1,073,334,215HARRIS TX
Number of Claims
Number of Home Health Agencies
Number of PatientsTotal PaymentProvider County
Provider State
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Growth Trend
Trend by Payment Amount
$0
$50,000,000
$100,000,000
$150,000,000
$200,000,000
$250,000,000
Jan
Feb
Mar
Apr
May
Jun
Jul
Aug
Sep Oct
Nov
Dec Jan
Feb
Mar
Apr
May
Jun
Jul
Aug
Sep Oct
Nov
Dec Jan
Feb
Mar
Apr
May
Jun
Jul
Aug
Sep Oct
Nov
Dec
2006 2007 2008
CO Payment NM Payment OK Payment TX Payment

4
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Fraud Indicators
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Extensive Home Care Episodes
• Background: Home health care is usually temporary. The goal of home health care is rehabilitation. If a home health agency has a high percentage of beneficiaries receiving long term home care services, it may indicate fraud/abuse.
• Time Frame: April, 2006 – March 31, 2009
• Findings: In three years, Medicare paid around $4.2 billion for beneficiaries with five or more consecutive home care episodes. Out of the $4.2 billion, over $1.1 billion were paid for beneficiaries with twelve or more consecutive home care episodes. An initial threshold of 40 percent was established by the home health subject matter expert to flag aberrant providers.
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Consecutive Home Care EpisodesSummary by State
$4,163,283,216Grand Total
$3,549,824,046Subtotal
28,029$985,801,179More than 12 Episodes
1,565157,193$2,564,022,867(More than 5 Episodes, Less than 12 Episodes)
TX
$541,286,690Subtotal
5,796$168,912,079More than 12 Episodes
20523,449$372,374,611(More than 5 Episodes, Less than 12 Episodes)
OK
$50,855,557Subtotal
408$11,890,298More than 12 Episodes
492,401$38,965,259(More than 5 Episodes, Less than 12 Episodes)
NM
$21,316,923Subtotal
168$4,579,632More than 12 Episodes
571,017$16,737,291(More than 5 Episodes, Less than 12 Episodes)
CO
Number of Home Health AgenciesNumber of PatientsPaymentNumber of Home Health Episodes
Provider State

5
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Outlier Payment Claim
• Background: Home Health outlier payment is identified by the value code 17. Additional PPS reimbursement is based on the number of visits, often in the $10,000 range. PPS assumes the cost of care exceeds the threshold dollar amount resulting in an outlier payment.
• On July 30, 2009 CMS proposes to cap outlier payments at 10 percent per agency and target total aggregate outlier payments at 2.5 percent of total HH PPS payments for calendar year 2010. An initial threshold of 50 percent was established by the home health subject matter expert to flag aberrant providers.
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Home Health Outlier – Summary by County
0.060.080.046,7382,014$13,865,001245159$854,118EDDYNM
0.040.040.0315,0075,816$38,260,750393256$1,405,791DONA ANANM
0.030.020.0225,35515,887$71,182,890403260$2,039,689ARAPAHOECO
0.060.030.0328,44317,272$75,635,586875465$4,286,026DENVERCO
0.070.030.0368,75022,447$167,094,6122,007742$12,322,113TULSAOK
0.110.050.04101,96830,804$255,233,5564,5271,619$28,603,974OKLAHOMAOK
0.070.030.03278,77578,497$798,415,3257,6932,631$55,210,502HARRISTX
0.160.050.06168,26750,079$481,189,36210,7062,749$76,372,653TARRANTTX
0.260.080.12149,82749,208$443,424,19518,5854,052$115,709,588BEXARTX
0.210.120.10329,03154,075$865,246,00133,3116,395$185,583,072HIDALGOTX
0.250.080.10322,71274,472$996,815,92931,6725,945$248,218,141DALLASTX
Ratio Payment (Outlier Payment / Total Payment)
Ratio Pats (Outlier Patients / Total Patients)
Ratio Claims (Outlier Claims / Total Claims)
Total Claims
Total PatientsTotal Payment
Outlier Claims
Outlier PatientsOutlier Payment
Provider County
Provider State
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Home Health Outlier – Summary by State
• Findings: There were over 100 home health agencies that had 50 percent or more outlier payment claims. Out of these providers the majority concentrates in the State of Texas. The total outlier payment made in ZPIC Zone 4 states was over $270 million in a three‐year time period.
$429,589,221$274,367,004127Grand Total
$410,093,209$263,880,584117TX
$17,784,424$9,478,0294OK
$1,711,589$1,008,3916CO
Total Payment (for the Home
Health Agencies with 50% or more
Outlier Payment Claims)Outlier Payment
Number of Home Health Agencies
(with 50% or more Outlier
Payment Claims)Provider State

6
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Single Referring Part B Physician
• Background: This indicator is to look for home health referring providers who referred the majority of the patients to home health agencies. An initial threshold of 40 percent of claims was established to flag aberrant providers.
• Time Frame: April 1, 2006 – March 31, 2009
• Findings: Thirty‐one home health agencies had 40 percent or more of their patients referred by an individual Part B physician. The home health payment referred by these physicians was over $28 million. Some of these agencies shared one common Part B Physician who is currently under investigation.
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
HIPPS Code Indicators
• 1st position ‐ prior to 2008 always an H, effective 1/1/2008 numbers 1‐5, dependent on episode and therapy services
• 2nd position ‐ Clinical Severity Domain• 3rd position ‐ Functional Status Domain• 4th position ‐ Service Utilization Domain• 5th position ‐ prior to 2008 data validity flag, effective
1/1/2008 alpha/numeric related to supplies
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Power of a HIPPS Code ‐ Therapy
RangeRange--$1,800$1,800--$2,200$2,200$7,023.96$7,023.965BGKW 5BGKW (20+ therapy) (20+ therapy)
$2,979.11$2,979.11$5,220.86$5,220.864BGKW 4BGKW (14(14--19 therapy)19 therapy)
$2,241.75$2,241.753BGKW 3BGKW (0(0--13 therapy)13 therapy)
$2,626.32$2,626.32$4,813.12$4,813.122BGKW 2BGKW (14(14--19 therapy)19 therapy)
$2,186.80$2,186.801BGKW 1BGKW (0(0--13 therapy)13 therapy)
Increase in $$Increase in $$PPS ReimbursementPPS ReimbursementHIPPS CodeHIPPS Code

7
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
HIPPS Code First Position ‐ Therapy Visits
• Background: Medicare made changes to the Home Health Prospective Payment System (HHPPS) effective January 1, 2008. The first position of a HIPPS code with a value 5 signifies 20 or more therapy visits. An initial threshold of 40 percent of claims was established to flag aberrant providers.
• Time Frame: February 1, 2008 – January 31, 2009 (1 Year)
• Findings: 4 home health agencies were selected for further investigationin that they had a percentage as high as 87 percent of billing the HIPPS code with a value 5 in the first position. The total payment for this HIPPS code billed by these 4 providers was over $4.5 million in a one‐year time period.
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
HIPPS Code Second Position ‐ Clinical Severity
• Background: The second position of a HIPPS code with a value C signifies the most severe clinical condition. An initial threshold of 40 percent of claimswas established to flag aberrant providers.
• Time Frame: February 1, 2008 – January 31, 2009 (1 Year)
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
HIPPS Code Third Position ‐ Functional Status
• Background: The third position of a HIPPS code with a value H signifies the lowest level of functional status. An initial threshold of 40 percent of claimswas established to flag aberrant providers.
• Time Frame: February 1, 2008 – January 31, 2009 (1 Year)

8
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Static Diagnosis Code
• Background: This indicator is to look for home health agencies billing the same diagnosis codes for the majority of their beneficiaries. An initial threshold of 50 percent of claims was established to flag aberrant providers.
• Time Frame: April 1, 2006 – March 31, 2009
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Exact Five Visits per Claim
• Background: Medicare makes a low‐utilization payment adjustment (LUPA), if at the end of an episode there have been four or fewer services. The home health agency will be compensated based on a per visit amount, which is much less than an episode rate.
• This indicator looks for home health agencies with a high percentage of beneficiaries with exact five visits per claim. An initial threshold of 40 percent of claims was established to flag aberrant providers.
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
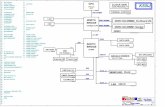
Decision Tree

9
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Predictive Modeling
• Predictive models depend on a property known statistically as stationarity, meaning that its statistical properties do not change over time.
• Training Data: Predictive Modeling starts with a training data set. The training data set consists of cases (also known as observations, examples, instances, or records). Associated with each case is a vector of input variables (also known as predictors, explanatory variables) and a target variable (also known as a response, outcome, or dependent variable).
• Score Data: Predictive Modeling ends with a score data set. The score data set has the same structure as the training data set, but lacks a target variable.
• Predictions: The bridge between the training and score data is the predictions generated by the analysis. The predictions represent the best guess for the unknown target variable score data, based on the known input variables and associations between the input variables and target variable learned from the training data.
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Model Essentials
• Predict New Cases: the simplest type of prediction is the decision. Decisions usually are associated with some kind of action (such as classifying a home health agency as potentially fraudulent or not fraudulent). For this reason, decisions are also known as classifications.
• Select Useful Inputs: to select an independent set of inputs that are correlated with the target.
• Optimize Complexity: Underfitting versus. Overfitting
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Data Splitting
• For honest assessment of model performance, data splitting is performed. A portion is used for fitting the model, that is, the training data set. The remaining data is separated for empirical validation.
• The validation data set is used for monitoring and tuning the model to improve its generalization. The tuning process usually involves selecting among models of different types and complexities.

10
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Decision Trees
• Decision Trees addresses each of the modeling essentials described earlier. Cases (home health agencies) are scored using prediction rules. A split search algorithm facilitates input selection. Model complexity is addressed by pruning.
• Decision Tree Prediction Rules: The rules are arranged hierarchically in a tree‐like structure with nodes connected by lines. The nodes represent decision rules, and the lines order the rules.
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Decision Tree Split Search• Split Search starts by selecting an input for partitioning the available training data.
For a selected input and fixed split point, two groups (branches) are generated. A Pearson Chi‐Square statistic is used to test if the proportion of zeroes and ones in the left branch is significantly different than the proportion in the right branch. A large difference in outcome proportions indicates a good split.
• The statistic is converted to a p‐value. For large data sets, these p‐values can be very close to zero. For this reason, the quality of a split is reported by logworth = ‐log(chi‐squared p‐value). SAS Enterprise Miner uses a logworth of approximately 0.7.
• The process repeats until there are no more allowed splits whose logworth exceeds the thresholds. The resulting partition of the input space is known as the maximal tree. It is likely that the maximal tree will fail to generalize well on an independent set of validation data.
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Decision Tree Split Search

11
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Pruning a Decision Tree
• To avoid potential overfitting, many predictive modeling procedures offer some mechanism for adjusting model complexity. For decision trees, this process is known as pruning. The general idea of pruning is to select the simplest model with the best validation performance.
• Misclassificationmeasures the fraction of cases where the decision does not match the actual target value. Decisions require low misclassification.
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Pruning a Decision Tree
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Conclusion• In three years, Medicare paid around $4.2 billion for beneficiaries with five or
more consecutive home care episodes. Out of the $4.2 billion, over $1.1 billion were paid for beneficiaries with twelve or more consecutive home care episodes.
• There were over 100 home health agencies that had 50 percent or more outlier payment claims. Out of these providers the majority concentrates in the State of Texas. The total outlier payment made in ZPIC Zone 4 states was over $270 million in a three‐year time period.
• Based on the fraud indicators and decision tree rules, an initial selection of 24 home health agencies currently are under investigation. The total Medicare payment at risk is over $365 million.
• Investigative Findings: These providers were found to bill for a large percentage of their patients who were either not home bound, not in need of a skilled level of care, or have been educated to self‐administer insulin injections for an extended period of years. Due to the high volume of fraud found in our states, a separate task order was initiated for this effort.

12
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
References
• Applied Analytics Using SAS Enterprise Miner 5
• Code of Federal Regulations
• CMS Manual Publication 100‐01, 100‐02, 100‐03, 100‐04
A wholly owned subsidiary of Quality Health Strategies
Contact Information
Holly Pu
Chief StatisticianHealth Integrity, LLC9240 Centreville RoadEaston, MD 21601email: [email protected]: 410‐770‐3058Fax: 410‐819‐8698