Proximal Humerus Fractures ORIF & Arthroplasty
description
Transcript of Proximal Humerus Fractures ORIF & Arthroplasty

Proximal Humerus Fractures ORIF &
ArthroplastyReza Omid, M.D.
Assistant ProfessorDepartment of Orthopaedic
SurgeryKeck School of Medicine of USC

Introduction
• 5-7% of all fractures
• 80% treated nonoperatively (Neer)
•Bimodal incidence
•Bone quality- important factor in obtaining secure fixation

Etiology
Elderly– fall onto outstretched hand– direct blow- fall– bone fragility- a/w distal radius fractures
Young– high energy– seizures, electrical injury

OITE Facts
•How many with neurologic injury?– 21-36%– recent study- 45%- fx or dislocation on EMG
•Which nerves?– Axillary, suprascapular, radial, musculocut.
•How many with persistent motor loss?– 8%

Codman’s Description Neer’s Classification

AO Classification

ClassificationNeer’s classification
Sidor, Zuckerman, JBJS 1993
Gerber, JBJS, 1993
– poor inter and intra observer reliability
– best results among trained shoulder surgeons
– suggested CT scans would increase reliability

Proximal Humeral Anatomy
Understanding Fracture PatternsUnderstanding Fracture Patterns–4 bony fragments4 bony fragments»Lesser TubLesser Tub»Greater TubGreater Tub»HeadHead»ShaftShaft
Neer, JBJS ‘70

Proximal Humerus Assesment
Neer ClassificationNeer Classification–1 cm displaced1 cm displaced–45 deg angulated45 deg angulated–Excessive rotationExcessive rotation

Proximal Humerus Fractures
Fracture PatternsFracture Patterns–StableStable»Fx not controlled by muscleFx not controlled by muscle
–UnstableUnstable»Fx controlled by attached muscleFx controlled by attached muscle

Proximal Humerus FractureFracture AnatomyFracture Anatomy
–Greater Tub – posterior, proximalGreater Tub – posterior, proximal–Lesser Tub – medial, inferiorLesser Tub – medial, inferior–Head – remaining tub or Head – remaining tub or fx energyfx energy
–Shaft – medial, superiorShaft – medial, superior

X-Rays
AP view scapular plane (Grashey)
AP view of shoulder

X-RaysAxillary Lateral
Scapular Y

Proximal Humerus FractureRadiographic AnalysisRadiographic Analysis
–Normal AppearanceNormal Appearance»Axillary: lesser tub, greater tub Axillary: lesser tub, greater tub not seennot seen

Proximal Humerus Fracture
Radiographic AnalysisRadiographic Analysis– Normal AppearanceNormal Appearance
» AP: external rotation shows AP: external rotation shows
greater tubgreater tub» AP: internal rotation, AP: internal rotation,
greater tub not seengreater tub not seen


Proximal Humerus FractureFracture AnatomyFracture Anatomy

Consideration for Surgery
Bone Quality
Comorbidities
Functional demand
Vascularity???

Gerber JBJSAm 1990: 1486-94
Vascularity– anterior humeral circumflex
» Anterolateral branchOf AHC (arcuate artery)Along lateral aspect of groove

Brooks JBJSBr 1993: 132-136
•Vascularized through interosseous anastomoses
•Between metaphyseal vessels (via posterior humeral circumflex) and the arcuate artery after ligation of the anterior circumflex humeral.

Coudane JSES 2000: 548
•Arteriography done on 20 patients after proximal humerus fractures.
•80% had disruption of AHC artery
•15% had disruption of PHC artery•Since AVN is rare (bw 1-34%)
after fx it suggests the PHC artery may be dominant supply

Hettrich JBJSAm 2010: 943-8
–MRI cadavers–posterior humeral circumflex
–supplied 64% of head (superior, lateral and inferior).

Hertel Criteria
Hertel et al JSES 2004:13:427
–Medial calcar segment <8mm–Medial hinge is disrupted (>2mm displacement of the diaphysis)
–Comminution of the medial metaphysis
–Anatomic neck fracture

Bastian JSES 2008: 2-8
• Follow-up study by Hertel showed that initial predictors of humeral head ischemia doesn’t predict development of AVN.
•80% of patients with “ischemic heads” did NOT collapse
• Fixation is worth considering even if signs of ischemia are present

Nonoperative Treatment
Immobilize initially
Passive ROM 2-3 weeks– supine FE– supine ER– pendulums
AROM at 6 weeks or when consolidated
77% good to excellent results-Zuckerman 1995

Optimal Treatment
•UNKOWN????•JSES 2011: 1118-1124 (RCT ORIF vs Non-op)
•JSES 2011: 747-55 (RCT ORIF vs Non-op
•JSES 2011: 1025-1033 (RCT Hemi vs Non-op)
•JOT 2011 (RCT ORIF vs Non-op)

Percutaneous PinningSurgical Technique
– Retrograde Pins» Start Anterior» Diverge Pins
– Antegrade Pins» Supplemental» GT to Medial Shaft

Percutaneous PinningReduction Maneuver
•Surgical neck– flexion, adduction, traction– anterior pressure
•Greater tuberosity– engage and move
anteriorly/inferiorly

Percutaneous Pinning
Pin Placement– Slight medial placement of head to
shaft» Allows placement of one pin centrally
– Wide spread of pins for stability– *Remember normal humeral head
retroversion for pin placement– Pin entry is just above the deltoid
insertion
Pins– Three 2.5mm terminally threaded pins
» 2 lateral pins» 1 anterior pin» 1-2 pins from GT to medial shaft
Jaberg H. JBJS. 74A. 1992. 508-15.

Structures At Risk
Cadaveric Study– Lateral pins
» 3mm from Ant branch Ax» Penetration of head
articular cartilage
– Anterior pins» 2mm from biceps tendon» 11mm from cephalic v.
– Proximal tuberosity pins» 6-7mm from ax n. &
posterior circumflex artery
Rowles DJ, McGrory JE. “Percutaneous Pinning of the Proximal Part of the Humerus. JBJS. 83A(11)2001.1695-99.

Recommendations
Starting point of proximal lateral pin– At or distal to a point
2x the distance from the superior aspect of the humeral head to the inferior margin of the head
Greater tuberosity pins– Engage medial cortex
>2cm from the inferior most aspect of the humeral head
Rowles DJ, McGrory JE. “Percutaneous Pinning of the Proximal Part of the Humerus. JBJS. 83A(11)2001.1695-99.

Greater Tuberosity Fractures
Displacement
– Superior» Impingement
– Posterior» Block to ER

Greater Tuberosity Fractures
Displacement?– 5mm maybe problematic (McLaughlin et al.) – 3mm maybe problematic in the athlete or heavy
laborer (Park et al.)– Concern for RTC tears in minimally displaced fxs
Positioning critical – *Exposure
» Approach: Superior, Posterior, Anterior
Reduction– Head height 6-8mm superior to GT
» Posterior displacement more tolerated than superior displacement

Greater Tuberosity Fractures
– Surgical Approach» Superior» Deltopectoral
– Fixation Options» Sutures» Screws» Plate
– Interval Closure

Three-Part Fractures
Surgical Neck
Greater Tuberosity Lesser Tuberosity
+

Three-Part Fractures
Fixation Options– Percutaneous Pins– Interfragmentary Suture/Wire
–Plate/Screws– IM Nail– Blade Plate
–Hemiarthroplasty

Three-Part Fractures
–Approach»Deltopectoral»Closed Reduction/Pinning
–Goals»Tuberosity Fixation»Longitudinal Stability

Hemiarthroplasty
•Rarely Indicated•Older Patients•Osteopenic Bone•Fracture-Dislocations
– > 40% Impression Defect

Three-Part Fractures
Complications–Nonunion–Malunion–Hardware Problems (screw cutout)
–AVN

Indications for ORIF of Four-part Fractures
Valgus impacted four part with an intact medial soft tissue hinge
Four part in a young patient (less than 40)

Indications for PinningValgus impacted 4 part proximal
humerus fracture– Vascularity preserved by feeding vessels in attached
capsule

Valgus Impacted Four PartReduction Maneuver
Small incision (2 cm) anterior
shoulder
Line of fracture usually lies 5 mm
lateral to intertubercular
groove

Percutaneous PinningReduction ManeuverValgus Impacted 4 Part

Valgus Impacted Four Part
Pinning Technique
Pin fragments

Valgus Impacted Four Part47 y.o. female, trip and fall

When to plate?Factors
–High energy/low energy–Displacement»2 part vs 3 or 4 part»Integrity of soft tissue sleeve

Proximal Humerus Fractures
3 part

Proximal Humerus Fractures
3 part- locking plate

46 yo male
Rollover dirt bike

8 wks post op

46 yo malehigh speed auto accident

Post op

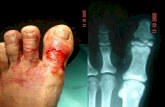
Fracture-Dislocation

Fracture-Dislocation

Clinical Example

ORIF Technique

Reduction & Grafting
•Impaction grafting of head
•Iliac crest cube•Fibular strut

Tag Tuberosities

Reduction & Grafting

Close Book

Plate

Indications for Hemiarthoplasty
Anatomic neck and four part fractures: Isolate
anatomic humeral head from its blood supply
Some three part fractures with severe
osteoporosis in the elderly
Split humeral head fractures

Hemiarthroplasty Technique

Patient Position

Surgical Technique
Extended deltopectoral exposure: deltoid origin
and insertion intact

Surgical TechniqueIdentify the LHB and Tuberosities
Evaluate the rotator cuff injury

Surgical TechniqueRemove the humeral head
Evaluate the glenoid

Muscular AnatomySupraspinatus
–Usually starts just post to bicipital groove–Pt. > 60 yo - strong possibility of RCT
Sher, et al JBJS ‘95

Tuberosity Suture TechniquePlace suture at the tendon bone
interface

Doug Robertson, MDDoug Robertson, MDLouis U Bigliani, MDLouis U Bigliani, MDEvan L Flatow, MDEvan L Flatow, MD
Ken Yamaguchi, MDKen Yamaguchi, MDJBJS ‘00

ResultsAnatomy
–Retroversion: avg 19°, range: 9-31°–Posterior offset: avg 2mm, range:-1-8mm–Head thickness: avg 19mm, range:15-24mm–Inclination:avg 41°, range: 34-47°–Thickness linked to Radius (avg 23mm)

Head Size
Solutions–removed head is guide»thickness > radius
–error towards undersize–check gross appearance

Position of Greater Tuberosity
Height Relative to Humeral Head

Surgical TechniqueAssess the humeral height and version
Trial tuberosity reduction
Mark the stem position
Lesser
Tuberosity
Height ofthe GreaterTuberosity
5-8 mm

Tuberosity Height = Prosthetic Height
Height ofthe GreaterTuberosity
Lesser Tuberosity
5-8 mm

Determining Height
–Superior border of Pectoralis tendon (5.6cm±0.5cm)–Side to Side comparison (x-ray)–View calcar contour (gothic arch)

Determining Height

Proximal Humerus Fracture

Humeral Version

VersionEffect of Incorrect Version
Too Anteverted Too Retroverted

Bicipital Groove Anatomy
–Anterior to head center–Anterior to keel location–Location dependant on shaft depth»Variable retroversion distal

Biceps Groove Version
Groove shifts medially from proximal to distal, changing
retroversion values 15.9° from the upper to lower part of the bicipital
groove (Itamura)

Bicipital Groove Anatomy

Surgical TechniquePrepare the fixation sutures for ORIF of the
tuberosities.– 2-3 vertical and 2 horizontals, one medial one lateral

Surgical Technique

Surgical TechniqueTuberosity fixation and
bone graftBiceps tenodesis
Wound drains and closure

Results of Hemiarthroplasty for
Acute FracturesGoldman et. al. J. Shoulder
and Elbow 199526 patients with acute fractures
73% had slight or no painAverage forward flexion 107
degrees: stiff73% had difficulty with at least 3
of the 10 ASES question of ADL

Results of Hemiarthoplasty for Late Reconstruction
Dines et. al. J. Shoulder and Elbow 1993
Demanding procedure with wide variation in results: average 80
points (HSS Scale)Stiffness, scar, hardware
problemsTuberosity malposition

Results of Hemi. Early vs Late
Frick et. Al. Orthopaedics 1991
Pain scores better in acuteFunction no different
More complications in the late reconstruction group

Results of Hemi. Early vs Late
Norris et al J. Shoulder and Elbow 1995
Good pain relief in both but better results in the acute
group.
Only 53% had ability to use arm above shoulder level post op in late reconstruction, 15%
pre-op

Results of Hemi. Early vs Late
Tanner and Cofield CORR 1983
16 acute hemi, 27 late reconstructionBoth had good pain relief
Both had had average active shoulder elevation to 105-110 degrees
Acute surgeries was easier and with less complications

Factors Affecting Outcome
•Bone density•Rotator cuff tissue quality•Tuberosity healing•Restoration of anatomic
humeral head height•Restoration of anatomic
humeral version•Rehabilitation

Sequelae of Proximal Humerus Fractures
Boileau proposed a classification scheme for
proximal humerus fracture sequelae and
treatment recommendations (CORR
2006:442:121-130)


Reverse for Fracture
•Age >70-75 (I will consider for age >65)
• Tuberosities heal more predictably and function is not as dependent on tuberosity healing
•More predictable outcome than with hemi
•Best outcome of a hemi is better than best outcome of a reverse

Conclusions•Best to perform repair for acute fracture•Anatomic restoration of humeral height
and version•Secure tuberosity fixation•Repair the cuff•Tenodesis of the LHB•Early protected PROM, close supervision
of the rehabilitation program

Conclusions
Pain relief is expected in >90% of cases
Active shoulder level elevation in >75% of
cases