Projection
description
Transcript of Projection

RAC/RA
Projection
• Types of Projection• Simple Projections
• Generalized Projection

RAC/RA
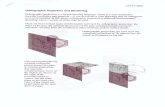
Clip againstview volume
Projectonto projection
plane
Transform intoviewport in 2D
devicecoordinates
3D worldcoordinates
Clipped worldcoordinates
2D devicecoordinates
Conceptual model of the 3D viewing processConceptual model of the 3D viewing process
Viewing In 3D

RAC/RA
ProjectionsIn general, projectionsprojections transform points in a coordinate system of dimension n into points in a coordinate system of dimension less than n.
We shall limit ourselves to the projection from 3D to 2D.
• The projection is onto a plane rather than a curved surface
• The projectors are straight lines rather than curves
We will deal with planar geometric projectionsplanar geometric projections where:

RAC/RA
A
BA'
B'
Center ofprojection
Projectors
Projectionplane
The projectionprojection of a 3D object is defined by straight projection rays (called projectorsprojectors) emanating from a center of projectioncenter of projection, passing through each point of the object, and intersecting a projection planeprojection plane to form the projection.
Projections

RAC/RA
Planer Geometric Projections
Two basic classes (on the basis of the distance of the centercenter of projectionof projection from the projection planeprojection plane) :
A
BA'
B'
Center ofprojection
Projectors
Projectionplane
Perspective projectionPerspective projection
• perspective projectionperspective projection : the distance is finite
A
BA'
B'
Center ofprojectionat infinity
Projectors
Projectionplane
Directionof
projection
Parallel projectionParallel projection
• Parallel projectionParallel projection : the distance is infinite

RAC/RA
A
BA'
B'
Center ofprojection
Projectors
Projectionplane
C
DC'
D'
1. 1. Perspective foreshorteningPerspective foreshortening The farther an object is from COP the smaller it appears
Perspective foreshorteningPerspective foreshortening
Perspective Projection-Anomalies

RAC/RA
2. 2. Vanishing PointsVanishing Points:: Any set of parallel lines not parallel to view plane appear to meet at some point.
Perspective Projection-Anomalies
x
y
z
z-axis vanishing point
Vanishing pointVanishing point

RAC/RA
3. 3. View ConfusionView Confusion:: Objects behind the center of projection are projected upside down and backward onto the view-plane.
Perspective Projection-Anomalies
x
y
z
P1
P2P3
P1`P2`
P3`C
O

RAC/RA
Perspective Projection-Anomalies
4. 4. Topological distortionTopological distortion: : A line segment joining a point which lies in front of the viewer to a point in back of the viewer is projected to a broken line of infinite extent.
P1
P3
P'3
C
Y
X
Z
P2
P'2P'1
View Plane
Plane containingCenter of Projection (C)

RAC/RASubclasses of planar geometric projectionsSubclasses of planar geometric projections
Planner Geometric Projections
V = ±N
Planar geometricprojections
Parallel Perspective
Orthographic Oblique
Top
Front
Side
Axonometric
Isometric Other
Cavaliertan -1 (2)
Other
One-point
Two-point
Three-point
COPCOP = COP = d
N,V
N V
N=axis
Cavaliertan -1 (1)
N V
zx
yProjection Plane

RAC/RA
Two types (on the basis of the relation between the directiondirection of projection Vof projection V and the normal to the projection plane Nnormal to the projection plane N) :
• orthographicorthographic : VV and NN are the same or the reverse of each other.
• obliqueoblique : VV and NN are neither same nor reverse.
Parallel Projections
Y
X
Z
Orthographic
Oblique
N

RAC/RA
Projection plane(top view)
Projection plane(side view)Projection plane
(front view)
Orthographic parallel projectionsOrthographic parallel projections
Orthographic Projections

RAC/RA
Axonometric ProjectionsAxonometric Projections use projection planes that are not normal to a principal axis.On the basis of projection planeprojection plane normal N = (dnormal N = (dxx, d, dyy, d, dzz) subclasses are:
• IsometricIsometric : | ddx x | = | = | ddy y | = | = | ddz z || i.e. NN makes equal angles with all principal axes.
• othersothers : NN makes unequal angles with one or more principal axes.
Axonometric Projections

RAC/RA
Oblique Projections
: is the angle the projection makes with x-axis : angle between view plane and direction of projectionl : original length of a line perpendicular to view planel : projected length of a line perpendicular to view plane
z
y
x
l
l'
l'sin
l'cos

RAC/RA
Cavalier & Cabinet
x
z
y
x
z
y
= 30 = 45
1
1
1
1
1
1
x
z
y
x
z
y
= 30 = 45
11/2
1 1
11/2
Cavalier projection = 45l = l
Cabinet projection = 63.4l = l/2

RAC/RA
Projective Projection

RAC/RA

RAC/RA
Perspective Projections
3-Vanishing Point
1-Vanishing Point
2-Vanishing Point

RAC/RA

RAC/RA
y
x
z
view direction
center ofprojection
plane ofprojection
d
Settings for perspective projectionSettings for perspective projection
Projective Transformations

RAC/RA
y
P(y,z)y
zP'(y p ,z p)
d-z
plane ofprojection
1,,,1,,, ddz
ydz
xzyx
dzdz
xxdx
zx
dzyy
dy
zy
pp
pp
Projective Transformations
z

RAC/RA
1
/
/
1????????????????
ddz
ydz
x
zyx
dzzyx
zyx
1????????????????
dzzyx
zyx
d 10100010000100001
Matrices for Projective Trans.

RAC/RA
11000000000000
01
0,,
zyx
d
dd
dz
dydx
zpypxp
zdz
dxxdz
dyy pp
Projective Transformations
C(0,0,-d)
y
x
z xp
P(x,y,z)
P(xp,yp,0)
x
Alternative approach,
Projection plane at Z=0
And Center at
Z=-d

RAC/RA
10
11000000000100001
yx
zyx
y
x
zview direction
plane ofprojection
direction ofprojection
Orthogonal Projection Matrix

RAC/RA
Projection
• To studyFoley: 6.1, 6.1.1, 6.1.2Schaum: 7.1, 7.2, 7.3
• Problems: 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.10, 7.11, 7.12

RAC/RA

RAC/RA

RAC/RA

RAC/RA