Potassium – Sparing Diuretics
-
Upload
rhimineecat71 -
Category
Documents
-
view
5 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Potassium – Sparing Diuretics

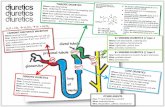
POTASSIUM – SPARING DIURETICS

Potassium-sparing diuretics: • reduce Na+ reabsorption • reduce K+ secretion
These are not potent diuretics when used alone
They are primarily used in combination with other diuretics.

Three Types of Potassium – Sparing Diuretics
Amiloride (Midamor)
Spironolactone (Aldactone)
Triamterene (Dyrenium)

• Interfere with sodium-potassium exchange in collecting ducts and convoluted tubules
• Competitively bind to aldosterone receptors– Block the reabsorption of sodium and water
• Prevent potassium from being pumped into the tubule, thus preventing its secretion
Potassium-Sparing Diuretics Mechanism of
Action

• Sodium and water are excreted

Therapeutic Uses
These drugs are generally used in combination with a thiazide or loop diuretic to treat
hypertension CHF refractory edema
They are also used to induce diuresis in clinical situations associated with hyperaldosteronism:
adrenal hyperplasia in the presence of aldosterone-producing
adenomas when surgery is not feasible.

Pharmocokinetics these drugs are well absorbed protein bound, and widely distributed
they are metabolized in the liver and primarily excreted in urine
these diuretics cross the placenta and enter breast milk * routine use during pregnancy is not appropriate, and they should be saved for situations in which the mother has pathological reasons for use, not pregnancymanifestations or complications , and the benefit to the mother clearly outweighs the risk to the fetus.

* If one of these drugs is needed during lactation, another method of feeding the baby should be used, because of the potential for adverse effects on fluid and electrolyte changes in the baby.
Contraindications
these drugs are contraindicated for use in patients with allergy to the drug,hyperkalemia, renal disease , or anuria.are given cautiously during pregnancy and lactation.

Adverse Effects These agents can cause hyperkalemia, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, and arrhythmias.
Spironolactone is associated with gynecomastia and can also cause menstrual abnormalities in women.
These drugs are contraindicated in renal insufficiency, especially in diabetic patients.
They are contraindicated in the presence of other potassium-sparing diuretics and should be used with extreme caution in individuals taking an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor.

Spironolactone
Act as antagonists to aldosterone, competes with aldosterone for receptor sites in DCT
Results in decreased Na+ reabsorption in DCT
Promotes Na+ and water loss
Decreased Na+ reabsorption balanced by K+
retention at this site (and H+).
Used in combination with diuretic e.g.. frusomide
Potassium-sparing diuretics

Triamterene and Amiloride
Similar effect to spironolactone by reducing Na+ absorption and H+/K+ secretion in DCT
Independent of aldosterone Have little diuretic effect Used in conjunction with diuretics In low doses blocks entry of Na+ into tubule
cells across luminal membrane Decrease availability of Na+ to Na+-K+-ATPase at
basal cell membrane Called Na+ channel blockers

Drug Name Usual Dosage Usual Indications
amiloride (Midamor) 15 -20 mg/d PO with monitoring of electrolytes
All of the potassium – sparing diuretics are indicated for the adjunctive treatment of edema caused by congestive heart failure, liver disease, or renal disease; hypertension; hyperkalemia; and hyperaldosteronism; Special considerations: Not for use in children
Spironolactone (Aldactone)
100 – 200 mg/d PO for edema; 100 – 400 mg/d PO for hyperaldosteronism; 50 – 100 mg/d PO for hypertensionPediatric: 3.3 mg/kg per day PO
Special considerations: Can be used in children with careful monitoring of electrolytes
Triamterene (Dyrenium)
100 mg/D PO b.i.d Special considerations: Not for use in children