Plate Tectonics and Geology. Genesis of Earth Earth is 4.6 billion years old. Same age as all other...
-
Upload
dale-wilson -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
1
Transcript of Plate Tectonics and Geology. Genesis of Earth Earth is 4.6 billion years old. Same age as all other...

Plate Tectonics and Geology

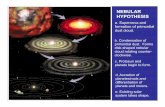
Genesis of EarthEarth is 4.6 billion years old. Same age as all other planets and the sun.
Earth formation. Nebular hypothesis. Diffuse cloud of matter
rotating in space, formed a disk shaped body, which later formed into sun and planets. Planets are cooled and condensed gases that surrounded the sun.


Core Development Earth was a homogeneous planet immediately after
formation But then, a profound reorganization as Earth initially
heated up due to collision with other rocky bodies heat of compression Radioactive decay of elements
Earth heated up such that much of the interior melted causing dense elements like iron and nickel to sink to the core lighter elements like silicon and aluminum float to the crust Resulted in a stratified Earth - core, mantle, crust

Distribution of Elements More than 100 elements in entire Earth, but
99% of Earth's mass is made up of only 8 elements
Whole Earth: Fe>O>Si>Mg>Ni>S>Ca>Al (others constitute < 1%)
Earth's crust O>Si>Al>Fe>Mg>Ca>K>Na (other constitute <1%)

Composition of Earth’s CrustComposition of Earth’s CrustComposition of Earth’s CrustComposition of Earth’s CrustEarth’s CrustEarth’s Crust
Oxygen 46.6%Oxygen 46.6%
Silicon 27.7%Silicon 27.7%
All others 1.5%All others 1.5%
Magnesium 2.1%Magnesium 2.1%
Potassium 2.6%Potassium 2.6%
Sodium 2.8%Sodium 2.8%
Calcium 3.6%Calcium 3.6%
Iron 5.0%Iron 5.0%
Aluminum 8.1%Aluminum 8.1%
Fig. 10.4, p. 213

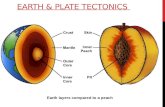
Layers of the Earth
Crust The surface of the
Earth is a very thin layer made of rocks, minerals and clay
We live on the crust of the earth
crust

Layers of the Earth
Mantle- Upper and Lower The mantle is the
biggest part of the earth; the magma is rich in iron and magnesium
Convection occurs here and is thought to drive plate tectonics
mantle
crust

Layers of the Earthcrust
mantle
Outer core
•Outer CoreOuter Core•The outer core The outer core consists of molten consists of molten iron and magmairon and magma•The outer core The outer core rotates giving the rotates giving the Earth a magnetic Earth a magnetic fieldfield

Layers of the Earth Inner Core
The inner core is made of solid iron
The closest model of the inner core we have is an iron nickel meteorite
The inner core is under extreme pressure
crust
mantle
Outer core
Inner Core

How do we know about the layers of the Earth?
To date, humans have never drilled through the crust of the Earth.
Scientists study where waves from earthquakes end up around the globe.
The waves move differently through different densities of material.

GEOLOGIC PROCESSES

Spreading centerCollision between
two continentsOcean trench
Plate movement
Subduction zone
Oceanic crust
Continental crust
Continental crust
Material cools as it reaches
the outer mantle
Cold dense material falls back through
mantle
Hot material
rising through
the mantle
Mantle convection
cell
Two plates move towards each other. One is subducted back into the mantle on a falling convection current.
Mantle
Hot outer core Inner
core
Plate movementTe
cton
ic
plat
e
Oceanic tectonic
plate
Oceanic tectonic plate
Oceanic crust

The Earth’s Major Tectonic PlatesEURASIAN PLATEEURASIAN PLATE
NORTH NORTH AMERICAN AMERICAN PLATEPLATE
ANATOLIAN ANATOLIAN PLATEPLATE
JUAN DE JUAN DE FUCA PLATEFUCA PLATE
CHINA CHINA SUBPLATESUBPLATE
CARIBBEAN CARIBBEAN PLATEPLATE
PHILIPPINE PHILIPPINE PLATEPLATE
ARABIAN ARABIAN PLATEPLATEAFRICAN AFRICAN
PLATEPLATEPACIFIC PACIFIC PLATEPLATE SOUTH SOUTH
AMERICAN AMERICAN PLATEPLATENAZCA NAZCA
PLATEPLATEINDIA-INDIA-
AUSTRALIAN AUSTRALIAN PLATEPLATE
SOMALIAN SOMALIAN SUBPLATESUBPLATE
ANTARCTIC PLATEANTARCTIC PLATE
Divergent plate boundaries
Convergent plate boundaries
Transform faults

The Earth’s Major Tectonic PlatesThe Earth’s Major Tectonic Plates

Hawaiian Island Hot Spot

How the hotspot works

History of Continental Drift Hypothesis 1596 Abraham Ortelius: fit of South American & African
coasts 1620 Francis Bacon: noted same fit 1782 Benjamin Franklin: suggested that crust of Earth
"floated" on fluid interior (crust broken and disordered by movement of fluids)
1885 Edward Suess Similarities between Late Paleozoic plant fossils of Africa, India,
South America, Australia & Antarctica Carboniferous glaciers on Africa, S. America, Australia, Inda Southern supercontinent of Gondwana Gondwana named after province in India where there was glacial and
plant evidence (Glosopteris flora) Landbridges, which sank beneath the sea, connected present continent

Continental movement not a new idea Wegener developed hypothesis of "continental drift”. Proposed "continental drift" - published "Origin of
Continents and Oceans" in 1915 Pangaea ("all land") existed about 200 Ma Showed breakup in series of maps Few supporters - mostly European and African geologists Ridiculed by American geologists Can't "sail" continents through oceans (granitic continents
too weak to move through stronger basaltic crust No mechanism to explain movement (Wegener's tidal
forces => too weak) Land bridges the answer to explain fossils