The Microscopic World of Cells Cell membranes and transport Cell Organelles Plant vs. animal cell.
Plant cell vs Animal cells
-
Upload
science-maksci -
Category
Education
-
view
242 -
download
5
description
Transcript of Plant cell vs Animal cells







Domains of Life
ArchaeaBacteriaEukarya

Eukaryotes
Any organism with one or more cells that have
membrane-bound nuclei and organelles.

Components
•Cytoplasm w/ Ribosomes
•DNA•Cell Membrane

Components• Nucleus• ER• Golgi
apparatus• Mitochondria• Cytoskeleton
• Chloroplasts• Centrioles• Lysosomes• Vacuoles• Cell Wall

Components• Nucleus• ER• Golgi
apparatus• Mitochondria• Cytoskeleton
• Chloroplasts• Centrioles• Lysosomes• Vacuoles• Cell Wall

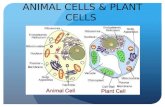
Plant Cell vs. Animal Cell

Plants• Multicellular eukaryotic
photoautotrophs• Cellulose-containing cell walls• Store surplus carbohydrates
as starch

Chloroplast• Found in plant cells and
other photosynthetic organisms
• Contains the green pigment chlorophyll
• Site of food (glucose) production
• Bound by a double membrane







Onion bulbs contain little to no chloroplasts
because they are underground.

Cell Wall• Cell walls are strong.
–prevent a plant cell from exploding when in contact with pure or almost pure water
–act as skeletal system for plant cells



Plant cell walls are side by side for support and
protection.

Vacuoles• Large central vacuole
usually in plant cells• Many smaller
vacuoles in animal cells
• Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc.



Plant cells contain only ONE nucleus

Lysosomes are very rarely
found in plant cells.

Animals• Multicellular,
eukaryotic heterotrophs.• Lack rigid cell walls.• All animals are motile, if only at
certain life stages.


Animal cells have only few small vacuoles.

Animal cells can have more than one nucleus in a
cell.

Animal cells can have many
different shapes and sizes.

Centrioles• a two-part rod-shaped structure
located in pairs near the nucleus.• During cell division, centrioles move
to opposite ends of the cell and form the poles of the spindle fibers that pull the chromosomes apart.


Plant vs. Animal Cells• PLANT CELLS
– 1. Cell wall– 2. One large vacuole– 3. Chloroplasts– 4. No/rare lysosomes– 5. Rectangular– 6. Photosynthesis
• ANIMAL CELLS– 1. No cell wall– 2. A few small vacuoles– 3. No chloroplasts– 4. Lysosomes– 5. Roundish– 6. Cell Respiration