Plant & animal cells
-
Upload
san-antonio-de-padua-center-for-alternative-mathematics -
Category
Science
-
view
498 -
download
0
Transcript of Plant & animal cells

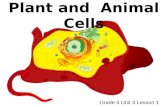
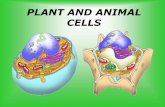
Plant & Animal Cells

Robert Hooke discovered the first cells. Cork Cells were thought to have been these cells. Anton von Leeuwenhoek was first to observe one celled living things. Examples of these were bacteria and parameciums.

The Cell Theory
All organisms are composed of one or more cells.
Cells are the smallest living things.
All organisms living today are descendents of an ancestral cell.
Cells arise only by division of previously existing cells.
The cell theory (proposed independently in 1838 and 1839) is a cornerstone of biology.
Schleiden
Schwann

Two Fundamentally Different Types of Cells
A prokaryotic cell
A eukaryotic cell

Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes

Animal and Plant Cells Have More Similarities Than Differences

Cytosol
Cytoplasm refers to the jelly-like material with organelles in it. If the organelles were removed, the soluble part that would be left is called the cytosol. It consists mainly of water with dissolved substances such as amino acids in it.

Section 7-2
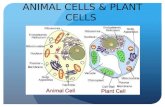
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Animal Cell
NucleusNucleolus
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
1. Nucleus Nickname: “The Control Center” Function: holds the DNA Parts:
1. Nucleolus: dark spot in the middle of the nucleus that helps make ribosomes

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Animal Cell
NucleusNucleolus Ribosomes
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
2. Ribosomes Function: makes proteins Found in all cells, prokaryotic and
eukaryotic

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
3. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Nickname: “Roads” Function: The internal delivery
system of the cell

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Animal Cell
NucleusNucleolus
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm
Ribosomes

Endoplasmic Reticulum 2 Types:
1. Rough ER: Rough appearance because it has
ribosomes Function: helps make proteins, that’s
why it has ribosomes2. Smooth ER:
NO ribosomes Function: makes fats or lipids

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Animal Cell
NucleusNucleolus
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Ribosomes
Golgi Complex
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
4. Golgi Complex Nickname: The shippers Function: packages, modifies, and
transports materials to different location inside/outside of the cell
Appearance: stack of pancakes

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Animal Cell
NucleusNucleolus
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Ribosomes
Golgi Bodies
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
5. Lysosomes: circular, but bigger than ribosomes)
Nickname: “Clean-up Crews” Function: to break down food into
particles the rest of the cell can use and to destroy old cells

Cell suicide (suicide is bad for cells, but good for us!)
(The lysosome is not found in plant cells)

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal CellsAnimal Cell
NucleusNucleolus
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Ribosomes
Golgi Bodies
MitochondriaCell Membrane
Cytoplasm

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
6. Mitochondria Nickname: “The Powerhouse” Function: Energy formation
Breaks down food to make ATP ATP: is the major fuel for all cell
activities that require energy

Animal Cell
NucleusNucleolus
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Ribosomes
Golgi Bodies
MitochondriaCell Membrane
Cytoplasm

Now let’s talk about structures only found in PLANT Cells!!

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Plant Cell
Cell Membrane
Vacuole

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
7. Vacuole (central) Function: stores water
This is what makes lettuce crisp When there is no water, the plant wilts
The Central Vacuole Controls Turgor Pressure

The Central Vacuole Controls Turgor Pressure
flaccid
turgid

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Plant Cell
Cell Membrane
Vacuole
Chloroplasts

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
8. Chloroplasts Function: traps energy from the sun
to produce food for the plant cell Green in color because of
chlorophyll, which is a green pigment

Chloroplasts
Think of the chloroplast as the solar panel of the plant cell.

Section 7-2
Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells
Go to Section:
Plant Cell
Cell Membrane
Vacuole
Chloroplasts
Cell Wall

Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function
9. Cell Wall Function: provides support and
protection to the cell membrane Found outside the cell membrane in
plant cells

Plant Cell
Cell Membrane
Vacuole
Chloroplasts
Cell Wall
Nucleolus
Nucleus
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Golgi Bodies
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Cytoplasm