Pipe Jacking of CIP Pipes (Kubota)
-
Upload
yam-balaoing -
Category
Documents
-
view
143 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Pipe Jacking of CIP Pipes (Kubota)

15-1 Pipe Jacking Pipe jacking method can be used to install a pipeline in the ground without trenchexcavation. This method is applicable for negotiating obstacles such as roads,railways, canals and rivers.
15-1-1 Jacking ductile iron pipeBody portion of jacking ductile iron pipe is sheathed with reinforced concrete to makethe whole outside diameter uniform along the pipe axis. Jacking force is transferred tothe socket face through the puddle flange welded on the spigot of the connected pipe.There are two types of joint for jacking ductile iron pipe. They are push-on type (TDtype joint) for DN300 to DN1600 and mechanical type (UD type joint) for DN700 toDN2600. Basically jacking ductile iron pipes are manufactured in accordance withJapanese standard (JIS). The nominal pipe outside diameter by Japanese standard isslightly different from that by ISO standard, therefore change collars or changespigots shall be used to connect pipes of these standards. (Refer to Chapter 12)However DN700 to DN1600 jacking ductile iron pipe with push-on joint may besupplied with ISO standard pipe.
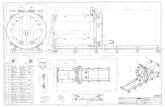
15-1-2 Jacking methodThere are some pipe jacking methods such as automatic jacking, semi-shield jackingand hand-mining jacking. Automatic jacking and semi-shield jacking methods employspecial jacking machines. In case of hand-mining jacking, pipe is pushed into theground by hydraulic jacks and persons should enter the pipe to carry out the soil inthe pipe. This hand-mining method is recommended to DN1000 and larger pipes.An example of equipment for hand-mining jacking is shown in Fig 15-3.
Chapter 15 Piping under Special Conditions
114
UD-type jacking ductile iron pipe (DN700 to DN2600) Fig. 15-1
TD-type jacking ductile iron pipe (DN300 to DN1600) Fig. 15-2

Chapter 15 Piping under Special Conditions
115
15-1-3 Allowable resistance force of jacking pipePipes shall be jacked within the allowable resistance force of the jacking pipe given inthe below table.
Note The above values should be distributed evenly around the circumference of the pipe.
General arrangement of pipe jacking equipment Fig. 15-3
DN Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Class K9 Class K10 Class K11300 2,060 - 1,770 - - -350 2,450 - 1,770 - - -400 2,840 2,450 2,160 - - -450 2,840 2,840 2,450 - - -500 3,730 3,330 2,840 - - -600 3,730 3,730 3,730 - - -700 6,570 5,790 4,810 4,540 5,870 6,570800 6,570 6,570 5,790 5,410 6,570 6,570900 6,570 6,570 6,570 6,350 6,570 6,570
1000 9,020 9,020 8,040 7,360 9,020 9,0201100 9,020 9,020 9,020 8,450 9,020 9,0201200 9,020 9,020 9,020 9,020 9,020 9,0201400 9,020 9,020 9,0201500 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,3601600 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,3601800 12,360 12,360 12,360 - - -2000 18,670 18,670 18,670 - - -2200 18,670 18,670 18,670 - - -2400 18,670 18,670 18,670 - - -2600 23,240 23,240 23,240 - - -
Class of pipe by Japanese standard Class of pipe by ISO standardAllowable resistance force (kN)
Allowable resistance force of jacking ductile iron pipe Table 15-1