PHP7 - A look at the future
-
Upload
radu-murzea -
Category
Software
-
view
20 -
download
0
Transcript of PHP7 - A look at the future

PHP 7 – A look at the future
by Radu Murzea
25 July 2015

Agenda
A bit of History
Most important new features of PHP 7 Mini-demo of each one
Q&A

PHP – A bit of high-level historyPHP < 5
1995 - 2008
PHP with most known
features
Zend Engine 1

PHP – A bit of high-level historyPHP < 5
1995 - 2008 2004 - 2017
PHP 5
PHP with most known
features
Zend Engine 1
Zend Engine 2
NewObject-Oriented
Model

PHP – A bit of high-level historyPHP < 5
1995 - 2008 2004 - 2017 2015 - ?
PHP 5 PHP 7
PHP with most known
features
Zend Engine 1
Zend Engine 2
Zend Engine 3
NewObject-Oriented
Model Keep reading

AST-based CompilationSeparation of parser and compiler
Higher Maintainability Decouple syntax issues from technical issues
Performance Improvement
Usually 10 – 20 % faster But requires more memory
Removes many syntax limitations
See “Uniform Variable Syntax” Chapter
Reference
https://wiki.php.net/rfc/abstract_syntax_tree
AST looks
like this

Uniform Variable SyntaxConsistent left-to-right variable dereferencing
Stuff like this is now possible:
$foo['bar']->baz->oof()::$rab explode(‘|’, $x)[3] $foo()[‘bar’]() foo()() (function() { return 1+2+3; })() ‘Foo’::$bar
Reference
https://wiki.php.net/rfc/uniform_variable_syntax

Return Type Declarations (I)Motivation
Prevent unintended return values Document return type in a way that is not easily removed (like phpdoc
comments)
Rules
In case of inheritance -> invariant enforcement If return type is declared, NULL may not be returned Not allowed on __construct(), __destruct() and __clone()
Multiple return types are NOT allowed

Return Type Declarations (II)
Reference
https://wiki.php.net/rfc/return_types
Example
class MyClass { function a() { //return type is optional return 123; } function b(): int { //fatal error - "int" doesn't exist return 123; } function c(): ClassB { //fatal error - can't return null here return null; }}

Anonymous Classes (I)Motivation
Anonymous classes are frequently used in other languages (Java, C#)
Basic Rules
Instantiating requires providing values to constructor arguments Inheritance and Traits works just like for named classes Attempting to serialize will result in an ERROR
Use Cases
In very simple cases, where dedicated file + class-doc = overkill When it’s small + you need it only once during execution When you don’t want to hit the autoloader for extremely simple classes Primitive support for situations where inner classes would make sense
Reference
https://wiki.php.net/rfc/anonymous_classes

Anonymous Classes (II)Examples
$x = new class(123) { public function __construct($a) { $this->a = $a; }};
(new class extends SomeClass implements SomeInterface { public function init() { /* ... */ }})->doStuff();
class MyClass extends MyOtherClass { public function getInstance() { return new class implements MyInt { /* ... */ }; }}

Many Fatal Errors become ExceptionsMotivation
Execution immediately aborted, cannot be recovered from finally blocks or __destructor() s are not called
Solution
Reference
https://wiki.php.net/rfc/engine_exceptions_for_php7 https://wiki.php.net/rfc/throwable-interface https://trowski.com/2015/06/24/throwable-exceptions-and-errors-in-php7/

Context Sensitive LexerMotivation
PHP reserved words prevent good/natural API designs
Example
This is now possible:
Finder::for(‘project’) ->where(‘name’)->like(‘%secret%’) ->and(‘priority’, ‘>’, 9) ->or(‘code’)->in([‘4’, ‘5’, ‘7’]) ->and()->not(‘created_at’)->between([$t1, $t2]) ->list($limit, $offset);
Reference
https://wiki.php.net/rfc/context_sensitive_lexer

Grouping Use Declarations (I)Motivation
Cut verbosity when importing classes, functions or constants Easier to identify which entities belong to the same module
Reference
https://wiki.php.net/rfc/group_use_declarations
Example
This:
use Foo\Bar\StuffA;use Foo\Bar\StuffB as MyB;
becomes this:
use Foo\Bar\{ StuffA, StuffB as MyB};

Null Coalesce OperatorMotivation
Operations like “if data exists, use it; otherwise use default” are quite cumbersome to do
Description/Examples
Denoted by ?? Returns result of 1st operand if it exists and is not NULL; otherwise
returns 2nd operand The following 2 statements are equivalent:
$a = isset($_GET[‘a’]) ? $_GET[‘a’] : ‘default’;
$a = $_GET[‘a’] ?? ‘default’; The following 2 statements are equivalent as well:
if (($a = A::$value) === null) { $a = $default; }
$a = A::$value ?? $default;Reference
https://wiki.php.net/rfc/isset_ternary

Unicode Code Point Escape SyntaxMotivation
Proper escape syntax for Unicode characters Support for more than 16-bit-length BPM characters Syntax is \u{xxxxxx} – with variable length
Examples
echo "\u{202E}Right-to-left text";will print: txet tfel-ot-thgiR
echo “\u{1F602}”; //Emoji – Face with Tears of Joywill print:
Reference
https://wiki.php.net/rfc/unicode_escape

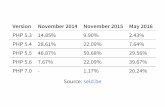
Performance – MediaWiki – Requests/s
Source: http://talks.php.net/velocity15#/mwbench

Performance – Wordpress - Latency
Source: http://talks.php.net/velocity15#/wpbench

Q & A






![Welcome [connortumbleson.com] · 2/6/2018 · PHP7: December 3, 2015 ๏ 2018 already! You need to be on PHP7+ ๏ Security enhancements ๏ Speed enhancements ๏ Features and deprecations](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5fd0f3c8daabef3d6322fad6/welcome-262018-php7-december-3-2015-a-2018-already-you-need-to-be.jpg)