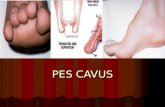
Pes Cavus Amjad Moiffak Moreden, M.D. The General Assembly of Damascus Hospital Ministry of Health...
-
Upload
shavonne-fox -
Category
Documents
-
view
248 -
download
0
Transcript of Pes Cavus Amjad Moiffak Moreden, M.D. The General Assembly of Damascus Hospital Ministry of Health...

Pes CavusPes Cavus
Amjad Moiffak Moreden, M.D.Amjad Moiffak Moreden, M.D.The General Assembly of Damascus HospitalThe General Assembly of Damascus Hospital
Ministry of HealthMinistry of HealthDamascus, SyriaDamascus, Syria
Jan. 30, 2007Jan. 30, 2007

Synonyms Synonyms
high arch, cavus foot, cock-up deformity, clawtoe high arch, cavus foot, cock-up deformity, clawtoe deformity, foot pain, talipes cavus, contracted foot, deformity, foot pain, talipes cavus, contracted foot, exaggerated arch exaggerated arch

DefinitionDefinition Pes cavus is a high arch Pes cavus is a high arch
that does not flatten that does not flatten with weightbearing. No with weightbearing. No specific radiographic specific radiographic definition of cavus foot definition of cavus foot exists. The deformity exists. The deformity can be located in the can be located in the forefoot, midfoot, or forefoot, midfoot, or hindfoot or in a hindfoot or in a combination of these combination of these sites. sites.

What’s the problem?What’s the problem? clawing of the toes, posterior clawing of the toes, posterior
hindfoot deformity hindfoot deformity (described as an increased (described as an increased calcaneal angle), contracture calcaneal angle), contracture of the plantar fascia, and of the plantar fascia, and cock-up deformity of the cock-up deformity of the great toe. This can cause great toe. This can cause increased weightbearing for increased weightbearing for the metatarsal heads and the metatarsal heads and associated metatarsalgia associated metatarsalgia and callus. and callus.

Etiology Etiology
80% of the time caused from 80% of the time caused from malunion of calcaneal or talar malunion of calcaneal or talar fractures, burns, sequelae of fractures, burns, sequelae of compartment syndrome, residual compartment syndrome, residual clubfoot, and neuromuscular disease. clubfoot, and neuromuscular disease.
20% of cases are idiopathic and 20% of cases are idiopathic and nonprogressive .nonprogressive .

Residual clubfootResidual clubfoot

Etiology Cont…Etiology Cont… Neuromuscular diseases Neuromuscular diseases
cause muscle imbalance that leads to an cause muscle imbalance that leads to an elevated arch. These diseases include elevated arch. These diseases include muscular dystrophy, Charcot-Marie-Tooth muscular dystrophy, Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease, spinal dysraphism, (CMT) disease, spinal dysraphism, polyneuritis, intraspinal tumors, polyneuritis, intraspinal tumors, poliomyelitis, syringomyelia, Friedreich poliomyelitis, syringomyelia, Friedreich ataxia, cerebral palsy, and spinal cord ataxia, cerebral palsy, and spinal cord tumors. A patient with new onset of a tumors. A patient with new onset of a unilateral deformity but without history of unilateral deformity but without history of trauma must be evaluated for spinal tumor. trauma must be evaluated for spinal tumor.

Etiology Cont…Etiology Cont…
Multiple theories :Multiple theories :
-Intrinsic muscle imbalance causing the elevated arch.-Extrinsic muscle causes the muscle imbalance.-Combination of the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles is the cause of the imbalance.

Etiology Cont…Etiology Cont…Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT)Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT)
The anterior tibialis muscle and the peroneus muscle The anterior tibialis muscle and the peroneus muscle develop weakness. Antagonist muscles, posterior develop weakness. Antagonist muscles, posterior tibialis and peroneus longus, pull harder than the tibialis and peroneus longus, pull harder than the other muscles, causing deformity. Specifically, the other muscles, causing deformity. Specifically, the peroneus longus pulls harder than the weak anterior peroneus longus pulls harder than the weak anterior tibials, causing plantarflexion of the first ray and tibials, causing plantarflexion of the first ray and forefoot valgus. The posterior tibialis pulls harder forefoot valgus. The posterior tibialis pulls harder than the weak peroneus brevis, causing forefoot than the weak peroneus brevis, causing forefoot adduction. Intrinsic muscle develops contractures adduction. Intrinsic muscle develops contractures while the long extensor to the toes, recruited to while the long extensor to the toes, recruited to assist in ankle dorsiflexion, causes cock-up or assist in ankle dorsiflexion, causes cock-up or clawtoe deformity. With the forefoot valgus and the clawtoe deformity. With the forefoot valgus and the hindfoot varus, increased stress is placed on the hindfoot varus, increased stress is placed on the lateral ankle ligaments and instability can occur. lateral ankle ligaments and instability can occur.

Etiology Cont…Etiology Cont…Polio Polio
The deformity is in the hindfoot and The deformity is in the hindfoot and caused by the weakness in the caused by the weakness in the gastrocsoleus complex, leading to a gastrocsoleus complex, leading to a marked increase in the calcaneal marked increase in the calcaneal pitch angle with normal forefoot pitch angle with normal forefoot alignment. alignment.

Polio
Normal

Clinical presentationClinical presentation
Patients can present with lateral foot pain Patients can present with lateral foot pain from increased weightbearing on the from increased weightbearing on the lateral foot. Metatarsalgia is a frequent lateral foot. Metatarsalgia is a frequent symptom, as is symptomatic intractable symptom, as is symptomatic intractable plantar keratosis. Ankle instability can be a plantar keratosis. Ankle instability can be a presenting symptom, especially in patients presenting symptom, especially in patients with hindfoot varus and weak peroneus with hindfoot varus and weak peroneus brevis muscle. brevis muscle.
Patients with neuromuscular disease Patients with neuromuscular disease complain of weakness and fatigue, the complain of weakness and fatigue, the severity of the presenting symptoms is as severity of the presenting symptoms is as variable as the symptoms themselves. variable as the symptoms themselves.

Orthopaedic Residents

Work Up Work Up
- Family history- Family history - Neuro exam - Neuro exam - X-rays of entire spine - X-rays of entire spine - EMG and nerve conduction - EMG and nerve conduction studiesstudies - MRI meylogram - MRI meylogram

Evaluation Evaluation
Thorough history and complete Thorough history and complete examination in an attempt to try to examination in an attempt to try to determine the etiology. determine the etiology.

Imaging Studies Imaging Studies Standing radiography of the Standing radiography of the
feet and ankles is essential. feet and ankles is essential. Radiographs should be Radiographs should be inspected for degenerative inspected for degenerative arthritis, positioning of the arthritis, positioning of the calcaneus, and forefoot calcaneus, and forefoot alignment. A calcaneal alignment. A calcaneal pitch angle can be pitch angle can be measured by drawing a line measured by drawing a line along the plantar aspect of along the plantar aspect of the calcaneus and the the calcaneus and the ground. An angle greater ground. An angle greater than 30° is significant for than 30° is significant for hindfoot varus. The hindfoot varus. The positioning of the first ray positioning of the first ray compared to the axis of the compared to the axis of the talus viewed on the lateral talus viewed on the lateral radiograph determines if radiograph determines if the first ray is plantar the first ray is plantar flexed.flexed.

Imaging Studies Cont…Imaging Studies Cont…
MRI of the spine should be obtained MRI of the spine should be obtained if unilateral progressive cavus is if unilateral progressive cavus is present in a patient without history present in a patient without history of trauma. of trauma.

TreatmentTreatment
The goal of treatment is to produce a The goal of treatment is to produce a plantigrade foot that allows even plantigrade foot that allows even distribution of weight. distribution of weight.
Failure to maintain an asymptomatic Failure to maintain an asymptomatic plantar grade foot is an indication for plantar grade foot is an indication for surgery. The contraindication to surgery. The contraindication to surgery is poor vascularity, and surgery is poor vascularity, and ulcers. ulcers.

Treatment Cont…Treatment Cont…Medical therapy Medical therapy
Ambulate with symptomatic relief Ambulate with symptomatic relief Physical therapy to stretch tight muscles Physical therapy to stretch tight muscles
and strengthen weak muscles.and strengthen weak muscles. Orthotics with extra-depth shoes to offload Orthotics with extra-depth shoes to offload
bony prominences and prevent rubbing of bony prominences and prevent rubbing of the toes. lateral wedge sole modification to the toes. lateral wedge sole modification to the shoes can improve function. Bracing the shoes can improve function. Bracing for supple deformities or foot drop, and for supple deformities or foot drop, and Plastizote linings for sensation deficite.Plastizote linings for sensation deficite.

Treatment Cont…Treatment Cont…Surgical therapy Surgical therapy
Patient must understand the rationale Patient must understand the rationale for treatment and understand that for treatment and understand that surgical reconstruction does not surgical reconstruction does not provide a normal foot. The goal of provide a normal foot. The goal of surgery is to produce a plantigrade foot surgery is to produce a plantigrade foot and pain relief. Also, repeat surgical and pain relief. Also, repeat surgical procedures may be required, especially procedures may be required, especially if the deformity is progressive.if the deformity is progressive.

Treatment Cont…Treatment Cont…Surgical therapySurgical therapy
No single procedure is appropriate No single procedure is appropriate for all patients, and frequently, for all patients, and frequently, multiple individual procedures need multiple individual procedures need to be performed. to be performed.
Tendon transfers and osteotomies Tendon transfers and osteotomies can provide correction of the can provide correction of the deformity without performing an deformity without performing an arthrodesis which is used only as a arthrodesis which is used only as a salvage procedure, preserving the salvage procedure, preserving the joints if possible is the current trend joints if possible is the current trend ..

Treatment of Early Treatment of Early DeformityDeformity - treatment involves soft-tissue releases and/or tendon transfers.- treatment involves soft-tissue releases and/or tendon transfers.
- any proposed osseous procedures must not affect growth of the foot, such as - any proposed osseous procedures must not affect growth of the foot, such as calcaneal and/or metatarsal osteotomies.calcaneal and/or metatarsal osteotomies.
Planter releasePlanter release:: - indicated for patients less than 10 years of age w/ cavus deformity w/ - indicated for patients less than 10 years of age w/ cavus deformity w/
significant plantar flexion of first ray.significant plantar flexion of first ray.Plantar medial release:Plantar medial release: - indicated for rigid hindfoot w/ fixed varus angulation.- indicated for rigid hindfoot w/ fixed varus angulation. - involves planter release along w/ medial tarsal structures.- involves planter release along w/ medial tarsal structures. - released medial structures include talonavicular joint capsule, superficial - released medial structures include talonavicular joint capsule, superficial
deltoid ligament, and possibly the long toe flexors.deltoid ligament, and possibly the long toe flexors.Tendon transfers:Tendon transfers: - indicated for patients w/ a supple inversion deformity w/ weak evertors.- indicated for patients w/ a supple inversion deformity w/ weak evertors. - a prerequisite for this procedure is a plantagrade foot which is achieved w/ - a prerequisite for this procedure is a plantagrade foot which is achieved w/
planter release.planter release. - consider lateral transfer of tibialis antirior tendon into the mid-tarsal region - consider lateral transfer of tibialis antirior tendon into the mid-tarsal region
along the long axis of third ray.along the long axis of third ray.

Treatment of Rigid Treatment of Rigid Deformity Deformity - - fixed bony deformity is better managed by a combination of fixed bony deformity is better managed by a combination of
calcaneal and metatarsal osteotomies and may require the calcaneal and metatarsal osteotomies and may require the use of AFO's.use of AFO's.
Calcaneal osteotomyCalcaneal osteotomy:: - for correction of hindfoot varus deformity & mid-tarsal - for correction of hindfoot varus deformity & mid-tarsal
osteotomy for correction of midfoot cavus and varus osteotomy for correction of midfoot cavus and varus deformity.deformity.
- calcaneal osteotomy does not impede growth since it is not - calcaneal osteotomy does not impede growth since it is not made thru cartilage growth surface.made thru cartilage growth surface.
- posterior displacement calcaneal osteotomy is effective in - posterior displacement calcaneal osteotomy is effective in correcting calcaneocavus deformity of the type II neuropathy.correcting calcaneocavus deformity of the type II neuropathy.
- in young patients w/ milder deformity, translate the distal and - in young patients w/ milder deformity, translate the distal and posterior calcaneal fragment laterally w/o removal of an posterior calcaneal fragment laterally w/o removal of an osseous wedge.osseous wedge.
- lateral slide osteotomy is cut slightly obliquely, passing from - lateral slide osteotomy is cut slightly obliquely, passing from superior position on lateral surface to a more inferior position superior position on lateral surface to a more inferior position on the medial surface.on the medial surface.
- distal fragment can be translated laterally as much as 1/3 of - distal fragment can be translated laterally as much as 1/3 of its transverse diameter, thus allowing for conversion of wt-its transverse diameter, thus allowing for conversion of wt-bearing from a varus to a slight valgus position.bearing from a varus to a slight valgus position.
- w/ severe deformity consider: triplearthodesis.- w/ severe deformity consider: triplearthodesis.


Treatment Cont…Treatment Cont…Surgical therapySurgical therapy
Plantar fascia release:Plantar fascia release:
Is usually combined with tendon Is usually combined with tendon transfer, osteotomy, or both. This is transfer, osteotomy, or both. This is frequently the first step in improving frequently the first step in improving the deformity. Stripping the fascia off the deformity. Stripping the fascia off the calcaneus and complete the calcaneus and complete resection of the plantar fascia. resection of the plantar fascia.

Treatment Cont…Treatment Cont…Surgical therapySurgical therapy
Great toe Jones procedure:Great toe Jones procedure: Performed for cock-up deformity of the great Performed for cock-up deformity of the great
toe with associated weakness of the anterior toe with associated weakness of the anterior tibialis muscle. extensor hallucis longus (EHL) tibialis muscle. extensor hallucis longus (EHL) has been recruited to assist in ankle has been recruited to assist in ankle dorsiflexion, which causes hyperextension at the dorsiflexion, which causes hyperextension at the MTP joint and hyperflexion at the MTP joint and hyperflexion at the interphalangeal (IP) joint. This procedure interphalangeal (IP) joint. This procedure transfers the EHL to the neck of the first transfers the EHL to the neck of the first metatarsal with arthrodesis of the IP joint to metatarsal with arthrodesis of the IP joint to improve the dorsiflexion of the ankle and improve the dorsiflexion of the ankle and remove the deforming force at the MTP joint. remove the deforming force at the MTP joint.

Treatment Cont…Treatment Cont…Surgical therapySurgical therapy
Extensor shift procedure: Extensor shift procedure: Transfer of the EHL and the extensor Transfer of the EHL and the extensor
digitorum longus (EDL) to the first, third, digitorum longus (EDL) to the first, third, and fifth metatarsals. The technique and fifth metatarsals. The technique includes completion of the Jones includes completion of the Jones procedure with incisions in the second and procedure with incisions in the second and fourth web space. The tendons are fourth web space. The tendons are harvested. The second and third tendons harvested. The second and third tendons are transferred through a drill hole on the are transferred through a drill hole on the third metatarsal, and the fourth and fifth third metatarsal, and the fourth and fifth tendons are transferred to the fifth tendons are transferred to the fifth metatarsal. metatarsal.

Treatment Cont…Treatment Cont…Surgical therapySurgical therapy
Girdlestone-Taylor transfer:Girdlestone-Taylor transfer:
This procedure is used for flexible This procedure is used for flexible clawtoe deformities. The deforming clawtoe deformities. The deforming force of the flexor digitorum longus force of the flexor digitorum longus tendon is transferred to the tendon is transferred to the extensors.extensors.

Treatment Cont…Treatment Cont…Surgical therapySurgical therapy
Base of the first metatarsal Base of the first metatarsal osteotomy:osteotomy:
In patients with a fixed plantar-flexed first In patients with a fixed plantar-flexed first ray, a base of the metatarsal closing ray, a base of the metatarsal closing wedge osteotomy corrects the deformity, wedge osteotomy corrects the deformity, which is especially observed in CMT which is especially observed in CMT disease. This procedure is usually disease. This procedure is usually combined with a plantar fascia release in a combined with a plantar fascia release in a mild deformity or a Jones procedure.mild deformity or a Jones procedure.

Treatment Cont…Treatment Cont…Surgical therapySurgical therapy
Midfoot osteotomy:Midfoot osteotomy:
Tarsal osteotomy has been described Tarsal osteotomy has been described for deformities through the midfoot. for deformities through the midfoot. however, these osteotomies require however, these osteotomies require cutting through multiple joints.cutting through multiple joints.

Treatment Cont…Treatment Cont…Surgical therapySurgical therapy
Peroneus longus to peroneus Peroneus longus to peroneus brevis tenodesis:brevis tenodesis:
In patients with CMT disease that In patients with CMT disease that have a weak peroneus brevis (PB) and have a weak peroneus brevis (PB) and a preserved peroneus longus (PL), a a preserved peroneus longus (PL), a tenodesis can be performed to help tenodesis can be performed to help stabilize the ankle. This is frequently stabilize the ankle. This is frequently combined with a calcaneal osteotomy. combined with a calcaneal osteotomy.

Treatment Cont…Treatment Cont…Surgical therapySurgical therapy
Calcaneal osteotomy:Calcaneal osteotomy:
Patients with hindfoot involvement usually Patients with hindfoot involvement usually require a calcaneal osteotomy to correct require a calcaneal osteotomy to correct the deformity. The osteotomy can include the deformity. The osteotomy can include a closing wedge, a vertical displacement, a closing wedge, a vertical displacement, or a combination (triplanar osteotomy). or a combination (triplanar osteotomy). This procedure is usually combined with a This procedure is usually combined with a plantar fascia release and frequently a plantar fascia release and frequently a tendon transfer.tendon transfer.

Treatment Cont…Treatment Cont…Surgical therapySurgical therapy
Beak triple arthrodesis:Beak triple arthrodesis: The Siffert beak triple arthrodesis corrects The Siffert beak triple arthrodesis corrects
the deformity through wedge resection and the deformity through wedge resection and a triple arthrodesis. This is used for a rigid a triple arthrodesis. This is used for a rigid fixed deformity in adults. The technique fixed deformity in adults. The technique involves mortising the navicular into the involves mortising the navicular into the head. The technique involves mortising the head. The technique involves mortising the navicular into the head of the talus and navicular into the head of the talus and depressing the navicular, cuboid, and depressing the navicular, cuboid, and cuneiforms to improve the forefoot cavus cuneiforms to improve the forefoot cavus deformity.deformity.

ComplicationsComplications
The complications of these procedures The complications of these procedures include nonunion, malunion, infection, include nonunion, malunion, infection, undercorrection, overcorrection, undercorrection, overcorrection, recurrence of the deformity, progression of recurrence of the deformity, progression of the deformity, nerve injury, and continued the deformity, nerve injury, and continued pain. pain.
For progressive disorders, deformities can For progressive disorders, deformities can recur; patients need to be educated about recur; patients need to be educated about this prior to the initial surgery. this prior to the initial surgery.

Thank youThank you
THE ENDTHE END

MoKazem.com
من • تقديمها و إعدادها تم محاضرات سلسلة من هي المحاضرة هذه , دمشق مشفى في العظمية الجراحة شعبة في المقيمين األطباء قبل
. . ميرعلي بشار د إشراف تحت• . المحاضرة هذه في الواردة األخطاء عن مسؤول غير الموقع
•This lecture is one of a series of lectures were prepared and presented by residents in the department of orthopedics in Damascus hospital, under the supervision of Dr. Bashar Mirali.
•This site is not responsible of any mistake may exist in this lecture.
كاظم. مؤيد Dr. Muayad Kadhimد