Periodic Trends. Describe factors that affect electron position around a nucleus. Include: nuclear...
-
Upload
chrystal-small -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Periodic Trends. Describe factors that affect electron position around a nucleus. Include: nuclear...

Periodic Trends

• Describe factors that affect electron position around a nucleus.
Include: nuclear charge, distance, shielding.
• Explain periodic trends using above factors.
Include: atomic / ionic radii, ionization energy, electronegativity.

The force on an electron will affect its position around the atom. The force depends on 3 factors:
1. Nuclear charge - more protons, more attraction.
2. Distance – further apart two charges are, lower their force of attraction (Coulomb’s Law).
3. Shielding Effect - Inner electrons shield the force of the nucleus from outer electrons.

Measured as half the distance between two nuclei when two like atoms are bonded together.
ATOMIC RADIUSSize of atoms tends to vary from substance to
substance due to different interaction.

Decrease Across• same quantum level (same size / n value)
• increase in nuclear charge ( pulls orbitals closer)
Increase Down• new quantum level (larger size / n value)
• increased shielding (decreased force on outer e-)

Cl:
17 e-
Na:11 p+
11 e- 17 p+

Ion size differs from atom size.
IONIC RADIUS

*Same* basic trend as atomic radius.

Positive ions - smaller radii• increased proton - electron balance (lost e-)
• more nuclear charge on remaining e-
• sometimes loss of a quantum level.
Negative ions - bigger radii• decreased proton - electron balance (gain e-)
• Less nuclear charge on remaining e-
• repulsion of additional e- causes expansion.

ClNa+ -

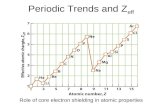
Energy required to remove an electron from an atom forming an ion – energy depends on force on e-.
A(g) + energy → A+(g) + e−
There are multiple ionization energy values for each element – one for each electron being removed.
A+(g) + energy → A+2
(g) + e−
Ionization Energy

Increases Across• increased nuclear charge (increasing p+ number)
• same quantum level
Decreases Down• new quantum levels (increased distance)
• increased shielding (decreases force on outer e-)

ClNa+

Na
Cs

IE increases with each electron removed
• Increased proton-electron ratio (small change)• Less shielding (small change)• Lower quantum level – closer (BIG change)

Electronegativity Attraction an atom has for bonding electrons.
bigger the number, the harder they pull
Periodic Trend:EN increases across the table and decreases down.

Cl:Na:
Lower ionization energy.Lower Electronegativity.
HIGHER ionization energy.HIGHER Electronegativity.
WEAKER nuclear charge.Less attraction - large radius.
STRONGER nuclear charge.More attraction - small radius.

The greater the electronegativity difference the more polar the bond.
Large enough difference – ionic bonds form.
+ -
Cl H
δ+δ-
Polar covalent
C HH
non-polar covalent
00

EN Difference Bond Type Percent Ionic
less than 0.4 non-polar covalent 0% − 5%
0.4 − 1.9 polar covalent 5% − 60%
greater than 1.9 ionic > 60%


CAN YOU / HAVE YOU?
• Describe factors that affect electron position around a nucleus.
Include: nuclear charge, distance, shielding.
• Explain periodic trends using above factors.
Include: atomic / ionic radii, ionization energy, electronegativity.