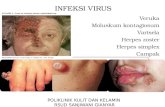
Penyakit Infeksi
-
Upload
kamilla-rd -
Category
Documents
-
view
19 -
download
4
description
Transcript of Penyakit Infeksi
-
Asikin Nur Bagian Biomedika Kedokteran Gigi FKG UGM
PENYAKIT INFEKSI
-
Objectives
2. Interaksi kompleks penyebab infeksi
3. Mekanisme patogenesis mikroorganisme
1. Definisi infeksi dan penyakit
-
Infection:
invasion or colonization and multiplication of microorganisms in body tissues
The presence of a particular type of microorganism in apart of body where it is not normally found
Usually caused by a pathogenic microorganism
-
Disease
Pathological condition that affects part or all of an organism, as a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs. Occurs when an infection results in any change from a state of health An abnormal state in which part or all of the body is not properly adjusted or incapable of performing its normal functions.
-
Pathogencity & Virulency
Patogenitas: kemampuan suatu mikro-organisme dalam menyebabkan penyakit
Virulensi: derajat patogenitas yang dinyatakan dengan jumlah mikroorganisme atau mikrogram toksin yang dibutuhkan untuk membunuh hewan percobaan
-
Interaction of Host - MO
Simbiosis: a relationship between two organisms in which at least one organism is dependent on the other
-
Interaction of Host - MO Comensalism: one of the organism benefits and the other is unaffected Ex. S. epidermidis (skin surface), corynebacteria (surface of eye), mycobacteria (ear and external genitals)
Mutualism: a type of symbiosis that benefits both organisms Ex. E. coli (synthesize vit K and B)
Parasitism: one organism benefits by deriving nutrients at the expense of the other Ex. Disease causing-bacteria
-
Opportunistic Microorganism:
Ordinarily do not cause disease in their normal habitat in a healthy person but may cause infection in different site/ environments Ex. - E.coli: urinary tract infection, pulmonary
infection and meningitis or organ abscesses
- Pneumocystis jirovecii: Pneumocystis pneumonia (compromised host)
-
Etiology of Infectious disease
Koch`s Postulates: 1. The same pathogen must be present in every case of the
disease.
2. The pathogen must be isolated from the diseased host and grown in pure culture.
3. The pathogen from the pure culture must cause the disease when it is inoculated into a healthy, susceptible laboratory animal.
4. The pathogen must be isolated from the inoculated animal and must be shown to be the original organism.
-
Exception to Koch`s Postulates:
Treponema pallidum --- syphilis, but virulent strains have never been cultured on artificial media.
Mycobacterium leprae --- leprosy, has also never been grown on artificial media.
Many rickettsial and viral pathogens cannot be cultured on artificial media because they multiply only within cells.
-
Clasification of Infectious Disease
Communicable disease --- contagious disease Ex: chicken fox, measles, genital herpes,
thypoid fever, TBC Noncommunicable disease
Ex: Tetanus: Clostridium tetani
How it behave whitin a host and population
-
Frequency of occurance:
Sporadic disease: occasionally Ex: Typhoid fever
Endemic disease: constantly present in a
population Ex: common cold
Epidemic disease: many people in an area
acquire a certain disease in short period Ex: influenza
-
Severity or duration of a disease
Acute Ex: influenza
Chronic
Ex: TBC, Hepatitis B
Subacute Ex: Sclerosing panencephalitis
Latent Ex: Herpes: Varicella
-
Extent of Host Involvement
Local infection: (limited, small area) Ex: Boils and abscesses
Systemic infection: (spread throughout the
body) Ex: Measles
Focal infection: (enter blood or lymphatic vessel
and spread to other part od body) Ex: Endocarditis caused by oral bacteria
-
Primery Infection: an acute infection that causes the initial illness
Secundary Infection: caused by opportunistic
pathogen after the primary infection
The state of host resistance:
-
Transmission of Disease Contact Transmission:
Direct Transmission: hepatitis A, Staphylococal infection Indirect Transmission: hepatitis B Droplet Transmission: influenza
Vehicle Transmission: salmonela infection Vector Transmission: typhoid fever (feces)
-
Development of Disease
Tortora et al 2013, Microbiology An Introduction
-
How Bacteria Develop Infection
Generate a biofilm 90% of infection cases are related to
biofilm formation
Biofilm is 1000 X stronger than a planktonic
mode
-
BIOFILM
Generate a biofilm 90% of infection cases are related to
biofilm formation Biofilm is 1000 X stronger than a planktonic
mode
-
BIOFILM
Monroe D., et al. Bacterial Biofilms, PLOS Biology Vol. 8 No.11
-
Biolm model developed by S. intermedius at the presence of Extracellular DNA
Biofilm development Cells + DNA
Dispersal
Cells only Adherence Microcolony
-
Brain and liver abscesses caused by oral infection with S. intermedius
Wagner et al, Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology, 2006; 102: e21-e23
A large liver abscess lesion
Panoramic radiograph showing periodontal lesions near the upper right and left molar
Brain abscess lesions in the left frontal lobe
-
Brain abscesses mimicking brain metastases. (A) Time course of T1/T2 weighted MR images, Gd: Gadolinium. (B) Papanicolaou staining and (C) gram staining of Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) material.
Erne et al, Lancet, 2010, 375: 2050
Brain abscess caused by lung infection with S. intermedius
-
References
1. Tortora G. J., Funke B.R. and Case C.J., 2013, Microbiology An Introduction, 11th ed., Pearson, Boston
2. Brooks G.F., Carrol K.C., Butel J.S., Morse S.A. and Mietzner TA., 2010, Jawetz, Melnick & Adelberg`s Medical Microbiology, 25th ed., The McGraw-Hill Comp. Inc.











![Bab 1-6 Rinirepo.stikesicme-jbg.ac.id/2798/3/PSmarkup_Bab 1-6 Rini.doc.pdf · PENDAHULUAN 1.1 Latar Belakang [11] Salah satu penyakit yang timbul akibat infeksi bakteri patogen yaitu](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5e9df09d79c10529333e9426/bab-1-6-1-6-rinidocpdf-pendahuluan-11-latar-belakang-11-salah-satu-penyakit.jpg)






