· Paul Painlevé studied nonlinear differential equations with second order, which have no...
Transcript of · Paul Painlevé studied nonlinear differential equations with second order, which have no...
-
Content: Natural or social phenomena are governed by chance. Probability and statistics provide an important way to analyze these phenomena. For example, in order to analyze failure of electronic equipment and its maintenance, application of stochastic processes is indispensable with sensor technology to observe the state. Also because of development of observation technology, it is to increase in importance of big data analysis using machine learning. The most important topics in stochastic processes are Gaussian and Markovian processes. Markov processes including diffusion process that is represented by the stochastic differential equation are used in financial economics. An application of the stochastic processes is targeted to reliability theory and social systems engineering. The graph on the left is the numerical example of the Brownian Bridge that is Brownian motion starting and ending points fixed to 0. Stochastic processes dominated by coincidence suggest that even control. However, the graph below is the numerical solution of stochastic differential equations in Brownian Bridge. Closer to the end for the numerical error does not control.
Keywords:Stochastic Processes, Optimization E-mail: [email protected]> Tel. +81-88-656-7295 Fax: +81-88-656-7295
crack
-
Content: My research theme is "Linear systems and Automorphism Groups on Algebraic Curves". Recently, we prove that every automorphism of a smooth plane curve should be either a homology type, a decsendent type or an exceptional type. According to this result, we prove that automorphism is homology type if and only if a Galois point type or a point projection which is a composition of Galois covering and some covering. When a projection is a composition of Galois covering and some covering, its Galois closure can be embedded in a wreath product of a Galois group and some typical group. As a corollary of this result, we can construct a Galois closure of some covering of a smooth plane curve whose Galois group contains a B-type Coxster group. Similary, we can calculate the invariant ring and invariant polynomials by the action of a linear representation of a given group G, and we can construct an algebraic curve C whose defining ideal is generated by some invariant polynomials. The automorphism group of this curve C includes G or a factor group of G by its center as a subgroup. By this way, we can construct a smooth space curve of genus 9 whose automorphism group contains a factor group of a F4 Coxeter group (i.e. an automorphism group of 4-dimensional regular 24 cell) by its center which is isomorphic to
F4/Z≅((A4×A4):C2):C2(order 576).
Keywords:Algebraic Curve, Linear System, Automorphism Group E-mail: [email protected] Tel. +81-88-656-7297 Fax: +81-88-656-7297 HP : http://www-math.ias.tokushima-u.ac.jp/~ohbuchi/
crack
顔写真 (省略可)
4
1 0 0 0 0 1 0 00 1 0 0 1 0 0 0
, ,0 0 1 0 0 0 0 10 0 0 1 0 0 1 0
F
− =< −
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 11 1 1 1 1 1 1 11 1,1 1 1 1 1 1 1 12 21 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
− − − − − − − − − − > − − − − − − − − − −
Generators of a group F4 of order 1152
Coxeter-Dynkin Diagram of F4
F4 Type regular polytope (regular 24 cell) in 4-dimensional space (the image of a projection from a point to 3-dimensional Euclid space)
-
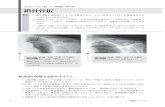
Elliptic Asymptotics of the first Painlevé equations Content: It is important to study connection problems of solutions of differential equations between two points in many fields of mathematical sciences. The global study on ordinary linear differential equations is still developing. Paul Painlevé studied nonlinear differential equations with second order, which have no movable branch points (so called the Painlevé property). He and his pupil, Gambier, classified all of such equations in six types around 1900. Many nonlinear equations appeared in physics has the Painlevé property, and we can solve connection problems on such equations. We expect that the Painlevé equations play the same important role in nonlinear analysis as the Bessel functions or hypergeometric functions play in linear equations. The Painlevé equations are also obtained by monodromy preserving deformations. We can show the corre-spondence between global data of linear equations and local data of the Painlevé functions and we can study nonlinear connection problems or the nonlinear Stokes phenomenon on the Painlevé differential or difference equations.
Keywords:Classical Analysis, the Painlevé equations, monodromy problems E-mail: [email protected] Tel. +81-88-656-7541 Fax: +81-88-656-7541 HP: http://math0.pm.tokushima-u.ac.jp/~ohyama/index_e.html
crack
A graph of the first Painlevé transcendents on the complex domain
Paul Painlevé (left) was a former prime
minister of France. He is the first
mathematician who flew on the airplane. He was a passenger
of Wilber Wright (right) on 1908.
http://math0.pm.tokushima-u.ac.jp/%7Eohyama/index_e.htmlhttp://math0.pm.tokushima-u.ac.jp/%7Eohyama/index_e.htmlhttp://math0.pm.tokushima-u.ac.jp/%7Eohyama/index_e.html
-
Content: By using the functional analysis approach, I study on the structure of solutions and the decay estimate of energy for nonlinear PDEs that describe the nonlinear phenomena. In a study of nonlinear equations, detailed analysis of the corresponding linear equation becomes essential. I examine the relationship of the nonlinearity of the equations and the functional spaces to which the solutions belong, and I investigate on global solvability in time of solutions or blow-up problems for PDEs. In addition, I research on decay estimates the energy function and the derivatives. Nonlinear degenerate dissipative Kirchhoff equations are nonlinear PDEs that describe the nonlinear wave phenomena. Solutions of these equations have decay estimates of the same polynomial order from above and blow. Vlasov-Poisson systems are basic equations that describe plasma phenomena, in particular, the solution of the Vlasov-Poisson-Fokker-Plank system is asymptotic to the solution of the corresponding linear Fokker-Plank system.
Keywords :Nonlinear Analysis, PDEs Field :Mathematical Sciences E-mail : [email protected] Tel. +81-88-656-7218 Fax : +81-88-656-7218 HP : http://www-math.ias.tokushima-u.ac.jp/
crack
-
Content: It is well known that that Euclidean algorithms in the integer ring and the existence of the unique prime factorization in the integer ring. But it is not always true for general integer rings of algebraic number fields. In the special case of imaginary quadratic fields, A. Baker and H. M. Stark independently proved the Gauss’s conjecture that there are finitely many imaginary quadratic fields with class number one. From 1990 and 2000, we have generalized these class number one problem for several family of infinitely many real quadratic fields. In these cases we used analytic class number formula and upper estimate of class numbers and calculations of class numbers using the computer. Recently, we have been investigating the structure of Diophantine equations related to the unit groups of algebraic number fields. We also concern the applications of these investigations to the theory of cryptography.
Keywords:Number Theory, Diophantine equations E-mail: [email protected]> Tel. +81-88-656-7228 Fax: +81-88-656-7228 HP: Visit Following URL http// www-math.ias.tokushimau.ac.jp/~katayama/index.htm
crack
The following diagram represents that the results of Barnig (1963) which generates all the primitive Pythagorean triples using 3X3 matrices, by cutting Farey trees and modified Farey trees naturally induces the 2X2 matrices generates all the primitive Pythagorean triples. We reported this result in J. Mathematics Tokuhsima University, 47( 2013).
-
Content: The main subject of our research is the ideal class groups of algebraic number fields. We have particularly investigated Greenberg‘s conjecture and Vandiver’s conjecture on the class numbers of real cyclotomic fields by using computers. Furthermore, we are also interested in new applications of algebraic systems such as algebraic number fields and elliptic curves, which have strong connections with cryptography. A lot of mathematicians have been interested in Riemann zeta function (cf. Fig.1). Its special values have deep relations with the ideal class groups of cyclotomic fields (cf. Fig.2). These relations are expressed as correspondences of the class numbers of real cyclotomic fields and the indices of their circular units in full ones. Greenberg‘s conjecture states that their p-parts are bounded in the Zp-extension. Moreover, Vandiver's conjecture states that they are trivial for p-cyclotomic fields. We have been studied these conjectures by using arithmetic special elements such as cyclotomic units, Gauss sums, p-adic L-functions and auxiliary prime numbers. As results, we could find a lot of examples for which Greenberg's conjecture holds, and a lot of exceptional prime numbers for the Iwasawa invariants (cf. Fig.3).
Keywords:algebraic number field, class number, elliptic curve, cryptography E-mail: [email protected] Tel. +81-88-656-7549 Fax: +81-88-656-7549 HP : http://hiro2.pm.tokushima-u.ac.jp/
crack
Fig.2 Irregular primes and indices
Fig.3 The number of exceptional primes
Fig.1 log|ζ(s)| (ζ(s): Riemann zeta function)
-
Content: Pharmacokinetics plays an important role in efficacy and safety pharmacotherapy. The estimation of individual pharmacokinetic parameters from a few concentration data is desirable in quick therapy. Bayesian estimation using the population pharmacokinetic parameters is useful for the estimation of individual pharmacokinetic parameters. Here, population pharmacokinetic para-meters mean statistic including average, variance and correlation coefficient. The numerical calculation of nonlinear optimization is essential to Bayesian estimation or computation for population pharmacokinetic para-meters. In addition, the theoretical value of concentration data may be given with a nonlinear differential equation. The stable computation in nonlinear optimization for pharmacokinetics is difficult because of the strong nonlinearity. I am developing a stable and high-precision numerical method for nonlinear optimization problem in population pharmacokinetics and Bayesian estimation.
Keywords: Numerical analysis, Nonlinear optimization E-mail: [email protected] Tel. +81-88-656-7544 Fax: +81-88-656-7544
crack
S = 2! 2cmX
j = 1
logc(tj ; x) +mX
j = 1
(cj ¡ c(t j ; x))2
f c(t j ; x)g2+ ! 2c
nX
i = 1
(xi ¡ ¹ i )2! 2i ¹ 2i
(a) Objective function in nonlinear optimization problem
C(t) = c(t;Vd;Vmax ;K m) : Concentration8>>><
>>>:
dX a(t)dt
= ¡ ka Xa(t)
dC(t)dt =
F ka XaVd
¡Vmax C
Vd(K m + C)
ti 5 t < ti + 1 ( i = 1;2;¢¢¢)
X a(t i ) =
8<
:
D1Di + limt ! t i ¡ 0
Xa(t)C(ti ) =
8<
:
0 i = 1
limt! t i ¡ 0
C(t) i = 2
(b) Di®erential equations(phenytoin)
Fig. 1 Bayesian estimat ion for pharmacokinet ics
MTC(Minimum Toxic Concent rat ion)
MEC(Minimum E®ect ive Concent rat ion)
Therapeutic Range
Fig. 2 Prō le of the concentration and the therapeutic range
-
Content: 2D Lotka-Volterra equations cannot have limit cycles. That is, except for conservative systems, the limit set consists of equilibria only. On the other hand, 3D Lotka-Volterra systems allow various types of complicated dynamics. As long as we restrict 3D competitive Lotka-Volterra systems, the possibility of the dynamics is limited. Hirsch showed that competitive systems have the order preserving property, and there is an invariant manifold (called the carrying simplex) which attracts all orbits except for the origin. Thus, in 3D competitive systems, the Poincare-Bendixson theorem holds, and therefore the limit set consists of equilibria, limit cycles and heteroclinic orbit only. Zeeman has divided all possible phase portraits of 3D competitive Lotka-Volterra systems into 33 classes and showed that six classes can have the Hopf bifurcation. Hofbauer and So constructed an example with two limit cycles in Zeeman's class 27. In this study, we present a concrete example with multiple limit cycles for 3D competitive Lotka-Volterra systems. For instance, we obtain an example with three limit cycles in Zeeman’s class 27 as shown in figures.
Keywords: differential equations, Hopf bifurcation, limit cycles E-mail: [email protected]> Tel. +81-88-656-7221 Fax: +81-88-656-7221
crack
Fig.1 Phase Portrait of Zeeman’s class 27
Fig.2 Limit cycles of Zeeman’s class 27
-
Content: The relation between differential structure and topologic properties that the maps on the closed manifold has are studied for a long time, and there is much result. For example, the relationship between uniformly hyperbolic properties and expansive properties and shadowing properties, non-uniformly hypebolic properties is a hyperbolic of partially hyperbolic and dominated splitting and the phase shift of the relationship. Recently, a new concept that the topological nature was re-captured from the measure theory point of view, such as expansion of and follow-up property can be considered, it has been investigated the relationship between the set with a uniform hyperbolicity. Although research the current has remained on the relationship between the uniformly hyperbolic properties are expected to lead the relationship between non-uniformly hyperbolic properties by adding the viewpoint of measure theory. In this study, it is intended that I check the relations with these properties for the meeting having non-uniformly hyperbolic properties in addition to the uniformly hyperbolic properties. Particularly, I think that I can find the connection of a gauging theory-like property and a topologic property by clarifying the topologic property that the one Pesin set of the meeting having non-uniformly hyperbolic properties has.
Keywords:hyperbolic structure, stability, Pesin set E-mail: [email protected] Tel. +81-88-656-7220 Fax: +81-88-656-7220
crack
-
Content: Mathematical optimization is defined as finding the best solution for mathematical problems formulating real world problems, e.g. production planning, location, etc. An important issue for applying mathematical optimization is “uncertainty”, which can divided into the following two types: one is “randomness”, which is included in random factors, e.g. weather, economic conditions, etc. The other is “fuzziness”, which is included in evaluation or judgment of human beings. Because real world problems include both randomness and fuzziness, I study modeling for mathematical optimization by applying “fuzzy random variables”, representing them simultaneously. Formulated mathematical problems often have enormous decision variables and conditions with complex characteristics. Because of difficulty of solving them strictly, we study evolutional computing, e.g. GA and PSO, for finding their good solutions efficiently.
Keywords: Operations Research (OR), Soft Computing E-mail: [email protected] Tel. +81-88-656-7294 Fax: +81-88-656-7294 HP : http://www-math.ias.tokushima-u.ac.jp/~uno/
crack
-
Content: I am interested in the study of a comparison principle and a strong comparison principle for semicontinuous solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations. As partial differential equations I considered the minimal surface equation, the prescribed mean curvature equation, the level set equation of the mean curvature flow equation, the level set equation of an anisotropic curvature equation and p-Laplace diffusion equation. As well known the above equations are degenerate and singular. Usually for such equation, we cannot expect existence of classical solutions. So I will consider such equations with viscosity solutions. For elliptic equations: Comparison principle: Let u be a lower semicontinuous supersolution, and let v be a upper semicontinuous subsolution. On the boundary of the domain we considered if u is greater than or equal to v, then it holds in the whole domain. Strong comparison principle: Assume in the whole domain u is greater than or equal to v. If u touches v in a interior point of the domain, then u is equivalent to v in the whole domain. Keywords:partial differential equation, viscosity solution E-mail: [email protected] Tel. +81-88-656-7225 Fax: +81-88-656-7225
crack
-
Nonlinear Analysis Associate professor Atsuhito Kohda
Content: One main theme is elliptic partial differential equation, in particular, equation of constant mean curvature. It is a very interesting subject. It is known that there are two kind of solutions for it. One is a small solution, which is stable one, and another is a large solution which is unstable. Fig.2 shows its simple example. It is an important problem if there is third solution or not under suitable conditions.
Another topic is hyperbolic systems of conservation laws, for example, Burgers' equation. It is well-known that there shall be discontinuous solution. But non-linearity prevents one from applying modern mathematical techniques such as distribution solution. So one needs to study discontinuity with a direct method, like measure theoretic notion. Fig.2 shows how discontinuity arises.
Keywords:Nonlinear PDE E-mail: [email protected] Tel. +81-88-656-7546 Fax: N/A HP : http://math0.pm.tokushima-u.ac.jp/lec-k/
crack Fig.1 a small and a large solution
Fig.2 discontinuity of solutions
-
Content: Computational complexity theory is a branch of the theory of computation in theoretical computer science that focuses on classifying computational problems according to their inherent difficulty, and relating those classes to each other. One aspect of computational complexity is related to an algorithm for solving instances of a problem. The computational complexity of an algorithm is a measure of how many steps the algorithm will require in the worst case for an instance or input of a given size. The number of steps is measured as a function of that size. Moreover, the theory of computational complexity involves classifying problems according to their inherent tractability or intractability, that is, whether they are “easy” or “hard” to solve. This classification scheme includes the well-known classes P and NP; the terms “NP-complete” and “NP-hard” are related to the class NP. In our research, given a problem, we clarify which class it is belong to, and develop an efficient algorithm for solving it if it is belong to the class P.
Keywords:computational complexity, algorithm E-mail: [email protected] Tel. +81-88-656-7223 Fax: +81-88-656-7223
crack
The class P consists of all problems that can be efficiently computed.
The P ≠ NP problem is whether P and NP are in fact the same.
The most fundamental classification is the distinction between problems whose growth rate in terms of time is polynomial and problems whose growth rate is exponential.
Time-Complexity Polynomial Time Exponential Time
The class NP is the set of decision problems whose solutions can be determined by a non-deterministic Turing machine in polynomial time.
P
NP
𝑂𝑂(log 𝑛𝑛)
𝑂𝑂(𝑛𝑛2) 𝑂𝑂(𝑛𝑛) 𝑂𝑂(𝑛𝑛𝑘𝑘)
𝑂𝑂(2𝑛𝑛) 𝑂𝑂(22𝑛𝑛) 𝑂𝑂(2𝑛𝑛2)
(𝑛𝑛 is the size of input data and 𝑘𝑘 is the constant number.)
P ≠ NP Problem
-
Some Symbolic Computation tools
Content: I am interested in symbolic computation. In computational mathematics, computer algebra, also called symbolic computation or algebraic computation, is a scientific area that refers to the study and development of algorithms and software for manipulating mathematical expressions and other mathematical objects. Although, properly speaking, computer algebra should be a subfield of scientific computing, they are generally considered as distinct fields because scientific computing is usually based on numerical computation with approximate floating point numbers, while symbolic computation emphasizes exact computation with expressions containing variables that have no given value and are manipulated as symbols, hence the name symbolic computation. Recently, I have been studying some special Gröbner bases algorithms to analyze polynomial (or differential equations) systems. I also have been studying algorithms for computing algebraic local cohomology classes ,to analyze hypersurface singularities.
Keywords: Mathematics, Computer Algebra, E-mail: [email protected] Tel. +81-88-656-7296 Fax: +81-88-656-7296 HP :http://www-math.ias.tokushima-u.ac.jp/~nabesima/
crack
Risa/Asir
Maple
Geogebra
-
Content: Sierpinski graphs 𝑆𝑆 𝑛𝑛, 𝑘𝑘 , 𝑛𝑛 ≥ 1, 𝑘𝑘 ≥ 2 are known to be graphs with self-similar structures and their various properties have been studied until now. It is also known that Sierpinski graphs are isomorphic to WK-recursive networks which have been proposed as interconnection networks for massively parallel computers because of their remarkable extendability. The purpose of this study is mainly to investigate their structural properties with applications to interconnection networks. In this study, we newly introduced the subdivided-line graph operation Γ and showed that 𝑆𝑆(𝑛𝑛, 𝑘𝑘) is obtained from 𝑆𝑆(𝑛𝑛 − 1,𝑘𝑘) by applying Γ. Although 𝑆𝑆(𝑛𝑛,𝑘𝑘) can be obtained by combining 𝑘𝑘 copies of 𝑆𝑆(𝑛𝑛 − 1,𝑘𝑘) based on the definition, the constructions by Γ help us to investigate structural properties of 𝑆𝑆(𝑛𝑛,𝑘𝑘) directly from those of 𝑆𝑆(𝑛𝑛 − 1,𝑘𝑘). So far, we have obtained results on structural properties of subdivided-line graphs concerning interconnection networks such as diameter, connectivity, edge-disjoint Hamiltonian cycles, several variants of dominating sets, completely independent spanning trees, and book-embeddings. Besides, we newly defined the class of universalized Sierpinski graphs apart from the class of subdivided-line graphs, and have been investigating their structural properties.
Keywords : subdivided-line graphs, universalized Sierpinski graphs E-mail: [email protected] Tel. +81-88-656-7216 Fax: +81-88-656-7216
crack Fig.1: Sierpiński graphs.
𝑆𝑆 3,3 𝑆𝑆 3,4
Fig. 2: Applications of the subdivided-line graph operation to the complete graph 𝐾𝐾4.
𝐾𝐾4
Γ(𝐾𝐾4)
Γ2(𝐾𝐾4)
Fig. 3: Universalized Sierpiński graphs.
𝐺𝐺 Υ(𝐺𝐺, 4)
-
Content: Boundary value problems of partial differential equations arise in a variety of contexts in mathematical sciences, for example, geometry, physics, mechanics, life sciences, economics and so on. In a long history of mathematical analysis, linear differential equations have been very fundamental and important in this area. Moreover, the theory of nonlinear equations is also interesting and in progress. Recently, topological and variational methods are systematically studied by many researchers and developed to a powerful tool in the theory of nonlinear partial differential equations. Our interest here is the qualitative theory of quasilinear elliptic differential equations. • Boundary value problem • Calculus of variations • Existence of solutions • Uniqueness and multiplicity of the solutions • Dependence on the parameter • Asymptotic properties • A priori estimates and regularity estimates In particular variational method is useful.
Keywords:mathematical analysis, nonlinear differential equations, boundary value problems, qualitative theory E-mail: [email protected] Fax: +81-88-656-2164
-
} : Sequence↓ ↑
F Z ∑ : Fourier series
(modular form)↓ ↑
| |: Dirichlet series(analytic continuation
and functional equation)
Find new unexpected interplay andtheir applications (complementaryeach other)
Content:
Objects
To study modular forms and its Dirichlet series. Namely, Iam interested in their interplay and applicationscomplementary each other.
Motivation
Arithmetic nature of the Fourier and Dirichlet coefficients.
Accordingly, I am interested in several aspects of modularforms.
Sales points
(1)explicit computations as far as possible
(2)use of analysis (integral transforms, special functionsand harmonic analysis) to get arithmetic consequence
(3)including higher degree case
(4) familiarity with Eisenstein series
Keywords:modular forms, Dirichlet seriesE-mail: [email protected]:http://pub2.db.tokushima-u.ac.jp/ERD/person/186508/profile-ja.html
-
Solvability of Hyperbolic Systems of Conservation Laws lecturer Kuniya Okamoto
Content: Hyperbolic systems of conservation laws described as the first order quasilinear partial differential equations have been extensively studied. The most remarkable feature is that not only this type of equations do not possess the smoothing effects but also the regularities of classical solutions will be lost in finite time even if the initial data are smooth. We introduce the notion of weak solutions which interprets the derivatives of solutions in the generalized sense, then we need to allow the presence of discontinuities in the solutions such as shock waves and discuss the solvability in the wider class. However, in contrast to the single conservation laws, the case of systems has not yet been successfully solved until recently, except for the case that the total variation of initial data is sufficiently close to the equilibrium. In terms of the interaction potential estimates of Glimm type, we study the approximate solvability of a system of conservation laws and the stability of weak solutions even if the total variations of initial data are not small for the presence of large oscillations.
Keywords:Hyperbolic systems, Conservation laws E-mail: [email protected] Tel. +81-88-656-9441 Fax: +81-88-656-9441 HP :
crack lコンタクト不良
応用確率過程� [キーワード:確率過程,最適化論] 教授 大橋 守Applied Stochastic Processes� Professor Mamoru Ohashiohbuchi_e.pdf代数曲線の射影モデル� [キーワード:代数曲線,線形系, 自己同型群] 教授 大渕 朗Projective Models of Algebraic Curves� Professor Akira Ohbuchi
ohyama_e.pdfパンルヴェ方程式の大域解析� [キーワード:古典解析学,モノドロミ、漸近解析] 教授 大山 陽介Global Asymptotics of the Painlevé equations� Professor Yousuke Ohyama
onok_e.pdf非線形現象の数理モデルと数学解析� [キーワード:非線形解析,エネルギー減衰,PDEs] 教授 小野 公輔 Mathematical Analysis of Nonlinear Phenomena� Professor Kosuke Ono
katayama_e.pdf代数体の代数構造と不定方程式� [キーワード:類数、単数、不定方程式] 教授 片山 真一Algebraic Structure of Algebraic Number Field and Diophantine Equations� Professor Shin-ichi Katayama
kuwabara_e.pdf多様体上の幾何・力学・解析構造の相互関係� [キーワード: リーマン構造,ハミルトン力学,量子力学] 教授 桑原 類史Classical and Quantum Dynamical Systems on Manifolds� Professor Ruishi Kuwabara
takahashi_e.pdf整数論と代数系の応用� [キーワード:代数体,類数,楕円曲線,暗号] 教授 高橋浩樹Applications of Number Theory and Algebraic Systems� Professor Hiroki Takahashi
takeuchi_e.pdf薬物動態解析における数値計算法の研究� [キーワード:数値解析,非線形最適化] 教授 竹内 敏己Numerical Computation for Population Pharmacokinetics� Professor Toshiki Takeuchi
murakami_e.pdf3次元Lotka-Volterra競争系の極限周期軌道� [キーワード:数理生物モデル,分岐理論] 教授 村上公一Limit Cycles for 3D Competitive Lotka-Volterra systems � Professor Kouichi Murakami
moriyasu_e.pdf微分構造と位相的性質について� [キーワード:一様・非一様双曲性,安定性,Pesin集合] 教授 守安 一峰Differential structure and topological properties� Professor Kazumine Moriyasu
uno_e.pdf曖昧性および確率的不確実性に耐えうる数理最適化�[キーワード:オペレーションズ・リサーチ(OR),ソフトコンピューティング] 准教授 宇野 剛史Mathematical Optimization with Randomness and Fuzziness� Associate Professor Takeshi Uno
ohnuma_e.pdf非線形偏微分方程式の比較原理および強比較原理� [キーワード:偏微分方程式,粘性解] 准教授 大沼 正樹A comparison principle and a strong comparison principle of nonlinear partial differential equations� Associate Professor Masaki Ohnuma
kohda_e.pdfスライド番号 1スライド番号 2
nakayama_e.pdf計算量理論� [キーワード:アルゴリズム,クラス P, クラス NP] 准教授 中山慎一Computational complexity theory� Associate Professor Shin-ichi NAKAYAMA
nabeshima_e.pdf計算機数学と代数算法の研究� [キーワード:数式処理,計算機代数,定理自動証明] 准教授 鍋島克輔 Symbolic Computation and Mathematical Softwares� A. Prof. Dr. Katsusuke Nabeshima
hasunuma_e.pdf自己相似性をもつグラフ族の生成と構造的性質の解明及び�その応用に関する研究� [キーワード:細分線グラフ,一般化シェルピンスキーグラフ] 准教授 蓮沼 徹Constructions of graphs with self-similar structures and their structural properties with applications � Associate Professor Toru Hasunuma
fukagai_e.pdf非線形楕円型方程式の定性的研究� [キーワード:数学、解析学、微分方程式論] 准教授 深貝 暢良Nonlinear partial differential equations of elliptic type: Qualitative theory� Associate Professor Nobuyoshi Fukagai
mizuno_e.pdfExplicit study of modular forms� Associate professor Yoshinori Mizuno保型形式の明示的研究� [キーワード:モジュラー形式,ディリクレ級数] 准教授 水野義紀
okamotok_e.pdfスライド番号 1スライド番号 2