PASSIVE TRANSPORT
description
Transcript of PASSIVE TRANSPORT

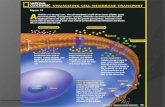
PASSIVE TRANSPORT• Movement of molecules across a
membrane that requires no energy and always occurs down a concentration gradient
• Types of passive transport include:–Diffusion–Osmosis–Facilitated diffusion

DIFFUSION• The movement of molecules from an area where
they are in high concentration to an area where the molecules are in low concentration.

Rate of diffusion depends on:• Temperature–The higher the temperature the faster the diffusion will take place.
• Size of the molecules–The smaller the molecules diffusing, the faster the molecules will diffuse

Concentration Gradient
• The difference between the concentration of a particular molecule in one area and the concentration in an adjacent area.
• Molecules move with or down the concentration gradient when moving from high to low concentration.

OSMOSIS• Diffusion of WATER across a selectively
permeable membrane, water moves down the concentration gradient.
• Selectively permeable (semi-permeable)-some substances can move through the membrane and some cannot.
• Solute-the dissolved substance in a solution (example: salt in water, the salt would be the solute)
• Solvent-the dissolving substance in a solution (ex. salt water, the water would be the solvent)



Hypertonic solution• Solution with a higher
concentration of solutes in comparison to the cell

Hypotonic solution• solution with a lower
concentration of solutes in comparison to the cell

Isotonic solution• A solution with the
same concentration of solutes the cell.
• The concentration of solutes outside the cell is equal to the concentration of solutes inside the cell.
• Water still moves into and out of the cell but at equal rates.