Passive Cooling (tropical architecture)
-
Upload
ansherinadelmundo -
Category
Education
-
view
332 -
download
3
description
Transcript of Passive Cooling (tropical architecture)

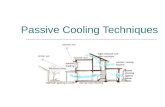
PASSIVE COOLINGPASSIVE COOLING

WHAT IS PASSIVE COOLING?WHAT IS PASSIVE COOLING? Is the least expensive means of cooling a Is the least expensive means of cooling a
home.home. Has the lowest environmental impact.Has the lowest environmental impact. Passive coolingPassive cooling maximises the efficiency maximises the efficiency
of the building envelope by minimising of the building envelope by minimising heat gain from the external environment heat gain from the external environment and facilitating heat loss to the following and facilitating heat loss to the following natural sources of cooling:natural sources of cooling:– Air movementAir movement..– Cooling breezesCooling breezes..– EvaporationEvaporation..– Earth couplingEarth coupling..

Passive coolingPassive cooling also maximises the ability of the also maximises the ability of the occupants to lose heat to natural sources of occupants to lose heat to natural sources of cooling.cooling.
Cooling requirementsCooling requirements in houses are generated in houses are generated predominantly by climate. Household activities predominantly by climate. Household activities have a lesser impact but are still important - have a lesser impact but are still important - especially during periods of "extreme" weather especially during periods of "extreme" weather conditions.conditions.
HeatHeat enters and leaves a home through the roof, enters and leaves a home through the roof, walls, windows and floor. Internal walls, doors and walls, windows and floor. Internal walls, doors and room arrangements affect heat distribution within room arrangements affect heat distribution within a home. These elements are collectively referred a home. These elements are collectively referred to as the building envelope.to as the building envelope.
Envelope designEnvelope design is the integrated design of is the integrated design of building form and materials as a total system to building form and materials as a total system to achieve optimum comfort and energy savings.achieve optimum comfort and energy savings.

ENVELOPE DESIGNENVELOPE DESIGN
GENERAL DESIGN PRINCIPLESGENERAL DESIGN PRINCIPLES– ReduceReduce or eliminate external heat gains or eliminate external heat gains
during the day with sound envelope during the day with sound envelope design.design.
– DesignDesign to allow lower night time to allow lower night time temperatures and air movement to cool temperatures and air movement to cool the building and its occupants.the building and its occupants.

The main elements of design for passive The main elements of design for passive cooling are:cooling are:
Orientation for exposure to cooling breezes.Orientation for exposure to cooling breezes. Increase natural ventilation by reducing barriers to air paths Increase natural ventilation by reducing barriers to air paths
through the building.through the building. Provision of fans to provide ventilation and air movement in the Provision of fans to provide ventilation and air movement in the
absence of breezes.absence of breezes. Floor plan zoning to maximise comfort for daytime activities and Floor plan zoning to maximise comfort for daytime activities and
sleeping comfort.sleeping comfort. Appropriate windows and glazing to minimise unwanted heat Appropriate windows and glazing to minimise unwanted heat
gains and maximise ventilation.gains and maximise ventilation. Effective shading (including planting).Effective shading (including planting). Adequate levels of appropriate insulation.Adequate levels of appropriate insulation. High thermal mass construction in regions with significant diurnal High thermal mass construction in regions with significant diurnal
ranges.ranges. Low thermal mass construction in regions with low diurnal range.Low thermal mass construction in regions with low diurnal range. Use of light coloured roofs and walls to reflect more solar radiation Use of light coloured roofs and walls to reflect more solar radiation
and reduce heat gain.and reduce heat gain.