Pascal’s triangle - A triangular arrangement of where each row corresponds to a value of n. VOCAB...
-
Upload
louisa-bradford -
Category
Documents
-
view
228 -
download
0
Transcript of Pascal’s triangle - A triangular arrangement of where each row corresponds to a value of n. VOCAB...

Pascal’s triangle - A triangular arrangement of where each row corresponds to a value of n.
VOCAB REVIEW:

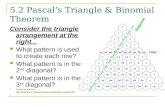
Pascal’s Triangle
This is a Pascal’s Triangle – Each row is labeled as n
• The first row is n = 0• Second is n = 1 etc…
– Each term is nCr • n is the row• r is the position in the row starting with 0
– Each term is the sum of the two directly above it.
n = 0; 20
n = 1; 21
n = 2; 22
n = 3; 23
n = 4; 24

1. The 6 members of a Model UN student club must choose 2
representatives to attend a state convention. Use Pascal’s
triangle to find the number of combinations of 2 members that
can be chosen as representatives.
2. Use Pascal’s triangle again
to find the number of combinations
of 2 members that can be chosen
if the Model UN club has 7
members.

The Binomial Theorem• Gives us the coefficients for a binomial expansion
• The values in a row of Pascal's triangle are the coefficients in a binomial expansion of the same degree as the row.
• A binomial expansion of degree n is (a + b)n.
• The variables are
anb0 + an-1b1 + … + a1bn-1 + anb0 + a0bn
Binomial Theorem

32x y
1st term
2nd term
Pascal’s #
3 2 1 02 2 2 2 x x x x
0 1 2 3 y y y y
1 3 3 1 6 4 2 2 33 3 x x y x y y
6 4 2 1 x x x
2 31 y y y
Expand a Power of a Binomial Sum

42a b
1st term
2nd term
Pascal’s #
4 3 2 1 0 a a a a a
0 1 2 3 42 2 2 2 2b b b b b
1 4 6 4 1
4 3 2 2 3 48 24 32 16a a b a b ab b
4 3 2 1 a a a a
2 3 41 2 4 8 16b b b b - -

Use the binomial theorem to write the binomial expansion.
1.
2.
53x
42 p q

3.
4.
42a b
35 2y

• Find the coefficient of in the expansion of
where rm/p
(1 ) (2 ) r n rn rC st nd
np qax by
mx
Find a Coefficient in an Expansion

• Find the coefficient of x⁴ in the expansion of (3x + 2)¹º.
n =
r =

1. Use the binomial formula to find the coefficient of the term in the expansion of
2. Find the coefficient of the x5 in the expansion of (x – 3)7?
3. Find the coefficient of the x3 in the expansion of (2x +5)8?
9q z 10
3q z
Binomial Formula
5x


12.3 An Introduction to Probability
What do you know about probability?• Probability is a number from 0 to 1 that
tells you how likely something is to happen.
• Probability can have two main approaches -experimental probability
-theoretical probability

Experimental vs.Theoretical
Experimental probability:
P(event) = number of times event occurs
total number of trials
Theoretical probability:
P(E) = number of favorable outcomes total number of possible outcomes

How can you tell which is experimental and which is theoretical probability?
Experimental:
You tossed a coin 10 times and recorded a head 3 times, a tail 7 times
P(head)= 3/10
P(tail) = 7/10
Theoretical:
Toss a coin and getting a head or a tail is 1/2.
P(head) = 1/2
P(tail) = 1/2

Experimental probability
Experimental probability is found by repeating an experiment and observing the outcomes.
P(head)= 3/10
A head shows up 3 times out of 10 trials,
P(tail) = 7/10
A tail shows up 7 times out of 10 trials

Theoretical probability
P(head) = 1/2P(tail) = 1/2Since there are only
two outcomes, you have 50/50 chance to get a head or a tail.
HEADS
TAILS

How come I never get a theoretical value in both experiments? Tom asked.
• If you repeat the experiment many times, the results will getting closer to the theoretical value.
• Law of the Large Numbers
Experimental VS. Theoretical
50
53.4
48.948.4
49.87
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
1
Thoeretical5-trial10-trial20-trial30-trial

Law of the Large Numbers 101
• The Law of Large Numbers was first published in 1713 by Jocob Bernoulli.
• It is a fundamental concept for probability and statistic.
• This Law states that as the number of trials increase, the experimental probability will get closer and closer to the theoretical probability.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Law_of_large_numbers

Contrast experimental and theoretical probability
Experimental probability is the result of an experiment.
Theoretical probability is what is expected to happen.



You must show the probability set up, the unreduced fraction,and the reduced fraction in order to receive full credit.






Geometric Probability
• Geometric probabilities are found by calculating a ratio of two side lengths, areas, or volumes according to the problem.

Find a Geometric Probability
• You throw a dart at the square board. Your dart is equally likely to hit any point inside the board. Are you more likely to get 10 points or 0? (use area)
2 5 10
0

• HW 37: pg 719, 13-43 odd








![3 Pappus’, Desargues’ and Pascal’s Theoremsmath2.uncc.edu/~frothe/3181alleuclid1_3.pdfIn Hilbert’s foundations [22], this theorem is named after Pascal. Pascal’s Pascal’s](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5ac266c87f8b9a1c768dea9e/3-pappus-desargues-and-pascals-frothe3181alleuclid13pdfin-hilberts.jpg)








