Parabolas
description
Transcript of Parabolas

ParabolParabolasas

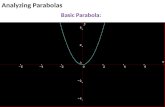
The Basic The Basic ParabolaParabola
- The parabola is a quadratic graph linking y and x2- The basic parabola is y = x2
e.g. Complete the table below by using the rule y = x2 to find and plot co-ordinates to draw the basic parabola.
x-5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5
y
-2-1
123456789
10
x y = x2
-2
-1
0
1
2
(-1)2
(-2)2
0
1
4
4
1
Note: the points of a basic parabola are easily drawn from the vertex by stepping out one and up one, then out two and up four, then out three and up nine etc...
VERTEX

Plotting PointsPlotting Points- As with straight line graphs we can use a rule to find and plot co-ordinates in order to draw any parabola.
e.g. Complete the tables below to find co-ordinates in order to plot the following parabolas:a) y = x2 – 3 b) y = x2 + 2 c) y = (x + 1)2 d) y = (x – 1)2 x y = x2 – 3 y = x2 + 2
-2
-1
0
1
2
x y = (x + 1)2
y = (x – 1)2
-2
-1
0
1
2
x-5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5
y
-4-3-2-1
12345678
(-1)2 – 3
(-2)2 – 3
-3
-2
1
1
-2 (-1)2 + 2
(-2)2 + 2
2
3
6
6
3
(-1 + 1)2
(-2 + 1)2
1
4
1
9
0 (-1 – 1)2
(-2 – 1)2
1
0
9
1
4

Transformations of the Basic Transformations of the Basic ParabolaParabola
1. Up or Down Movement- When a number is added or subtracted at the end, the basic parabola moves vertically
e.g. Draw the following parabolas:a) y = x2 b) y = x2 + 1 c) y = x2 – 5
x-5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5
y
-5-4-3-2-1
1234567
To draw vertical transformations, first find the position of the vertex Then draw in basic parabola shape

2. Left or Right Movement
- When a number is added or subtracted in the brackets, the basic parabola moves horizontally but opposite in direction
e.g. Draw the following parabolas:a) y = x2 b) y = (x + 3)2 c) y = (x – 2)2
x-5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5
y
-5-4-3-2-1
1234567
To draw horizontal transformations, first find the position of the vertex Then draw in basic parabola shape

3. Combined Movements
e.g. Draw the following parabolas:a) y = (x – 4)2 – 8 b) y = (x + 3)2 + 3 c) y = (x – 7)2 + 4 d) y = (x + 6)2 – 5
x-10 -8 -6 -4 -2 2 4 6 8 10
y
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
2
4
6
8
10
To draw combined transformations, first find the position of the vertex Then draw in basic parabola shape

Changing the Shape of the Basic Changing the Shape of the Basic ParabolaParabola
1. When x2 is multiplied by a positive number other than 1- the parabola becomes wider or narrower- Set up a table and use the rule to find and plot co-ordinates
e.g. Complete the tables and draw y = 2x2 and y = ¼x2
x y = 2x2 y = ¼x2
-2
-1
0
1
2
2 × (-1)2
2 × (-2)2
0
2
8
8
2
¼ × (-2)2
¼ × (-1)2
1
¼
0
¼ 1
x-5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5
y
-2-1
123456789
10
Use the grid to determine the x-values to put into your table

1. When x2 is multiplied by a negative number- it produces an upside down parabola- all transformations are the same as for a regular parabola
e.g. Draw the following parabolas: y = -x2
y = -(x + 2)2
y = -(x – 1)2 + 2 First find placement of the vertex
x-5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5
y
-5-4-3-2-1
12345
When plotting points move down instead of up.

Factorised Factorised ParabolasParabolasMethod 1: Set up a table, calculate and plot points
e.g. Draw the parabola y = (x – 3)(x + 1)Use the grid to determine the x-values to put into your table
x-5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5
y
-5-4-3-2-1
12345
x y = (x – 3)(x + 1)
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
(-3 – 3)(-3 + 1)12
(-2 – 3)(-2 + 1)5
0-3
-4
-3
0

Method 2: Calculating and plotting specific featurese.g. Draw the parabola y = (x – 3)(x + 1)
x-5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5
y
-5-4-3-2-1
12345
1. x-axis intercepts (where y = 0) solving quadratics: 0 = (x – 3)(x + 1)x = 3 and -1
2. y-axis intercept (where x = 0) y = (0 – 3)(0 + 1)y = -3
3. The position of the vertex- is halfway between x-axis intercepts- substitute x co-ordinate into equation to find y co-ordinate
y = (1 – 3)(1 + 1)y = -4
4. Join the points with a smooth curve
Vertex = (1, -4)

e.g. Draw the parabola y = x(x – 4)
x-8-7-6-5-4-3-2-1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
y
-9-8-7-6-5-4-3-2-1
12345678
1. x-axis intercepts 0 = x(x – 4) x = 0 and 4 2. y-axis intercept y = 0(0 – 4) y = 0 3. Position of vertex y = 2(2 – 4) y = -4 Vertex = (2, -4)
e.g. Draw the parabola y = (1 – x)(x – 5)1. x-axis intercepts 2. y-axis intercept 3. Position of vertex
0 = (1 – x)(x – 5) x = 1 and 5 y = (1 – 0)(0 – 5) y = -5 y = (1 – 3)(3 – 5) y = 4 Vertex = (3, 4)
Note: -x indicates parabola will be upside down

Expanded Form Expanded Form ParabolasParabolas
- Remember you can always set up a table and calculate co-ordinates to plot.- Or simply factorise the expression and plot specific points as shown earlier
e.g. Draw the parabolas y = x2 – 2x – 8 and y = x2 + 2x
Factorised Expression y = x(x + 2)y = (x – 4)(x + 2)
1. x-axis intercepts 2. y-axis intercept 3. Position of vertex
x = -2 and 4 y = -8 Vertex = (1, -9)
x = 0 and -2 y = 0 Vertex = (-1, -1)
x-8-7-6-5-4-3-2-1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
-10-9-8-7-6-5-4-3-2-1
12345678

Writing EquationsWriting Equations- If the parabola intercepts x-axis, you can substitute into y = (x – a)(x – b) - Or, you can substitute the vertex co-ordinates into y = (x – a)2 + b
e.g. Write equations for the following parabolas
x-5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 5
y
-5-4-3-2-1
12345
(a)
(b)
(c)
a)
c)
b)
Always substitute in the opposite sign x-value
y = (x – 2)(x – 4)or
Vertex = (3, -1)y = (x – 3)2 – 1
Vertex = (-2, 1)y = (x + 2)2 + 1
y = (x + 1)(x + 5)or
Vertex = (-3, 4)y = (x + 3)2 + 4
Add in a negative sign if parabola upside down
-
-