P1.1.4 Heating and Insulating Buildings. Specific Heat Capacity You will (hopefully) learn that: –...
-
Upload
dale-little -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of P1.1.4 Heating and Insulating Buildings. Specific Heat Capacity You will (hopefully) learn that: –...

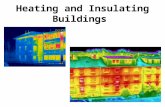
P1.1.4 Heating and Insulating Buildings

Specific Heat Capacity
• You will (hopefully) learn that:– The greater the mass of an object the more
energy is required to raise its temperature.– The material it is made from affects the amount of
energy required to heat it.– Each material has its own ‘specific heat capacity’.– Storage heaters rely on substances to store and
transfer energy.

Specific Heat Capacity (little ‘c’)
The specific heat capacity is the energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg by 1oC
E = m x c x θE = Energy transferred in Joules [J]m = mass in kilograms [kg]c = specific heat capacity [J/kg/oC]θ = change in temperature [oC]

Tasks
Answer the questions on the A5 sheet, showing all your working out. DO NOT WRITE ON THE SHEET
Look in the text book and answer the summary questions on page 39 in full sentences.

Big ‘U’
• Objectives:– To be able to describe the construction of a solar
panel.– To explain how, and why, houses are insulated and
the method by which heat transfer is reduced.– Recognise big ‘U’.– To calculate ‘payback’ time.

Answers to questions
a) 25%b)
Method of reducing energy loss
Installation cost
Saving on energy costs in one year
Number of years of saving needed to cover installation costs
A insulating the roof £320 £80 4
B fitting carpets on the floor
£600 £10 60
C fitting modern windows
£750 £25 30

Answers to questions
i) Insulating the roof because it has the shortest payback period. Ignore comments such as ‘it is the cheapest’, unless the time taken to recoup installation costs is discussed.
ii) White.iii) Walls thicker / cavity insulation / insulated / made from insulating
materialfloors thicker / made from insulating material e.g. polystyrene, wooddraught prevention /closing windows /closing doors / stop (hot) air escapingusing curtains /shutterswindows that face Sun / fewer windowsreducing temperature inside house
iv) Insulation traps air air is a bad conductor / good insulator or convection reduced in trapped air

Practicals
• Aluminium block connected to a SEP energy meter
• Model house