P ulmonary circulation. What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart ...
-
Upload
melissa-chapman -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of P ulmonary circulation. What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart ...
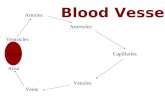
What is the cardiovascular system?
The heart is a double pump
heartarteries arterioles veinsvenules capillaries
PULMONARY CIRCULATIONWith blood returning FROM the Body TO the Heart…(via the Vena
Cava):
Right Atrium Tricuspid Valve Right Ventricle Pulmonary Semilunar
Valve Pulmonary Trunk Pulmonary Arteries (2) Alveoli in the Lungs
Capillaries in the Alveoli
ONCE BLOOD REACHES THE CAPILLARIES – GAS & NUTRIENTEXCHANGE OCCURS!
In Pulmonary Circulation, this means that Carbon Dioxide is released to the
alveoli in the lungs and Oxygen is picked up by the bloodstream.
Pulmonary Veins (4) Left Atrium Back to Systemic Circulation
REMEMBER…the Left & Right sides of the heart pump blood SIMULTANEOSLY!
4
Heart’s position in thorax• In mediastinum – behind sternum and pointing left,
lying on the diaphragm• It weighs 250-350 gm (about 1 pound)
Feel your heart beat at apex
(this is of a person lying down)
RIGHT VENTRICLE
1
23
Capillariesof right lung
3
Capillariesof left lung
4
LEFT ATRIUM5
LEFT VENTRICLE
6
Aorta
7Capillaries ofHead and arms
8
Capillaries ofabdominal organsand legs
9
Superiorvena cava
10
Inferiorvena cava
11
RIGHT ATRIUM
Pulmonaryvein
Aorta
Pulmonaryvein
Pulmonaryartery
Pulmonaryartery
Circulatory System Functions
• Carry O2 to cells and CO2 away from cells• Deliver nutrients through body (after
absorption in small intestine)• Carry liquid wastes away from cells (H2O,
salt, urea)• Help in fighting infections• Temperature regulation
1. Deoxygenated blood arrives at heart from systemic circuit:
– passes through right atrium and ventricle
– enters pulmonary trunk
Three circuits
• Pulmonary– Blood goes from heart to lungs to pick up oxygen
and release carbon dioxide
• Systemic– Blood pumped out of heart to the rest of the body– Sound of heart (lub/dub) made by valves closing
• Coronary– Heart muscle itself supplied with oxygen,
nutrients, etc.
Requirements of gas exchange
• Moist environment– O2 and CO2 must be dissolved to diffuse
– Lungs, gills, moist surface (slime) help
• Surface area--large area allows for more diffusion
• Cleaned and filtered
• Warmed
Movement of air into body
• Nose--external opening to allow entry– Air is filtered, cleaned, warmed, moistened
• Enters a series of tubes – Protected by cartilage to keep tubes firm/open– Mucus--traps foreign particles– Cilia-- “sweep” foreign material away from
lungs to be swallowed (or spit/coughed)
Diffusion of gases
• O2 concentration is higher in alveoli than blood: oxygen diffuses into blood– Remember High Conc. -> Low Conc.
• At body cells O2 concentration is higher in blood: oxygen diffuses out of blood
Oxygen Transport
• O2 diffuses from alveoli to the pulmonary capillaries.• O2-rich blood travels to heart and pumped to the body• O2 diffuses into cells. In tissues O2 levels are lower triggers
Hb to release O2
• In tissues, CO2 makes blood more acidic and causes Hb to change shape.
• CO2 diffuses from cells to blood. Travels to heart in form of Bicarbonate ions (HCO3
-)• Heart pumps blood to lungs where CO2 is released in in
gaseous form and then expelled.
Health of Respiratory System
• Colds– Caused by virus, Attacks nasal mucous membranes– Causes cells to produce histamine--eyes to tear, more mucus,
labored breathing
• Pneumonia– Caused by virus or bacteria, Inflammation of alveoli– Weak and tired due to less oxygen exchange
• Bronchitis– Caused by bacteria or virus (cold or flu), Inflammation
of bronchi– Cough to clear excess mucus
Health of Respiratory system
• Asthma– May be allergic, or response to stress, exercise,
etc.– Narrowed breathing passages (bronchi)– Treated with drugs that relax air passages
Smoking• Cigarette smoke contains
– Cyanide– Cancer-causing tar– Carbon monoxide– Radioactive materials– Nicotine
• Addictive
• Increased heart rate and narrowed blood vessels
• Cancer and smoking– Lung cancer from smoking– Mouth and throat cancers
from chewing tobacco• Other problems:
– Chronic coughing--due to paralyzed/destroyed cilia
– Emphysema--Labored breathing due to inelasticity of alveoli