Control of gonad growth, maturation and spawning in teleost fish a
OVERVIEW OF REPRODUCTION M.A.Kai-Kai. Learning Objectives. Understanding: the anatomy of the male...
-
Upload
lambert-flynn -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
4
Transcript of OVERVIEW OF REPRODUCTION M.A.Kai-Kai. Learning Objectives. Understanding: the anatomy of the male...

OVERVIEW OF OVERVIEW OF REPRODUCTIONREPRODUCTION
M.A.Kai-KaiM.A.Kai-Kai

Learning Objectives.Learning Objectives.
Understanding:Understanding: the anatomy of the the anatomy of the malemale and and female female reproductive systems reproductive systems the the gonad gonad as a as a cytogenic cytogenic and and endocrine endocrine organ.organ.the sequence of reproduction from gametogenesis in the testis the sequence of reproduction from gametogenesis in the testis and ovary to germ cells transported and fertilised in the female and ovary to germ cells transported and fertilised in the female uterine tube formation of zygote.uterine tube formation of zygote.the processes of the processes of folliculogenesis folliculogenesis and formation of the female and formation of the female gamete.gamete.spermatogenesis.spermatogenesis. fertilisation.fertilisation.

OVERVIEW OVERVIEW The GonadsThe Gonads
► MaleMale and and female female reproductive are reproductive are homologoushomologoussimilar similar embryologic origin, embryologic origin, structure and functions.structure and functions.
► Consists of gonads(Consists of gonads(testis testis and and ovaryovary) and ) and genitalgenital tubes/tubes/ductsducts..
► Paired gonads are Paired gonads are cytogeniccytogenic(gametogenesis)(gametogenesis)
and and endocrineendocrine(hormones) (hormones) ► GametogenesisGametogenesis► Genital Genital tubestubes transport transport
gametes.gametes.► Fertilisation and Fertilisation and
development of embryo development of embryo occurs in female tubes.occurs in female tubes.
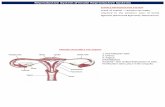
1.Developing follicles2.Mature follicle3.Mesovarium4.Uterine horn5.Blood vessels

1.1.Different partsDifferent parts of the female of the female reproductive system each with reproductive system each with specific specific functionsfunctions..►Paired Paired ovaryovary is is cytogeniccytogenic and and endocrine endocrine ►Paired Paired uterineuterine tubes tubesinfundibulum, infundibulum, ampulla and isthmusampulla and isthmustransporttransport oocytes,sperm and embryo,oocytes,sperm and embryo,►UterusUterusuterine horn,body and cervix.uterine horn,body and cervix.►Vagina, VestibuleVagina, Vestibule►External genitalia External genitalia Vulva,clotorisVulva,clotoris
2.2.Transient Transient seasonal changesseasonal changes in in structure and function.structure and function.
33 Functional sequenceFunctional sequence of the of the femalefemalegametogenesis/gametogenesis/
FolliculogenesisFolliculogenesisovulationovulationFertilisationFertilisationdevelopment.development.
44. . AgeAge changes in structure changes in structure
Uterine tubeMesosalpinx
Uterine horn
Mesometrium
IntercornualLig.
Suspensory Lig.
Suspensory ligament
Ovary
Uterine tube
Uterine horn
Bladder
Ureter
Body of uterus
Cervical canal
Vagina
Vestibular bulb
ConstrictorVestibuli muscle
Ischiourethralisand ischiocavernousmuscle
Urethral opening
Cervix
Vestibule
ClitorisFossa clitoridis
Labium
Reproductive tract of bitchOVERVIEW. The femaleOVERVIEW. The female

Descriptive TermsDescriptive TermsFemaleFemale animals can be: animals can be:► Reproductive cycleReproductive cycleanoestrus, proestrus,oestrus, anoestrus, proestrus,oestrus,
metoestrus, and dioestrusmetoestrus, and dioestrus► Ovulation(overt, cyclic)Ovulation(overt, cyclic)► Monoestrus.Monoestrus.► Polyoestrus Polyoestrus ► NulliparousNulliparous► ParousParous► MonocotousMonocotous► PolycotousPolycotous

Structure Of OvaryStructure Of Ovary

GAMETOGENESISFemaleFemaleoogenesis and oogenesis and
folliculogenesisfolliculogenesisMaleMalespermatogenesisspermatogenesisTwo phases:Two phases:► Hormone-independentHormone-independent
phasephasein foetal gonad and before in foetal gonad and before
pubertypuberty--gonocytes undergo --gonocytes undergo
mitosismitosis--primordial and primary --primordial and primary
follicles form in ovaryfollicles form in ovary--prespermatogonia form in --prespermatogonia form in
testis.testis.► Hormone-dependent Hormone-dependent
phase>phase>--begins at puberty--begins at puberty-- in ovary folliculogenesis -- in ovary folliculogenesis
and oogenesis form and oogenesis form hierarchy of hierarchy of folliclesfolliclesovulation.ovulation.
--testis--testisspermatogenesisspermatogenesis

GametogenesisGametogenesisGametogenesisGametogenesis--meiotic/reductiondivision--meiotic/reductiondivisionFirst meioticFirst meiotic division divisioncrossing crossing overover at prophase 1 between at prophase 1 between paternal and maternal paternal and maternal chromosomeschromosomesgenetic genetic variabilityvariability2 2 haploidhaploid germ cells germ cells
Second meioticSecond meiotic divisiondivisionnormal mitosisnormal mitosis4 4 haploidhaploid germ cells. germ cells.
--male germ cell undergo --male germ cell undergo morphogenesismorphogenesischange in cell change in cell morphology.morphology.
Germ cells from primordial Germ cells from primordial cellscellstwo processestwo processes
----OogenesisOogenesis in female in femaleovaova----Spermatogenesis Spermatogenesis in in malemalespermatozoaspermatozoa
MeiosisMeiosis2 divisions2 divisionsDiploidDiploid number restored at number restored at fertilisation.fertilisation.

FOLLICULOGENESISFOLLICULOGENESISFollicular HierarchyFollicular Hierarchy
Dependent on:Dependent on:
1.1.DimensionalDimensional criteria. Size criteria. Size
2.2.Morphological Morphological criteriacriteria
--thickness of the theca and --thickness of the theca and granulosa layergranulosa layer
--degree of vascularisation--degree of vascularisation
--position of antral cavities--position of antral cavities
--degree of vascularisation--degree of vascularisation
--quantity of muscle fibres and --quantity of muscle fibres and interstitial tissue.interstitial tissue.
33.Normal .Normal functionalfunctional follicles e.g. follicles e.g. corpus luteumcorpus luteum
44..AtreticAtretic follicles follicles

Follicular HierarchyFollicular Hierarchy►Primordial folliclesPrimordial follicles ►Follicular growthFollicular growth controlled Follicle Stimulating controlled Follicle Stimulating hormone(FSH) and estrogen hormone(FSH) and estrogen ►EarlyEarly Primary follicle Primary folliclelayer follicular cells.layer follicular cells.--eostrogen is mitogenic --eostrogen is mitogenic cells proliferate.cells proliferate.►Late Primary follicle.Late Primary follicle.--stratified Granulosa --stratified Granulosa --theca cells and zona pellucida(ZP) form.--theca cells and zona pellucida(ZP) form.►Secondary Follicle,Secondary Follicle, --more FSH,oestrogen receptors--more FSH,oestrogen receptors--formation of Corona radiata --formation of Corona radiata --granulosa cells secrete follicular fluid into --granulosa cells secrete follicular fluid into intercellular cleftsintercellular clefts►Graafian/preovulatory follicleGraafian/preovulatory follicledominantdominant follicles with more follicles with more FSHFSH receptors receptors --intercellular spaces coalesce into single --intercellular spaces coalesce into single antrumantrum --follicular --follicular liquorliquorcontains contains nutrientsnutrients and and hormones.hormones.----granulosagranulosa cells distributed into peripheral cells distributed into peripheral parietalparietal layer, layer,corona radiatacorona radiata and and cumulus cumulus oophorusoophorus . .--the --the CRCR support and accompany the oocyte at support and accompany the oocyte at ovulationovulation.Ovum devoid of CR do not fertilise..Ovum devoid of CR do not fertilise.

►Formation Formation and and developmentdevelopment of of ova and occurs in two stages. ova and occurs in two stages. 11. . Foetal gonadFoetal gonad, gonocytes , gonocytes undergo mitosis and induced into undergo mitosis and induced into meiosis(MIF).meiosis(MIF).--meiosis I arrested in --meiosis I arrested in prophase Iprophase I, , forms primary oocyte.forms primary oocyte.22.Puberty.Puberty-->FSH,LH,secretion -->FSH,LH,secretion leads to follicular development and leads to follicular development and oocyte maturation.oocyte maturation.----hormonal hormonal influence-->growth, influence-->growth, meiosis I and meiosis II in meiosis I and meiosis II in oocyteoocyteforms secondary oocyte.forms secondary oocyte.►folliculostatin/inhibinfolliculostatin/inhibin synchronisessynchronises events in events in ovulationovulation. . ----co-ordinatesco-ordinates growth and growth and maturation of oocyte and maturation of oocyte and granulosa cells. granulosa cells.
The OocyteThe Oocyte

OvulationOvulation► MechanismsMechanisms--hormonal--hormonal surge leads to increase in surge leads to increase in
enzyme activity; collagenaseenzyme activity; collagenase--increased intrafollicular pressure.--increased intrafollicular pressure.--neural--neural► OvulationOvulationrupture of ovarian wall rupture of ovarian wall
and follicleand folliclereleases gamete.releases gamete.► GameteGamete transported and fertilised transported and fertilised
in uterine tube.in uterine tube.► Granulosa cells and theca interna Granulosa cells and theca interna
become luteinisedbecome luteinisedform form corpuscorpus luteumluteum(CL), a transitory endocrine (CL), a transitory endocrine organ.organ.
► Luteal phaseLuteal phaseprogesterone progesterone secretion.secretion.
► Formation, maintenance and Formation, maintenance and regression of CL under regression of CL under hormonal hormonal controlcontrol..
► Life span of CL dependent on Life span of CL dependent on luterophic LH and luteolytic PG2a.luterophic LH and luteolytic PG2a.

Male Reproductive OrgansMale Reproductive Organs►Paired Paired testis testis in scrotum in scrotum ►GenitalGenital tubes tubesductuli ductuli efferensefferensepididymisepididymis
ductus deferens.ductus deferens.►Accessory Accessory sex glandssex glands,,
ampulla,vesicular,prostate, ampulla,vesicular,prostate,
Bulbouretral gland.Bulbouretral gland.►Penis.Penis.►SequenceSequence of reproduction of reproductionSpermatogenesisSpermatogenesistransporttransport
semensemenin vaginain vaginauterine uterine tubetubefertilisation at ampulla-isthmicfertilisation at ampulla-isthmic
junction. junction.

Gross structure of testis and genital ductsGross structure of testis and genital ducts
►Gross structure Gross structure
1.1.Testis Testis parenchymaparenchyma
2.2.MediastinumMediastinum(M) and rete (M) and rete testis.testis.►Genital ductsGenital ductsductuli ductuli efferentes,efferentes,
Epididymis[head(EH) body Epididymis[head(EH) body and tail(ET)].and tail(ET)].►PampiniformPampiniform plexus plexusblood blood vesselsvessels..

SpermatogenesisSpermatogenesisFunctionsFunctions::
1.1.RenewalRenewal of spermatogenic of spermatogenic stem cellstem cell
2.2.ReductionReduction of chromosome to of chromosome to haploid state by meiosis.haploid state by meiosis.
3. Metamorphogenesis of a 3. Metamorphogenesis of a convential cell into a flagella convential cell into a flagella spermatozoa.spermatozoa.MechanismMechanism::
1.1.SpermatocytogenesisSpermatocytogenesismitosis mitosis of stem cell spermatogonia A.of stem cell spermatogonia A.
2.2. MeiosisMeiosisreduction divisionreduction division
3.3.SpermiogenesisSpermiogenesismetamorphometamorphogenesisgenesis

SpermiogenesisSpermiogenesis►A process of A process of morphogenesismorphogenesis, , changing typical cell into spermatozoa changing typical cell into spermatozoa with flagella with flagella ►Consists ofConsists of
1. 1. Golgi phaseGolgi phasegolgi membrane golgi membrane forms cap over nucleus.forms cap over nucleus.
2. 2. Acrosome phaseAcrosome phaseformation of formation of Acrosome from Golgi Acrosome from Golgi
3. 3. SpermiogenesisSpermiogenesis..
Formation of flagellum.Formation of flagellum.
--organisation of contractile axoneme --organisation of contractile axoneme
--organisation of mitochondria in --organisation of mitochondria in
middle piece and principal piecemiddle piece and principal piece
--organisation of dense fibrous --organisation of dense fibrous sheath.sheath.►The The spermatozoa spermatozoa structurestructureacrosome, middle piece, acrosome, middle piece, the flagellum.the flagellum. axoneme
AX. AxonemePC. Posterior centrioleDC. Distal centriole

Hierarchy Of SpermatocytesHierarchy Of Spermatocytes

Transport of gametes,fertilisation and implantationTransport of gametes,fertilisation and implantation11.Ova ovulated from ovary, transported through uterine.Ova ovulated from ovary, transported through uterineTube.Tube.22.Sperm deposited in vagina.Sperm deposited in vaginatransportedtransportedcapacitation, acrosomecapacitation, acrosomecapacity capacity
to fertilise.to fertilise.33.Fertilisation at ampulla-isthmic junction..Fertilisation at ampulla-isthmic junction.4.4.Zygote transportedZygote transportedimplantated in endometrium.implantated in endometrium.
Fertilisation at Ampulla-isthmic junction
1
2
3 44
ovum
sperm

FertilisationFertilisationCapacitationCapacitationFertilisationFertilisation consists of:consists of:1.1.BindingBinding of sperm to zona of sperm to zona pellucidapellucida2.2.AcrosomeAcrosome reaction: reaction:3. 3. Penetration Penetration of Zona of Zona PellucidaPellucida4.4. The The cortical reactioncortical reaction ffusion of plasma membranes of sperm and egg5. 5. Sperm nucleus enters Sperm nucleus enters oocyte, forms pronucleus, oocyte, forms pronucleus, meiosis II complete.meiosis II complete.

Examples of sexual dimorphism in mammalian gametogenesisExamples of sexual dimorphism in mammalian gametogenesis
Female born with definite number of post Female born with definite number of post mitotic follicles and gametes needed in life.mitotic follicles and gametes needed in life.Meiosis begins in the fetal ovary, is arrested Meiosis begins in the fetal ovary, is arrested at prophase I and is resumed at puberty.at prophase I and is resumed at puberty.Meiosis imitated once in a definite group of Meiosis imitated once in a definite group of cellscellsDifferentiation of gametes occurs while Differentiation of gametes occurs while diploid in the first meiotic prophasediploid in the first meiotic prophaseGamete has typical cellular structure. Gamete has typical cellular structure. As well as forming a haploid nucleus, As well as forming a haploid nucleus, oogenesis builds up a store of cytoplasmic oogenesis builds up a store of cytoplasmic enzymes, mRNAs, organelles and metabolic enzymes, mRNAs, organelles and metabolic substrates. substrates. There are more variations in the mechanisms There are more variations in the mechanisms oogenesis according to patterns of oogenesis according to patterns of reproduction reproduction
Male gametes undergo mitosis Male gametes undergo mitosis throughout life, but Sertoli cells are post throughout life, but Sertoli cells are post mitoticmitoticMeiosis starts at puberty.Meiosis starts at puberty.
Meiosis initiated continuously in a Meiosis initiated continuously in a mitotically dividing stem cell population.mitotically dividing stem cell population.Differentiation of gametes occurs while Differentiation of gametes occurs while haploid after meiosis ends.haploid after meiosis ends.The spermatozoa has atypical structure.The spermatozoa has atypical structure.The spermatozoa is a motile gamete with The spermatozoa is a motile gamete with little cytoplasmic content.little cytoplasmic content.
There is less variation in the There is less variation in the mechanisms of spermatogenesis.mechanisms of spermatogenesis.

SummarySummaryThe The reproductive reproductive organs consists of paired gonads and organs consists of paired gonads and genital genital ductsducts
The gonads have The gonads have cytogeniccytogenic and endocrine functions. Germ cells undergo two meiotic and endocrine functions. Germ cells undergo two meiotic divisions by divisions by oogenesis oogenesis and spermatogenesis. The and spermatogenesis. The gametogenic gametogenic process produces process produces haploid gametes.haploid gametes.
The ovum is ovulated from the ovary and sperm is deposited in the female The ovum is ovulated from the ovary and sperm is deposited in the female reproductive tract.reproductive tract.
The gametes are transported through the genital tubes and fertilisation occurs in the The gametes are transported through the genital tubes and fertilisation occurs in the ampulla of the female. Fertilisation is marked by the fusion of the membranes of the ampulla of the female. Fertilisation is marked by the fusion of the membranes of the male and female gametes. The male and female gametes. The pronucleipronuclei from each parent fuse and the diploid state from each parent fuse and the diploid state of chromosome is restored. The of chromosome is restored. The ZygoteZygote is formed. is formed.
The zygote goes through The zygote goes through embryogenegsisembryogenegsis by the mechanisms of cleavage, by the mechanisms of cleavage, blastulation,gastrulation, neurulation and organogenesis.blastulation,gastrulation, neurulation and organogenesis.

ReferencesReferences
1. Alberts, B; Johnson, A; Lewis, J; Martin, R; Roberts, K; & Walter, P(2002).1. Alberts, B; Johnson, A; Lewis, J; Martin, R; Roberts, K; & Walter, P(2002).
The Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4The Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4thth.Edition. Garland Science Chapter 20..Edition. Garland Science Chapter 20.
2. Dyce, K; M.,Sack, W;O, & Wensing, C;J;G.(2006). 32. Dyce, K; M.,Sack, W;O, & Wensing, C;J;G.(2006). 3 rdrd. Edition. Textbook of . Edition. Textbook of Veterianry Anatomy.Pages183 – 202, 435 -453 Veterianry Anatomy.Pages183 – 202, 435 -453
3. Neill,J;D.(editor-in-Chief). Physiology of Reproduction. 33. Neill,J;D.(editor-in-Chief). Physiology of Reproduction. 3 rdrd.Edition. Elsevier. .Edition. Elsevier. London.Volume 1. Page3-113.London.Volume 1. Page3-113.