Nervous System. Organization of Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
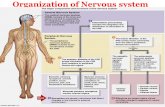
Organization of the Nervous System
description
Transcript of Organization of the Nervous System

Organization of the Nervous System
Overview of the Central (CNS),
Peripheral (PNS), Autonomic (ANS),
Enteric (ENS)Nervous Systems



Brain
• Structure– Ventricles– Meninges
• Organization• Function


Meningial Cell
• Cells that form the meningeal cell layers of the meninges covering the brain and spinal cord

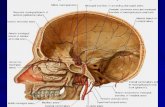
Meninges
• is a three layered covering of brain in which blood vessels travel and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is absorbed.
• Meninges means “covering”in Greek • Dura Mater: hard mother in Latin• Arachnoid Membrane: spider web like• Pia Mater : gentle mother in Latin



Dura Mater:
• tough inelastic leather-like membrane covering brain/spinal cord
• Blood vessels cross through it • Protects brain and spinal cord

Arachnoid Membrane:
• Spider-web like membrane
• Sub-arachnoid space is filled with CSF and the arachnoid villi of blood vessels of the arachnoid re-absorb the CSF

Pia Mater
• closely adheres to brain and spinal cord tissue
• Blood vessels penetrate pia to supply brain• Separated from arachnoid membrane by the
subarachnoid space

blood-brain barrier
• blood vessels have special anatomy that provides blood-brain barrier that prevents toxins, viruses and improper chemical environment from affecting brain cells.

Ventricles
• The brain is hollow, ie there are CSF-filled caverns and canals inside the brain
• Two lateral ventricles, left and right• 3rd ventricle• 4th ventricle


Ependymal Cell
• Epithelial cells that line the ventricular system
• Can also secrete CSF in some locations of the ventricles
• CSF cushions & protects brain and provides chemical environment for proper brain function


CSF
• Choroid plexus (epithelial cells) resides in 3rd & 4th ventricle and makes CSF
• Hydrocephalus (water on the brain) results from accumulation of CSF

Microglia
• Smallest glial cell• No known role in healthy nervous system\• Involved in repair of nervous system after
injury or infection• Multiply quickly, migrate to injured area
and phagocytize dead cells.• Behave like macrophages



Exam 1
• Cells: Chapter 1-Nolte-Human Brain• History: Chapter 1- Bear
• Organization of NS: Ch 7 Bear – Or
• any book on reserve has a chapter devoted to general organization