Optical Fibre & Introduction to TDM & DWDM
-
Upload
hasna-heng -
Category
Education
-
view
2.807 -
download
0
Transcript of Optical Fibre & Introduction to TDM & DWDM

MINI PROJECT PRESENTATION
Prepared By:
Hasna Heng Kamal Koh
0911796
Hasna Heng

DENSE WAVELENGTH-DIVISION MULTIPLEXING
(DWDM)
An Evolution of Optical Fiber Transmission
System
Hasna Heng

Objectives
To have a basic understanding on optical fiber
transmission system
To understand the basic principle of the DWDM
technology
Hasna Heng

OPTICAL FIBER
INTRODUCTION OF
Hasna Heng

OPTICAL FIBER
Fine threads of glass in layers
Diameter ≈ human hair
Core & Cladding + protection layers (polymers)
2 types of fiber profiles
Hasna Heng

STEPPED-INDEX FIBER
Multimode Fiber
Larger core (50-200µm)
Simultaneously transmit
numerous mode of light
1st generation system
(1975-1980)
Single-mode Fiber
Small core (<10µm)
Carries single mode of
light
Eliminate intermodal
dispersion
Hasna Heng

GRADED-INDEX FIBER
Multimode Fiber
Average velocity of all light rays approximately same
Light bent parabolic light wave
Higher bandwidth
Better compensation with dispersion
Hasna Heng

OPTICAL CARRIER
Optical Carrier Line Rate
(Mb/s)
OC-1 51.84
OC-3 155.52
OC-12 622.08
OC-48 2,488.32
OC-192 9.953.28
OC-768 39,813.12
Standardized set of
specification of Tx
bandwidth
digital signal carried
on SONET/SDH use
terms STS-n/STM-n
Optical signals: OC-n
Hasna Heng

WHY MOVE TO OPTICAL FIBER?
Expensive material
High power consumption
Large and heavy
Weak signal due to power degradation
Low signal capacity
Stealing cases
Low cost on installation
Low cost material
Lower power consumption
Smaller size & lighter
Minimize degradation of signal
Large data capacity
Expensive for construction and installation
Less flexible easily damaged
Copper Wiring Optical Fiber
Hasna Heng

RESOLVING THE BANDWIDTH DEMAND INTORDUCING TDM & WDM
Hasna Heng

40%/year
Internet growth
Statistical studies: Annual growth of the internet
= 40% !!
Upsurge of emerging services: 3G, broadband,
integrated multimedia services etc.
Network traffic became sophisticated
Increasing bandwidth demands
2 solutions:
Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM)
Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM)
Hasna Heng

Increase the bit rate
data
Increase the wavelength
TDM WDM
Input data
Arrange in sequence
Output
Input wavelength
Combine & Split
Wavelength
Output
Hasna Heng

WDM
Input Signals Output Signals
Output Signals
TDM
Input Signals
Hasna Heng

WDM Coarse WDM (CWDM)
Wide channel spacing (20nm)
Up to 16 wavelengths
Low cost
Dense WDM (DWDM)
Dense channel spacing (0.2nm)
Allows numerous wavelength transmission
simultaneously – high capacity
Hasna Heng

DENSE WAVELENGTH-DIVISION MULTIPLEXING DWDM
Hasna Heng

DWDM TECHNOLOGY Multiplex multiple signals on single optical fiber
using different wavelength
Channel signals carried by its wavelength
Using C-band (1550nm) or L-band (1625nm)
(Early development)
Hasna Heng

Hasna Heng

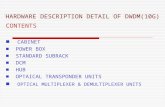
MAIN COMPONENTS IN DWDM
1. Terminal Multiplexer (MUX)
2. Intermediate Line Repeater
Optical Amplifier
Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA)
3. Optical Add/Drop Multiplexer (OADM)
4. Terminal De-multiplexer (DEMUX)
Hasna Heng

1. TERMINAL MULTIPLEXER (MUX) Transponder
O-E-O conversion
Each can convert one wavelength signal
Covert input signals into C-band laser
MUX
Combined multiple data streams into a single data
channel to be transmitted
Hasna Heng

2. INTERMEDIATE LINE REPEATER Booster for transmission signals
To overcome the issue of attenuation on a long-
haul network
Installed every 80-100km
Traditional amplifier need O-E conversion
Costly
Signal noise
Format restriction
Hasna Heng

TYPICAL OPTICAL AMPLIFIER Don’t need electrical regeneration
Independence of data format
Speed increment
Eg: Raman effect amplifier, semiconductor
optical/laser amplifier (SOA/SLA)
Hasna Heng

16 fiber pairs + 128 generators
1 fiber pair + 16 Optical Amplifier
Hasna Heng

ERBIUM-DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIER (EDFA)
Significant breakthrough for DWDM
system (1995)
Larger power output
Minimize noise factor
Operates on wide bandwidth network
No data format restriction
Hasna Heng

ENERGY-LEVEL DIAGRAM
Hasna Heng

3. OPTICAL ADD/DROP MULTIPLEXER (OADM)
aka Intermediate optical terminal
Allows wavelength to be added/dropped from the
signal as other wavelength passes through
Can substitute optical amplifier
Hasna Heng

ROADM
Disadvantages of OADM:
Inserting/replacing Wavelength-selective card manually
Costly
Optical signal interrupted
Hence Reconfigurable OADM (ROADM)
Switching wavelength configuration by remote
Efficient & cost-effective
More advanced OADM: the enhanced ROADM
(eROADM)
Hasna Heng

4. DEMUX Inverse function of
MUX
Multiple-wavelengths signals individual signals
Hasna Heng

WHY MOVE TO DWDM?
Capacity upgrade w/o adding fibers
Transparency – can carry any transmission
format
Scalability – Install additional equipment as
needed
Wavelength routing and switching – wavelength
is used as another dimension to time and space
Hasna Heng

ISSUES IN DWDM
Attenuation
Nonlinear inelastic scattering processes
Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS)
Stimulated Brillion Scattering (SBS)
Nonlinear variations in the refractive index due to
varying light intensity
Self Phase Modulation (SPM)
Cross Phase Modulation (XPM)
Four Wave Mixing (FWM)
Hasna Heng

LATEST ACHIEVEMENTS
HuaWei Global leading ICT solution provider
Pioneer in 100G DWDM
16 commercials + 50 trials of 100G networks
Recently: World’s first 400G long-haul DWDM system
(super channels)
Capacity up to 20Tbps over C-band
Transmission distance spanning 1000km w/o electrical
regeneration
Hasna Heng

CONCLUSION
DWDM plays an essential role in high capacity
optical networks
Theoretically, enormous capacity is possible
No communication system is as terrific as our
communication with our Creator, Allah the
Almighty.
No cost
No limitation
100% guaranteed !!
Hasna Heng

BIBLIOGRAPHY (n.d.). Retrieved from http://technologyinside.com/2007/03/30/making-sdh-dwdm-and-packet-
friendy/
Ciena Corporation. (1997). Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing. Natick: The Applied
Technologies Group.
Cisco Systems Inc. (2001, June 4). Introduction to DWDM Technology. Retrieved from
http://www.cisco.com/application/pdf/en/us/guest/products/ps2011/c2001/ccmigration_09186a00802
342cf.pdf
EXFO Inc. (n.d.). EXFOTube. Retrieved from www.youtube.com:
http://www.youtube.com/user/EXFOTube/
Fiber Optics For Sale Co. (n.d.). Retrieved from fiberoptics4sale:
http://www.fiberoptics4sale.com/wordpress/
Kartalopoulos, S. V. (2003). Optical Components and Optics. Retrieved from Global Spec:
http://beta.globalspec.com/reference/21551/160210/chapter-4-2-dwdm-network-topologies-review
Radmer, H. (2007). Basic DWDM Components. Retrieved from
http://www.nordu.net/development/fiber-workshop2007/Basic-DWDM-Components.pdf
Rahman, A. (n.d.). A Review of DWDM - The Heart of Optical Networks. Retrieved from
http://home.comcast.net/~dwdm2/DWDM_Review.PDF
Senior, J. M. (2009). Optical Fiber Communications - Principles and Practice (3rd ed.). Harlow:
Pearson Education Limited.
Song, S. (2001). An Overview of DWDM Networks. IEEE Canadian Review.
Hasna Heng

Hasna Heng