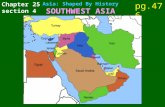
Chapter 25 section 4 Asia: Shaped By History SOUTHWEST ASIA pg.476.
Oil in Southwest Asia: How “Black Gold” Has Shaped a Region Chapter 24.
-
Upload
oliver-austin -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Oil in Southwest Asia: How “Black Gold” Has Shaped a Region Chapter 24.

Oil in Southwest Asia: How Oil in Southwest Asia: How “Black Gold” Has Shaped a “Black Gold” Has Shaped a
RegionRegion
Chapter 24Chapter 24

StandardStandard
SS7G7 The student will explain the SS7G7 The student will explain the impact of location, climate, impact of location, climate, physical characteristics, physical characteristics, distribution of natural resources, distribution of natural resources, and population distribution on and population distribution on Southwest Asia (Middle East).Southwest Asia (Middle East).

Enduring UnderstandingEnduring UnderstandingEU: Students will understand that EU: Students will understand that
location affects a society’s economy, location affects a society’s economy, culture, and development.culture, and development.

Essential QuestionEssential Question
How has the distribution of oil How has the distribution of oil affected the development of affected the development of Southwest Asia (Middle East)?Southwest Asia (Middle East)?

Note-Taking GuideNote-Taking Guide
If appropriate, students can use If appropriate, students can use the note-taking guide found in the the note-taking guide found in the Unit 4 folder to take notes on this Unit 4 folder to take notes on this presentation and discussion.presentation and discussion.

I. IntroductionI. IntroductionA.A. Southwest Asia has been transformed by oil.Southwest Asia has been transformed by oil.
1. This region has the world’s largest known oil 1. This region has the world’s largest known oil reserves.reserves.2. There are large reserves of natural gas.2. There are large reserves of natural gas.
B. Oil money has been used to better the lives of B. Oil money has been used to better the lives of the people in this region.the people in this region.1. Roads have been paved and modern 1. Roads have been paved and modern buildings have been builtbuildings have been built2. Improved medical care has helped people to 2. Improved medical care has helped people to live longerlive longer



II. Geographic SettingII. Geographic Setting
A.A. GeotermsGeoterms1. Crude oil: petroleum as it comes out of 1. Crude oil: petroleum as it comes out of the ground and before it has been the ground and before it has been refined or processed into useful productsrefined or processed into useful products2. Nonrenewable resource: a resource 2. Nonrenewable resource: a resource that takes so long to form that it can’t be that takes so long to form that it can’t be replaced. Oil, which takes millions of replaced. Oil, which takes millions of years to form, is such a resource.years to form, is such a resource.

3. Oil reserves: oil that has been 3. Oil reserves: oil that has been discovered but remains unused in the discovered but remains unused in the groundground4. Renewable resource: a resource that 4. Renewable resource: a resource that can’t be used up or that can be replaced can’t be used up or that can be replaced quickly as it is used up. Sunlight is a quickly as it is used up. Sunlight is a renewable resource that cannot be used renewable resource that cannot be used up. Wood is a renewable resource that up. Wood is a renewable resource that can be replaced by planting more trees. can be replaced by planting more trees. Sunlight, wind, water power, and Sunlight, wind, water power, and geothermal energy are additional geothermal energy are additional renewable power sources.renewable power sources.

Solar and Wind PowerSolar and Wind Power

B. Oil: Southwest Asia’s Hidden TreasureB. Oil: Southwest Asia’s Hidden Treasure1. More than half of the world’s proven 1. More than half of the world’s proven crude oil reserves lie under this region.crude oil reserves lie under this region.2. Developed countries depend on these 2. Developed countries depend on these fuels to meet their energy needs.fuels to meet their energy needs.
a. Transportation (gasoline and oil)a. Transportation (gasoline and oil)b. Electricity depends on oil and b. Electricity depends on oil and
natural natural gas to run power plantsgas to run power plantsc. Plasticsc. Plasticsd. Medicinesd. Medicines


3. S.W. Asia has grown rich, supplying the 3. S.W. Asia has grown rich, supplying the world’s oil needsworld’s oil needs4. Oil is a nonrenewable resource that will 4. Oil is a nonrenewable resource that will eventually run out.eventually run out.
C. Many Ethnic Groups, One Major ReligionC. Many Ethnic Groups, One Major Religion1. There are several ethnic groups: Arabs, 1. There are several ethnic groups: Arabs, Kurds, and PersiansKurds, and Persians2. Islam is the main religion of the region 2. Islam is the main religion of the region (Sunni, Shiite)(Sunni, Shiite)3. There is conflict among the different 3. There is conflict among the different ethnic and religions groupsethnic and religions groups

King of Saudi Arabia and Saddam King of Saudi Arabia and Saddam HusseinHussein

III. The Geology and Geography of III. The Geology and Geography of OilOil
A.A. Oil Was Formed Millions of Years AgoOil Was Formed Millions of Years Ago1. Tiny plants and animals died in the 1. Tiny plants and animals died in the oceans and sank to the ocean floor.oceans and sank to the ocean floor.2. Their remains were transformed into 2. Their remains were transformed into rock over a long period of time.rock over a long period of time.3. Weight of water, heat from the Earth’s 3. Weight of water, heat from the Earth’s core, and chemical changes transformed core, and chemical changes transformed some remains into oil and natural gas.some remains into oil and natural gas.4. Most of the oil and gas are trapped 4. Most of the oil and gas are trapped under cap rock below the Earth’s under cap rock below the Earth’s surface.surface.

Much of S.W. Asia was once under Much of S.W. Asia was once under water.water.

B. Oil Is Found in Pockets Deep in the EarthB. Oil Is Found in Pockets Deep in the Earth1. This area was once under water, 1. This area was once under water, allowing tiny animals to accumulate.allowing tiny animals to accumulate.2. Tectonic plates (Iranian Plate and 2. Tectonic plates (Iranian Plate and Arabian Plate) collided creating pockets Arabian Plate) collided creating pockets where oil formedwhere oil formed3. When drilling does not produce oil, 3. When drilling does not produce oil, petroleum engineers inject water or gases petroleum engineers inject water or gases into the well, creating more pressure to into the well, creating more pressure to force out the oil.force out the oil.4. Crude oil has to be refined to make 4. Crude oil has to be refined to make gasoline and other productsgasoline and other products


C. Oil Is Not Distributed C. Oil Is Not Distributed EquallyEqually1. Distribution of oil is 1. Distribution of oil is not even.not even.2. Saudi Arabia (the 2. Saudi Arabia (the largest country) has largest country) has approximately ¼ of approximately ¼ of the world’s known oil the world’s known oil reserves.reserves.3. Kuwait (a small 3. Kuwait (a small country) has1/10 of country) has1/10 of the world’s oil the world’s oil reserves.reserves.


IV. Oil Wealth and People’s Well-IV. Oil Wealth and People’s Well-BeingBeing
A.A. Oil Has Made Many People Better OffOil Has Made Many People Better Off1. Life expectancy has increased by 15 1. Life expectancy has increased by 15 years over the last 30 years.years over the last 30 years.2. Infant mortality rate (number of babies 2. Infant mortality rate (number of babies that die in their first year) fell.that die in their first year) fell.3. Gross domestic product (GDP): all the 3. Gross domestic product (GDP): all the goods and services produced by a goods and services produced by a country each year.country each year.

4. Per capita GDP, the average income of 4. Per capita GDP, the average income of the people in a country = GDP divided by the people in a country = GDP divided by the population, varies greatly for each the population, varies greatly for each countrycountry
a. UAE and Kuwait have high GDP a. UAE and Kuwait have high GDP and and low population numbers = high per low population numbers = high per capita GDPcapita GDP
b. Saudi Arabia and Iran have high b. Saudi Arabia and Iran have high GDP and high population numbers = GDP and high population numbers = lower per capita GDP.lower per capita GDP.

c. Bahrain has small oil reserves but c. Bahrain has small oil reserves but high per capita GDP because they high per capita GDP because they
earn earn money by the processing of money by the processing of crude oil crude oil and development of an and development of an international international banking system.banking system.
B. Per Capita GDP Does Not Tell the Whole B. Per Capita GDP Does Not Tell the Whole StoryStory1. Per capita GDP is an average wealth 1. Per capita GDP is an average wealth with some people extremely wealthy and with some people extremely wealthy and others very poorothers very poor

Poor and Poor and RichRich

2. Human Development Index (HDI) looks 2. Human Development Index (HDI) looks at the per capita GDP and factors like life at the per capita GDP and factors like life expectancy and education.expectancy and education.
a. Bahrain has the highest HDI, using a. Bahrain has the highest HDI, using its wealth to educate its population.its wealth to educate its population.b. Bahrain provides good health care b. Bahrain provides good health care which has contributed to its low infant which has contributed to its low infant mortality rate.mortality rate.

Education in Education in BahrainBahrain

C. Oil Has Not Improved Life for AllC. Oil Has Not Improved Life for All1. Yemen is one of the 20 poorest 1. Yemen is one of the 20 poorest countries in the world (low oil reserves and countries in the world (low oil reserves and large population)large population)2. Iraq has second largest oil reserve but a 2. Iraq has second largest oil reserve but a low HDI.low HDI.
a. Saddam Hussein used oil money a. Saddam Hussein used oil money for for building an armybuilding an army
b. Buying weapons and fighting wars b. Buying weapons and fighting wars has used up their moneyhas used up their money

Iraqi SoldierIraqi Soldier

V. The Price and Flow of OilV. The Price and Flow of Oil
A.A. Oil-Exporting Countries: Working to Oil-Exporting Countries: Working to Control the Price of OilControl the Price of Oil1. OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum 1. OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) was established in Exporting Countries) was established in 1960 to control the supply and income of 1960 to control the supply and income of oil producing countries.oil producing countries.
a. S.W. Asia members: Iran, Iraq, a. S.W. Asia members: Iran, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, UAE.Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, UAE.

b. Outside S.W. Asia members: b. Outside S.W. Asia members: Venezuela, Algeria, Libya, Nigeria, Venezuela, Algeria, Libya, Nigeria, IndonesiaIndonesia
c. S.W. Asia non-members: Bahrain, c. S.W. Asia non-members: Bahrain, Yemen, Oman, and SyriaYemen, Oman, and Syria2. OPEC can’t completely control oil prices and 2. OPEC can’t completely control oil prices and suppliessupplies
a. There are many non-OPEC oil a. There are many non-OPEC oil producers producers that compete with OPEC.that compete with OPEC.
b. OPEC members don’t always work b. OPEC members don’t always work together as a unit, under cutting each othertogether as a unit, under cutting each other

OPECOPEC

B. Oil-Importing Countries: Working to B. Oil-Importing Countries: Working to Protect the Flow of OilProtect the Flow of Oil1. Saddam Hussein attacked Kuwait to 1. Saddam Hussein attacked Kuwait to take over their oil fields.take over their oil fields.2. Countries who depended on oil from 2. Countries who depended on oil from Kuwait (oil importers) went to war to drive Kuwait (oil importers) went to war to drive out Iraqi forces. They feared that Hussein out Iraqi forces. They feared that Hussein would take over Saudi Arabia and cut off would take over Saudi Arabia and cut off the oil, thus damaging their economies.the oil, thus damaging their economies.


3. Oil producing 3. Oil producing (oil exporters) (oil exporters) countries also countries also feared losing feared losing control of their oil control of their oil reserves to Iraq.reserves to Iraq.4. Kuwait was 4. Kuwait was freed from Iraqi freed from Iraqi control.control.


VI. Beginning to Think GloballyVI. Beginning to Think Globally(summary)(summary)
A.A. Crude oil forms deep within Earth.Crude oil forms deep within Earth.B.B. Much of the world’s oil is under S.W. Much of the world’s oil is under S.W.
AsiaAsiaC. Oil reserves are not distributed evenly C. Oil reserves are not distributed evenly
among the region’s countriesamong the region’s countriesD. The wealth from oil sales is not evenly D. The wealth from oil sales is not evenly
distributed among the citizens of the distributed among the citizens of the countries.countries.

E. Oil is a nonrenewable resource – it will E. Oil is a nonrenewable resource – it will run out.run out.
F. Renewable resources are being F. Renewable resources are being developed.developed.

Questions to discussQuestions to discussHow does the unequal distribution of oil How does the unequal distribution of oil
affect where people live and work in the affect where people live and work in the Middle East?Middle East?
How will the diminishing supply of oil in How will the diminishing supply of oil in this region affect countries in years to this region affect countries in years to come?come?