Obturators
-
Upload
amanjot-singh -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
36 -
download
2
Transcript of Obturators

OBTURATORS

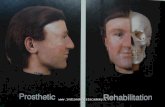
INTRODUCTION Obturator is a prosthesis used to
close a congenital or acquired tissue opening,primarily of the hard palate &/or contiguous alveolar structures.Prosthetic restoration of defect often includes use of a surgical obturator,interim obturator & definitive obturator.-GPT


USES OF OBTURATORS Provides a stable matrix for surgical
packing Reduces oral contamination Speech is effective post-operatively Permits deglutition Reduces the psychological impact of
surgery Reduce the period of hospitalization

LIMITATIONS OF OBTURATORS Require insertion and removal Have to redo periodically due to growth Can be lost or damaged May be very uncomfortable Compliance is often poor Do not permanently correct the problem Many centers use only if surgery is not
possible

DESIGN OF PROSTHESIS Must apply the basic principles of
support, retention and stability so as to minimize the stress generated to the structures of the mouth.
The location of the fulcrum line, retentive undercuts and potential for indirect retention will be important factors in determining the prognosis.
In general, the prosthesis will have a fulcrum line near the defect area.

If natural teeth or implants are present to provide retention and support for the prosthesis, the fulcrum line will pass between the most posterior occlusal rests on each side of the arch.
Retentive clasps placed into undercuts adjacent to the defect will resist the downward displacement of the prosthesis due to the effects of gravity.

Occlusal rests on the opposite side of the fulcrum line from the defect will act as indirect retainers. Long guide planes on the natural teeth will also assist in prevention of rotational dislodgment of the prosthesis.

TYPES OF OBTURATORS
1) Based on phase of treatment :-o Surgical obturators (immediate
surgical obturators & delayed surgical obturators)
o Interim obturatorso Definitive obturators

2) Based on the material used :-o Metal obturatorso Resin obturatorso Silicone obturators
3) Based on area of restoration :-o Palatal obturatoro Meatal obturators

SURGICAL OBTURATOR
Obturator on basis of phase of treatment
A temporary prosthesis used to restore the continuity of hard palate immediately after surgery or traumatic loss of a portion or all of the hard palate &/or contiguous alveolar structures like gingival tissue,teeth.-GPT
It is of two types :-
i. Immediate surgical obturator :- It is inserted at time of surgery.
ii. Delayed surgical obturator :- It is inserted 7-10 after surgery

CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS Surgical obturator is inserted on the day of
surgery. A preliminary cast is obtained before
surgery on which a mock surgery is performed.
A clear acrylic plate is fabricated & inserted after surgery.
If patient is dentulous,retention is obtained with simple clasps.

If the patient is edentulous,the obturator is wired into alveolar ridge & zygomatic arch.
The obturator is retained for 3-4 months post surgically.
It is replaced with an interim or definitive obturator after complete healing of the surgical wound.

INTERIM OBTURATOR A prosthesis that is made several weeks
or months following surgical resection of a portion of one or both maxillae.It frequently includes replacement of teeth in defect area.This prosthesis when used,replaces the surgical obturator that is placed immediately following the resection & may be subsequently replaced with a definitive obturator.-GPT

DEFINITIVE OBTURATOR
A prosthesis that artificially replaces part or all of the maxilla & the associated teeth lost due to surgery or trauma :-GPT

PALATAL OBTURATORObturator on basis of area of restoration
Closes or occludes opening caused by cleft or fistula
Used to facilitate separation of oral & nasal cavities for speech, feeding, & swallowing & hypernasality

PALATAL OBTURATORS

FABRICATION OF OBTURATOR Diagnosis & treatment planning – it is to
determine the size,location & extent of the obturator.
Preliminary impression using alginate – care should be taken to record the undercuts.The junction of graft & mucosa should be properly recorded,as it is an important retentive feature.
Fabrication of custom tray

PATIENT WITH ACQUIRED PALATAL DEFECT
PRIMARY CAST

ARAMANY’s CLASS IV DESIGN
SECONDARY IMPRESSION

Border moulding – the velo-pharyngeal extension can be recorded by asking the patient to swallow.
Final impression with elastic impression material – it can be made using alginate or elastomeric impression materials.The tray should be positioned properly & scar band area must be accurately reproduced.The elastic recoil or purse string action seen in scar band tissues is responsible for retention of obturator.If scar band is not effective,implants can be placed to improve retention.

METAL FRAME-WORK WITH WAX OCCLUSAL RIM
TEETH ARRANGEMENT IN ARTICULATOR AFTER FACEBOW TRANSFER

Jaw relation – it is very challenging to record the jaw relation for these patients.Acrylic denture bases are preferred because it is difficult to position other denture bases.
Teeth arrangement – it should be done such that balanced occlusion is obtained.
Insertion & post-insertional management

AFTER WAX BOIL OUT

THE DEFECT FILLED WITH TABLE SALT
& PACKED WITH HEAT CURE RESIN

AFTER PROCESSING,THE SALT IS POURED OUT
TO OBTAIN A HOLLOW BULB OBTURATOR


MEATAL OBTURATOR It is special type of obturator that extends up
to nasal meatus. It establishes closure with nasal structures at
a level posterior & superior to posterior border of hard palate.
The closure is established against the conchae & roof of nasal cavity.
It separates oral & nasal cavities. Indicated in patients with extensive soft
palate defects.


DISADVANTAGES OF MEATAL OBTURATORS Nasal air emission cannot
be controlled because it is in an area where there is no muscle function.
Nasal resonance will be altered.

PALATAL LIFT PROSTHESIS It is a special type of obturator,which is a
definitive prosthesis with a posterior extension.
It is helpful in restoring palato-pharyngeal incompetence where soft tissue musculature is compromised. e.g. myasthenia gravis,bulbar poliomylitis & cerebral palsy.
It is clubbed with obturator if needed.

ADVANTAGES OF PALATAL LIFT PROSTHESIS Minimized gag response Tongue physiology,swallowing,
mastication & speech are not compromised
Access to the nasopharynx for the obturator is facilitated
The palatal lift portion can be added later as desired.

CONTRAINDICATIONS FOR PALATAL LIFT PROSTHESIS If adequate retention is not
available for the basic prosthesis
If the palate is not displaceable Un-cooperative patients

REFERENCES
Sheldon Winkler, Essentials of complete denture prosthodontics (2nd edition)
Stewart,Rudd,Kuebker, Clinical removable partial prosthodontics (2nd edition)
Nallaswamy, Textbook of prosthodontics (1st edition)

THANK
YOU Presented by :-
Amanjot Singh
BDS 4th Prof.
Roll no.- 5