Obstructive Lung Diseases Dr. Raid Jastania. Respiratory System Components –Upper Respiratory...
-
date post
22-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
0
Transcript of Obstructive Lung Diseases Dr. Raid Jastania. Respiratory System Components –Upper Respiratory...

Obstructive Lung Diseases
Dr. Raid Jastania

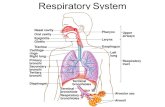
Respiratory System
• Components– Upper Respiratory tract– Lower Respiratory tract– Lungs:
• Airways
• Interstitium
• Blood vessels
– Pleura

Atelectasis


Atelectasis (Collapse)
• Atelectasis is loss of lung volume by decreased expansion of the airspaces
• Types– Resorption atelectasis (obstruction)
• Obstruction followed by resorption of air – collapse
• Causes: Post operative, Asthma, Chronic bronchitis, aspiration of foreign body, tumor

Atelectasis (Collapse)
Types:– Compression Atelectasis:
• Fluid, blood or air in the pleural cavity
– Contraction Atelectasis:• Fibrosis of lung and pleura
– Micro atelectasis:• Generalized loss of lung volume and expansion
• Loss of surfactant

Clinical Correlation• 25 year old man presented to the emergency room
with sudden, severe dyspnea. He is previously healthy, and has no previous episode of dyspnea.
• He also describes mild vague chest discomfort (pain) in the right side of the chest.
• On examination: RR is 30/minute, he has deviated trachea to the left side, decrease breathing movement of the right side, decreased vocal tactile fremitus on the right side, hyper resonance percussion on the right side, and decreased breath sound on the right side.
• X-ray shows air in the right chest with collapse of the right lung

Questions
• What is the differential diagnosis of lung collapse (atelectasis)?
• What is diagnosis in this young man?
• How do you manage his case?

Obstructive and Restrictive Lung Disease
• Obstructive: Limitation of airflow due to increase resistance– Asthma, emphysema, chronic bronchitis, bronchiolitis,
bronchiectasis, cystic fibrosis– FEV1/FVC is low
• Restrictive: Reduced expansion of the lung– Both FEV1 and FVC are low (normal ratio)– Extrapulmonary: severe obesity, kyphoscoliosis,
neuromuscular disorder– Interstitial lung disease: acute: acute respiratory distress
syndrome ARDS, pneumoconiosis, sarcoidosis, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis

• We will discuss:– Bronchial Asthma– Chronic Obstructive pulmonary disease– Emphysema– Chronic Bronchitis– Bronchiectasis

Bronchial Asthma

Bronchial Asthma
• Reversible, episodic bronchospasm
• Due to bronchial hypersensitivity to stimuli
• Persistent bronchial inflammation
• Chronic inflammatory disease of airways
• Episodic dyspnea, cough, wheeze
• 5% of adult, 7-10% of children

Bronchial Asthma
• Classified on the basis of presence or absence of immune disorder
1. Extrinsic Asthma (immune disorder)• Type I hypersensitivity• Exposure to extrinsic antigen
– Atopic: young people, severe attacks, associated with other allergies, family members involved, high eosinophils, high IgE
– Occupational– Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis

Bronchial Asthma
• Classified on the basis of presence or absence of immune disorder
2. Intrinsic Asthma (non immune)• Aspirin, infections, stress, exercise
• No family history
• No allergies
• Normal IgE

Bronchial Asthma
• Pathogenesis:– Bronchoconstriction (hyper responsiveness)– Bronchial inflammation– Type I hypersensitivity Reaction

Bronchial Asthma
• Extrinsic Asthma– Allergen – Immune response – sensitized T
cell, Th2 – Re exposure – IL-4, IL-5, IL-13 – IgE, mast cells, eosinophils – Early phase 30-60 minutes – late phase 4-8 hours
– Mast cell degranulation (primary, secondary mediators)
– Para sympathetic broncho spasm– Eosinophils

Bronchial Asthma
• Extrinsic Asthma– Early phase
• Lukotrienes C4, D4, E4: Bronchoconstriction, increase vascular permeability, increase mucin
• Prostaglandins D2, E2, F2: bronchoconstriction, vasodilatation
• Histamine: bronchospasm, increase permeability
– Late phase:• Leukotriene B4: chemotactic agent• IL-4, IL-5: enhance IgE production• TNF

Bronchial Asthma
• Extrinsic Asthma– Inflammatory cells
• Chemical mediators
• Epithelial cell injury
• Eosinophils: major basic protein, eosinophil peroxidase

Bronchial Asthma
• Intrinsic Asthma– Not well understood– ? Viral infection, inhaled pollutant– Similar to extrinsic asthma– Respiratory syncytial virus

Bronchial Asthma
• Morphology:– Hyperinflated lungs– Areas of atelectasis– Edema, hyperemia, inflammatory cells, eosinophils,
mast cells, macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells– Increase in mucus glands– Mucus plugs, Curschmann spirals– Epithelial injury and necrosis– Increase collagen (fibrosis)– Hypertrophy and hyperplasia of smooth muscle


Bronchial Asthma• Asthmatic attack • Status asthmaticus
• Wheeze, dyspnea, dry cough, tachycardia• Prolonged expiration• Use of accessory muscles• Hyperinflated chest• Severe attack: exhaustion and fear, inability to
speak, drowsiness, cyanosis, tachycardia, reduced breath sounds, “silent” chest

Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease

Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
• 10% of US adults
• 4th leading cause of death
• Definition:– Pulmonary function test: Persistent irreversible
airway obstruction– Chronic bronchitis and Emphysema: may be
pure or co-existence of both

Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
• The diagnosis is often based on three findings:
1. History of heavy smoking
2. Previous diagnosis of COPD or emphysema
3. Reduced breath sounds

Emphysema
• Permanent enlargement of airspaces distal to terminal chronchioles, with destruction of the alveolar wall
• In contrast, hyperinflation is enlargement with no destruction

Emphysema• Types:1. Centrilobular (centriacinar)
• The central part of the acini (respiratory bronchioles) is affected
• Affect upper lobes• Cigarette smoking
2. Panacinar (Panlobular)• Uniform enlargement from the level of respiratory bronchioles • Common in lower zones• Alpha1- antitrypsin deficiency
3. Paraseptal (Distal Acinar)• Distal near pleura and septae• In areas of fibrosis and scarring• Bullae formation




Emphysema• Incidence: common disease
• 50% of autopsies
• Common in heavy smokers

Emphysema• Pathogenesis
1. Protease – antiprotease imbalance
2. Oxidant – antioxidant imbalance
• Protease – antiprotease imbalance:• Like alpha1 antitrypsin deficiency
• It is enzyme in serum and macrophages
• In any inflammation there protease activity (eg. Neutrophils attracted by nicotine)
• Elastic destruction

Emphysema• Pathogenesis
1. Protease – antiprotease imbalance
2. Oxidant – antioxidant imbalance
• Oxidant – Antioxidant• Normal antioxidant: superoxide dismutase,
glutathione
• Smoke contains oxygen free radicals
• Deletion of antioxidant

Emphysema• Morphology:
– Large lung, pale– Thinning, destruction of alveolar walls– Large spaces– Airway collapse in expiration– Fibrosis (minimal) of respiratory bronchioles


Emphysema• Clinical:
– Dyspnea: progressive, pursed lip breathing, use of accessory muscles
– Weight loss– FEV1/FVC low– Barrel chest– Reduced chest expansion– Hyper resonance on percussion– Decreased breath sounds, Prolonged expiration– Gas exchange is adequate (till late in disease)– Pink Puffers– Secondary pulmonary hypertension due to
– Hypoxia-induced vascular spasm– Loss of capillaries
– Death: pulmonary failure, cor pulmonale

• Emphysema• Morphologic
definition• Acinus involved
(distal to terminal bronchioles)
• Chronic Bronchitis• Clinical definition• Involves small and
large airways

Chronic Bronchitis
• 20-25% of men 40-65 year of age
• Cigarette smokers
• Chronic bronchitis is persistent productive cough for at least 3 consecutive months in at least 2 consecutive years

Chronic Bronchitis
• Different forms
1. Simple chronic bronchitis• No airway obstruction
2. Chronic mucopurulent bronchitis• Associated with infection
3. Chronic asthmaticus bronchitis
4. Chronic obstructive bronchitis

Chronic Bronchitis
• Airflow obstruction is due to:
1. Inflammation, fibrosis, narrowing of bronchioles (chronic bronchiolitis)
2. Co-existent emphysema

Chronic Bronchitis
• Pathogenesis:• Smoking – increase mucus secretion –
inflammation – epthelial injury – metaplasia and hypertrophy of mucus glands

Chronic Bronchitis
• Morphology:• Enlarged mucus gland, endema
• Squamous metaplasia, dysplasia
• Inflammation
• Chronic bronchiolitis– Goblet cells in small bronchioles, inflammation, fibrosis,
smooth muscle hypertrophy


Chronic Bronchitis
• Clinical:– Cough and sputum
– Cyanosis, “blue bloater”
– Hyerinflated chest
– Reduced expansion
– Increased resonance on percussion
– Reduced breath sounds with end expiratory wheeze
– Right ventricular failure

Bronchiectasis

Bronchiectasis
• Bronchiectsis is permanent dilatation of bronchi and bronchioles caused by destruction of muscle and elastic tissue as a result from chronic necrotizing infection.
• It is secondary condition (not primary disease)• Diagnosed by history of persistent cough and
purulent sputum and imaging (x-ray) showing dilated bronchi and bronchioles



Bronchiectasis
• Predisposing conditions
1. Bronchial obstruction: like tumors or foreign body
2. Congenital and hereditary conditions• Cystic fibrosis, immunodeficiency, Kartagener
syndrome (autosomal recessive of abnormal cilia)
3. Necrotizing, suppurative pneumonia• Staph, Klebsiella

Bronchiectasis
• Pathogenesis• Obstruction – infection – destruction of the wall –
inflammation – fibrosis – permanent dilatation of the bronchi and bronchioles

Bronchiectasis
• Morphology:• Lower lobes bilaterally
• Acute and chronic inflammation
• Bronchial wall destruction, ulceration
• fibrosis

Bronchiectasis
• Clinical:• Fever, cachexia, sinusitis
• Persistent cough with large volume of mucopurulent, foul smelling sputum
• Clubbing of fingers
• Cyanosis if severe
• Coarse Inspiratory crackles
• Cor pulmonale

HomeworkTo be delivered in paper on 26/2/1429
• Compare between atelectasis and brochiectasis (definition, causes, clinical presentation, significance)
• List the clinical features of bronchial asthma. (presentation, symptoms and signs)
• Compare between emphysema and chronic bronchitis (definition, causes, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, and significance). What is their relation to COPD?
• What is chronic asthmatic bronchitis?