Objectives Identify that amino acids are coded by mRNA base sequences and are linked to become...
-
Upload
beverly-thomas -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Objectives Identify that amino acids are coded by mRNA base sequences and are linked to become...
Objectives
• Identify that amino acids are coded by mRNA base sequences and are linked to become proteins
• Describe how mRNA codons are translated into amino acids
• Summarize the process of protein synthesis
Review
• What was the purpose of transcription?– To transcribe (copy) DNA into a disposable copy
called mRNA to leave the nucleus.• What are the nitrogen bases of mRNA?
– A, U, G, C• What is the sugar for mRNA?
– Ribose• What are the 3 differences between DNA and
RNA?– Ribose sugar, single stranded, Uracil instead of
Thymine• What are the 3 different types of RNA?
– mRNA, rRNA, tRNA
Translation
• TRANSLATION: process that converts, or translates, an mRNA message into a protein (amino acid chain).
• How is mRNA translated??– By reading the nitrogen base sequences in
groups of 3. These groups of 3 are called Codons.
Codons
• Codon- a group of three nucleotides on mRNA that code for a particular amino acid
codon formethionine (Met)
codon forleucine (Leu)
• If you had the mRNA sequence:
UCGCACGGU
• The codons would be:
UCG CAC GGU
• What amino acids would be coded for?– Let’s find out!
Finding Amino acids from Codon
• Reading the mRNA codons left to right write the amino acid sequence of the protein translated from the mRNA.
Amino Acids• There are 64 possible three-base codons that
can be created using the four nitrogen bases (4 x 4 x 4 = 64)
• There are 20 different amino acids– There are multiple codons that code for the
same amino acids• AUG= start codon for protein synthesis or
methionine. This means that translation always begins with methionine (AUG).
• Three codons do not code for an amino acid so are considered stop codons that signals the end of an amino acid chain. - UAA, UAG, UGA
How does a cell interpret DNA?
• Write the following DNA sequence:– GAC AAG TCC ACA ATC
• Write the mRNA sequence that would be transcribed from this gene:– CUG UUC AGG UGU UAG
• Reading the mRNA codons, write the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide translated from the mRNA
• So proteins are determined by the chain of amino acids that make them up
• But how do our protein makers know which amino acids to add?
What’s Next…Translation!
– After mRNA LEAVES the NUCLEUS, it takes DNA’s message to the RIBOSOME (rRNA)
– Proteins are made on the rRNA using mRNA as a template.
– So translation occurs in the rRNA, which is located in the cytoplasm of the cell.
• Three steps to translation– Initiation– Elongation– Termination
REMEMBER: mRNA is READ 3 letters at a time in order to determine what protein is to be madeo These three letters are called a CODONCODONo The The CODONCODON on the mRNA matches up with on the mRNA matches up with
the the ANTICODONANTICODON on the on the tRNA moleculetRNA molecule
)
Initiation: The start of translation
• The small ribosomal subunit attaches to the strand of mRNA at the 5` end.
• A tRNA molecule with the start or initiator anticodon (UAC) attaches to the mRNA.
• The large ribosomal subunit attaches, locking the initiator tRNA in the P (peptide) site.
ElongationThe amino acid chain gets longer
• The second tRNA molecule, with an anticodon that is complementary to the second codon on the mRNA, attaches in the A site of the large subunit.
• A peptide bond is formed between the amino acid of the tRNA in the A site and that of the P site.
• The tRNA molecule in the P site is kicked out and the one in the A site (with the growing polypeptide chain) shifts into the P site.
• The process repeats many times until tRNA reaches a stop codon.
TerminationThe final step
• Toward the end of the coding sequence of the mRNA, a termination (stop) codon is encountered (UAG, UAA, or UGA).
• There are no tRNA molecules that match the stop codons, but a special protein called a release factor does recognize the sequence, and attaches.
• This special protein causes the newly created amino acid chain to be released.
• The ribosomal subunits disassemble.• Translation is complete!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
**Protein Synthesis in a Nutshell**
Transcription
-In NUCLEUS
-DNA copied to mRNA
-mRNA to Ribosome
Translation
-In RIBOSOME
-Codon/Anticodon pair
-codon determines what AA comes in
-AA combine-proteins
RNADNA
RNApolymerase
Adenine (DNA and RNA)Cystosine (DNA and RNA)Guanine(DNA and RNA)Thymine (DNA only)Uracil (RNA only)
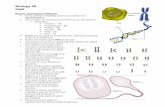
Transcription
Ribosome Translation direction
Lysine tRNA
tRNA
Growing polypeptide chain
mRNA
Ribosome
Translation Continued