Normal & Shear Stress - Chapter 1
-
Upload
ezoramajnun -
Category
Documents
-
view
236 -
download
32
description
Transcript of Normal & Shear Stress - Chapter 1

Chapter Objectives
ü Understand the concepts of normal and shear stress
ü Analyze and design of members subjected to axial load or shear
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

Equilibrium of a Deformable Body
ü External Loads
Surface & Body forces
ü Support Reactions
ü Equations of Equilibrium
ü Internal Resultant Loadings
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

External loads
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

Support Reactions
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

Equations of Equilibrium
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

Internal Resultant Loadings
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

Internal Resultant Loadings
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

READING QUIZ
1. What is the normal stress in the bar if P=10 kN and 500mm²?
a) 0.02 kPa
b) 20 Pa
c) 20 kPa
d) 200 N/mm²
e) 20 MPa
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

READING QUIZ (cont)
2. What is the average shear stress in the internal vertical surface AB (or CD), if F=20kN, and AAB=ACD=1000mm²?
a) 20 N/mm²
b) 10 N/mm²
c) 10 kPa
d) 200 kN/m²
e) 20 MPa
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

APPLICATIONS (cont)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
Will the total shear force over the anchor length be equal to the total tensile force σtensile A in the bar?

APPLICATIONS
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

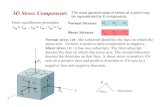
AVERAGE NORMAL STRESS
Will the total shear force over the anchor length be equal to the total tensile force σtensile A in the bar?
A
P=σ

AVERAGE SHEAR STRESS
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
A
Fz
Az
∆
∆=
→∆ 0limσ
A
F
A
F
y
Azy
x
Azx
∆
∆=
∆
∆=
→∆
→∆
0
0
lim
lim
τ
τ

EXAMPLE 1 (average normal stress)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
The bar in Fig. 1–16a has a constant width of 35 mm and a thickness of 10 mm. Determine the maximum average normal stress in the bar when it is subjected to the loading shown.

EXAMPLE 1 (cont)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
• Graphically, the normal force diagram is as shown.
• By inspection, different sections have different internal forces.
Solutions

EXAMPLE 1 (cont)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
• By inspection, the largest loading is in region BC,
• Since the cross-sectional area of the bar is constant, the largest
average normal stress is
Solutions
kN 30=BCP
( )( )( )
(Ans) MPa 7.8501.0035.0
1030 3
===A
PBCBCσ

DESIGN OF SIMPLE CONNECTION
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
• For normal force requirement
• For shear force requirement
allow
PA
σ=
allow
VA
σ=

EXAMPLE 2 (single shear stress)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
The rigid bar AB shown in Fig. 1–29a is supported by a steel rod AC having a diameter of 20 mm and an aluminum block having a cross sectional area of 1800mm2. The 18-mm-diameter pins at A and C are subjected to single shear. If the failure stress for the steel and aluminum is and respectively, and the failure shear stress for each pin is , determine the largest load P that can be applied to the bar. Apply a factor of safety of FS=2.
( ) MPa 680=failstσ
( ) MPa 70=failalσ
MPa 900=failτ

EXAMPLE 2 (cont)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
• The allowable stresses are
• There are three unknowns and we apply the equations of equilibrium,
Solutions
( )( )
( )( )
MPa 4502
900
..
MPa 352
70
..
MPa 3402
680
..
===
===
===
SF
SF
SF
fail
allow
failal
allowal
failst
allowst
ττ
σσ
σσ
( ) ( )
( ) ( ) (2) 075.02 ;0
(1) 0225.1 ;0
=−=+
=−=+
∑∑
PFM
FPM
BA
ACB

EXAMPLE 2 (cont)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
• We will now determine each value of P that creates the allowable stress in the rod, block, and pins, respectively.
• For rod AC,
• Using Eq. 1,
• For block B,
• Using Eq. 2,
Solutions
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )[ ] kN 8.10601.01034026 === πσ ACallowstAC AF
( )( )kN 171
25.1
28.106==P
( ) ( ) ( )[ ] kN 0.631018001035 66 === −BallowalB AF σ
( )( )kN 168
75.0
20.63==P

EXAMPLE 2 (cont)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
• For pin A or C,
• Using Eq. 1,
• When P reaches its smallest value (168 kN), it develops the allowable normal stress in the aluminium block. Hence,
Solutions
( ) ( )[ ] kN 5.114009.01045026 ==== πτ AFV allowAC
( )( )kN 183
25.1
25.114==P
(Ans) kN 168=P

EXAMPLE 3 (internal loadings)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

EXAMPLE 3 (cont)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

EXAMPLE 3 (cont)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

EXAMPLE 3 (cont)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

EXAMPLE 4 (double shear stress)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

EXAMPLE 4 (cont)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

EXAMPLE 4 (cont)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

EXAMPLE 4 (cont)
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

EXERCISES
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

EXERCISES
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

EXERCISES
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

EXERCISES
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

EXERCISES
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

EXERCISES
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd

CONCEPT QUIZ
1) The thrust bearing is subjected to the loads as shown. Determine the order of average normal stress developed on cross section through BC and D.
a) C > B > D
b) C > D > B
c) B > C > D
d) D > B > C
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd