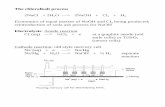
Net Ionic equations §A solution of Barium Chloride reacts with a solution of sodium sulfate §BaCl...
-
Upload
leslie-reed -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
0
Transcript of Net Ionic equations §A solution of Barium Chloride reacts with a solution of sodium sulfate §BaCl...
Net Ionic equationsA solution of Barium Chloride reacts with a
solution of sodium sulfateBaCl2 + Na2SO4 →
BaCl2 + Na2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2NaCl
Ba2+ + 2Cl1- + 2Na1+ + SO42- → BaSO4 + 2Na1+
2Cl1-
Ba2+ + 2Cl1- + 2Na1+ + SO42- → BaSO4 + 2Na1+
2Cl1-
Ba2+ + SO42- → BaSO4
Using Stoichiometry in the LaboratoryUsing Stoichiometry in the Laboratory
Na2SO3(aq) + 2AgNO3(aq) Ag2SO3(s) + 2NaNO3(aq)
20 ml 20 ml0.12 M 0.35 M
1. How many grams of silver sulfite would be produced?2. What would be the molarity of the sodium nitrate?3.What volume of silver nitrate is needed to completely
precipitate all of the sulfite ions.
Patterns of ReactivitySubstance + Oxygen gas Oxide of element
Active metals and oxygen: Li(s) + O2 Li2O(s)
sulfides and oxygen: ZnS(s) + O2 ZnO + SO2(g)
CS2(s) + O2 CO2(g) + SO2
ammonia and oxygen: NH3 + O2 NO2 + H2O(g)
Substances reacting with water
Metallic oxide reacting with water BaseLi2O + HOH Li+ + OH-
MgO (s) + HOH Mg(OH)2
Metal hydrides reacting with water Base + Hydrogen
LiH(s) + HOH Li+ + OH- + H2
CaH2 (s) + HOH Ca2+ + OH- + H2
Nonmetal halides reacting with water weak acid + strong acid (Keep ox # the same)PCl5 (s) + H2O H3PO4(aq) + H+ + Cl-
PBr3 (s) + H2O H3PO3(aq) + H+ + Br-
Nonmetal oxide reacting with water Acid (Keep ox # the same)
SO2(g) + H2O H2SO3(aq)
N2O5 + H2O H+ + NO31-
SO3 + H2O H+ + HSO4-
N2O3 + H2O HNO2(aq)
Hydrocarbon and oxygen: CH3OH(s) + O2 CO2 + H2O
Substances reacting with nonmetal oxide salt
Metal oxide and nonmetal oxide yields a saltCaO(s) + CO2 CaCO3(s)
MgO(s) + SO2 MgSO3
Base reacting with nonmetal oxide:OH- +CO2(g) CO3
2- +H2O (base is aqueous)
NaOH(aq) + CO2(g) Na+ + HCO3- + H2O
Ca(OH)2 (aq) + SO2(g) Ca+ + HSO3- + H2O
Ca(OH)2 (s) + SO2(g) CaSO3(s) + H2O
Metal carbides reacting with water Base + hydrocarbon
Na2C2(s) + H2O Na+ + OH- + C2H2
Salt of an amphoteric metal reacting with water complex
Al(NO3)3(s) + H2O Al(H2O)63+ + NO3
-
Substances reacting with an acidmetals reacting with acid salt + hydrogen
Zn(s) + H+ Zn2+ + H2
Cu(s) + H+ + HSO4- Cu2+ + SO2 + H2O (hot
conc. sulfuric acid)
Ca(s) + H+ Ca2+ + H2 (cold sulfuric acid)
Ag(s) + H+ + NO3- Ag+ + NO + H2O
(dilute (6M) nitric acid)
Ag(s) + H+ + NO3- Ag+ + NO2 + H2O (conc. nitric acid)
metal oxide reacting with hydrogen gas salt + water
FeO(s) + H+ + NO3- Fe3+ + NO2 + H2O
(conc. nitric acid)
metal oxide reacting with acid salt + gas + water
Fe2O3(s) + H2 Fe + H2O
Salt of a weak acid and strong acid salt of strong acid + weak acid
C2H3O2- + H+ HC2H3O2
C2H3O2- + H+ + HSO4
- HC2H3O2 + HSO4-
(equimolar sulfuric acid)
SO22- + H+ H2SO3 H2O + SO2
Na2S(s) + H+ Na+ + Cl- + H2S
Substances reacting with an Base
Al and Zn hydroxides with a strong base
Al(OH)3 + OH- [Al(OH)6]3-
Zn(OH)2 + OH- [Zn(OH)4]2-
salt of an amphoteric metal reacting with a strong acid
salt of a weak acid reacting with a strong baseNH4Cl + OH- NH3(g) + H2O + Cl-
HCO3- + OH- CO3
-2 (g) + H2O
Al(OH)3 + H+ Al3+ + H2O
Complex ions
Zn2+ + NH3(excess) [Zn(NH3)4]2+
Zn(OH)2(s) + NH3(ex) [Zn(NH3)4]2+ + OH-
Ag+1 + NH3(excess) [Ag(NH3)2] +
Cu(OH)2 + NH3(ex) [Cu(NH3)4]2+ + OH-
Fe+3 + NCS1- → FeNCS2+
orange/brown blood red
Oxidation-Reduction
Single Replacement (metals)
Al(s) + Cu2+ (aq) Cu(s) + Al3+ (aq)
Zn(s) + Sn2+ (aq) Sn(s) + Zn2+ (aq)
H2(g) + CuO(s) Cu(s) + H2O (aq)
Single Replacement (halogens)
F2(g) + Cl- (aq) Cl2(g) + F- (aq)
Oxidation-Reduction
Redox in an Acid Environment
Cr2O72- + Fe2+ + H+ Cr3+ + Fe3+ + H2O
Cr2O72- + I- + H+ Cr3+ + I2
+ H2O
MnO4- + Cl- + H+ Mn2+ + Cl2
+ H2O
H2O2 + I- + H+ H2O + I2 + H2O
Oxidation-Reduction
Important Oxidizers
MnO4- in acidic solution
Mn2+
Formed in the Reaction
MnO2 in acidic solution
Mn2+
MnO4- in basic solution
MnO2
Cr2O72- in acidic solution
Cr3+
HNO3, concentrated
NO2
HNO3, dilute NO
H2SO4, hot SO2
Oxidation-Reduction
Important Oxidizers Formed in the Reaction
Metal-ic ions Metal-ous ions
Free halogens halide ionsNa2O2 NaOH
HClO4 Cl-
H2O2 (in acidic sol’n)
H2O
H2O2 (in basic sol’n)
OH-
Important Reducers Formed in the Reaction
Halide ions Free halogens
Oxidation-Reduction
Free metals Metal ions
Sulfite ions (or SO2)
Sulfate ions
Nitrite ions
Nitrate ions Free Halogens (dil., basic)
Hypohalides (e.g. ClO-) Free Halogens (conc., basic) Halate ions (e.g. ClO3
-) Metal-ous Metal-ic
H2O2 O2
































![Cleaner Tannery Wastewater Using Chemical Coagulants · titration (Argentometria) [15]. Sulfate analysis was performed by precipitation with BaCl 2 to filtered effluent [15]. H2S](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5ba128d409d3f26b6b8bc057/cleaner-tannery-wastewater-using-chemical-coagulants-titration-argentometria.jpg)






