NERVOUS TISSUE Forms the nervous system which is divided into: Forms the nervous system which is...
-
Upload
lesley-rich -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of NERVOUS TISSUE Forms the nervous system which is divided into: Forms the nervous system which is...

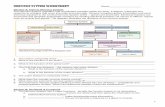
NERVOUS TISSUENERVOUS TISSUE Forms the nervous system which is Forms the nervous system which is
divided into:divided into:– Central Nervous System (CNS):Central Nervous System (CNS):
» BrainBrain
» Spinal cordSpinal cord
– Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):» Cranial nervesCranial nerves
» Spinal nervesSpinal nerves
Neurons (nerve cells): The units of Neurons (nerve cells): The units of nervous tissue. They nervous tissue. They receive and receive and transmit impulses.transmit impulses.
Neuroglial Neuroglial cellscells: : do not receive or do not receive or transmit impulses; instead, they transmit impulses; instead, they support neurons.support neurons.

NEURONSNEURONS
The units of nervous The units of nervous tissue. They tissue. They receive and receive and transmit nerve impulses transmit nerve impulses to & from the CNS.to & from the CNS.
A neuron = nerve cell A neuron = nerve cell body + all its processes:body + all its processes:– One axon.One axon.– One or more dendrites.One or more dendrites.

Types of NeuronsTypes of Neurons
Unipolar.Unipolar. Bipolar.Bipolar. Multipolar.Multipolar.

Unipolar NeuronsUnipolar Neurons
Formerly called Formerly called pseudounipolar.pseudounipolar.
Only one process that Only one process that divides into a divides into a peripheral branch peripheral branch (dendrite) and a (dendrite) and a central branch (axon). central branch (axon).
Present in the dorsal Present in the dorsal root ganglia of spinal root ganglia of spinal nerves.nerves.

Bipolar NeuronsBipolar Neurons
Two processes: Two processes: a single a single dendrite and a dendrite and a single axon.single axon.
Present in:Present in:– Nasal cavity Nasal cavity
(olfactory (olfactory epithelium).epithelium).
– Inner ear.Inner ear.– Retina.Retina.

Multipolar NeuronsMultipolar Neurons The most common type.The most common type. Multiple dendrites and a Multiple dendrites and a
single axon.single axon. Present throughout the Present throughout the
nervous system: e.g.nervous system: e.g.– Stellate cells: motor Stellate cells: motor
neurons in spinal cord.neurons in spinal cord.– Pyramidal cells: in Pyramidal cells: in
cerebral cortex.cerebral cortex.– Purkinje cells: in Purkinje cells: in
cerebellum.cerebellum.

Nerve Cell BodyNerve Cell Body
Nucleus: Nucleus: spherical, spherical, central with prominent central with prominent nucleolus.nucleolus.
Cytoplasm:Cytoplasm:– Abundant rER & Abundant rER &
polyribosomes.polyribosomes.– Prominent Golgi.Prominent Golgi.– Many mitochondria.Many mitochondria.– Only 1 centriole.Only 1 centriole.– Microtubules, Microtubules,
neurofilaments.neurofilaments.
Nissl Nissl bodiesbodies

Nerve Cell ProcessesNerve Cell Processes
Dendrites Axon
One or more processes. Single thin long process.
Wide base, tapering tip. Same diameter in any of its parts.
Give many branches. Few collateral branches.Ends by terminal arborizations.
Contain mitochondria, neurofilaments and Nissl bodies.
Contains mitochondria, neurofilaments but no Nissl bodies.
Carry impulse toward cell body. Carry impulse away from cell body.

Nerve FibersNerve Fibers
A nerve fiber = any long process of a nerve A nerve fiber = any long process of a nerve cell (axon or dendrite).cell (axon or dendrite).
Types of nerve fibers:Types of nerve fibers:– Myelinated:Myelinated:
» Covered by myelin sheath formed by Schwann cells Covered by myelin sheath formed by Schwann cells in PNS and oligodendrocytes in CNS.in PNS and oligodendrocytes in CNS.
» In white matter of CNS and all peripheral nerves.In white matter of CNS and all peripheral nerves.
– Unmyelinated:Unmyelinated:» Not covered by myelin sheath.Not covered by myelin sheath.» In grey matter of CNS and terminal parts of all In grey matter of CNS and terminal parts of all
peripheral nerve fibers.peripheral nerve fibers.

Peripheral Nerve TrunkPeripheral Nerve Trunk The whole nerve is The whole nerve is
covered by a C.T. covered by a C.T. covering, the covering, the epineuriumepineurium..
Consists of parallel Consists of parallel myelinated nerve fibersmyelinated nerve fibers, , arranged in bundles, arranged in bundles, separated by C.T. separated by C.T. septa, the septa, the perineuriumperineurium..
The individual nerve The individual nerve fibers are separated by fibers are separated by C.T., C.T., endoneuriumendoneurium..
Epineurium
Perineurium
Endoneurium

NEUROGLIAL CELLSNEUROGLIAL CELLS Supportive and protective to Supportive and protective to
neurons. They do not receive neurons. They do not receive or transmit nerve impulses.or transmit nerve impulses.
All are present in CNS except All are present in CNS except Schwann cell (in PNS).Schwann cell (in PNS).
Types:Types:– Astrocytes: nutritive function.Astrocytes: nutritive function.– Oligodendrocytes: formation of Oligodendrocytes: formation of
myelin in CNS.myelin in CNS.– Microglia: phagocytic (defence).Microglia: phagocytic (defence).– Schwann cells: formation of Schwann cells: formation of
myelin in PNS.myelin in PNS.