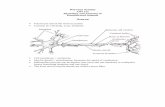
Nervous System. Parts of the Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Nerves.
Nervous System Chapter 14 Medical Terminology. Nervous System System of conducting tissues (nerves)...
-
Upload
clifford-pressman -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of Nervous System Chapter 14 Medical Terminology. Nervous System System of conducting tissues (nerves)...

Nervous System
Chapter 14
Medical Terminology

Nervous System
• System of conducting tissues (nerves) that receive information from the environment and control both voluntary and involuntary functions of the body and consciousness

Cellular Anatomy
• Two types of cells:– Neurons
• Transmit impulses (conduct)– Sensory neurons (afferent)
– Motor neurons (efferent)
– Mixed (both afferent and efferent)
– Neuroglia• Supporting cells

Neurons: Structure
• Cell body– Nucleus, cytoplasm, organelles
• Dendrites– Projections of the cell body– Receive and carry impulses
• Axons– Single, long projections from cell body– Also transmit impulses

Neurons: Structures
• Myelin sheath– Covering outer layer of axon– Lipid layer– White color– Makes up the white matter in CNS– Acts as an insulator – Speeds up impulse transmission in the axon

More about myelin
• Unmyelinated structures– Appear gray, gray matter– CNS and spinal column
• Peripheral nerve (PNS)– Schwann cell = myelin sheath– Neurilemma/neurolemma = this thin layer– Node of Ranvier = space between Schwann
cells

Neurons: Other terms
• Synapse– Space between neurons– Between axon terminal and dendrites of
adjacent neurons
• Axon terminal
• Neurotransmitter

Neuroglia: Four Types
Astrocytes
star shaped support cells for neurons
form capillary sheaths (BBB)
Oligodentrocytes
help in CNS myelin development
Microglia:
phagocytes

Neuroglia: Four Types
• Ependyma– Ciliated cells– Line cavities in CNS (ventricles)– Help CSF circulation

Nervous System Anatomy
• Central Nervous System (CNS)– Brain– Spinal Cord
• Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)– 12 pairs of cranial nerves (CN I-XII)
• From basilar surface of brain
– 31 pairs of spinal nerves• From spinal cord

CNS Anatomy: Brain
Meninges
three protective membranes around CNS
Cerebrum
corpus callosum
structures connecting hemispheres
gyri (gyrus) = folds or convolutions
sulci (sulcus) =fissues, furrows

CNS Anatomy: Brain
• Lobes of the brain:– Frontal– Parietal– Temporal– Occipital– Insula

Brain Anatomy
• Cerebral Cortex– Thin outer layer– Gray matter due to millions of cell bodies– Rest of cerebrum is myelinated axons (white)
• Cerebrum: Functions– Sensory perception, interpretation– Voluntary movement, language, memory– Emotional aspects of behavior

Other Structures in the Brain:
• Cerebellum– Posterior aspect– Coordinates and refines movement– Balance and equilibrium

Other Brain Structures
• Diencephalon (interbrain)– Thalamus
• Receives & transmits all sensory info except smell to the cerebrum
• Transmits impulses from cerebrum to efferents
– Hypothalamus• Coordinates autonomic impulses• Temperature regulation• Control of endocrine system

Other Brain Structures:
• Brainstem: control of respiration, cardiac activity
• Pathway between brain and spinal column– Midbrain (mesencephalon)– Medulla (oblongata)– pons

CNS structures: Spinal Cord
• Ascending tracts– Bring sensory input to CNS
• Descending tracts– Send impulses to muscles, end organs
• Cross-section:– Gray matter-inner part of cord– White matter—outer part of cord
• Spinal cavity– Spinal nerves exit from intervertebral spaces– Cauda equina

CNS: Meninges
• Dura– Outermost, very fibrous– Subdural space: filled with serous fluid
• Arachnoid– Thinner, looks like a spider web– Subarachnoid space: contains CSF
• Pia– Innermost layer, also thin– Contains blood vessels and lymphatics

Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
• Cranial Nerves
• Spinal Nerves
• Somatic Nervous system (SNS)
• Autonomic Nervous system (ANS)

PNS: Cranial Nerves
• Exit mostly from base of the brain
• Named and denoted by I through XII
• Mostly involve facial, eye, mouth movement and sensation and the special senses of hearing, taste, sight
• Are afferent, efferent, and mixed nerves

PNS: Spinal Nerves
• Exit from spinal cord and go to muscles and organs
• Each has two attachments to spinal cord:– Anterior root: motor fibers– Posterior root: sensory fibers

Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
• Voluntary functions
• Mostly supplies skeletal muscles

Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
• Supplies nerves (ennervates) involuntary functions
• Ennervates glands, smooth & cardiac muscles, etc
• Sympathetic system– Fight or flight
• Parasympathetic system– Functions that are the opposite, resting

Medical Word Elements
• Cerebro: cerebrum
• Cranio: cranium or skull
• Encephalo: brain
• Kinesio: movement
• Ganglio: knot or mass (a ganglion)
• Narco: sleep, stupor
• Neuro: nerve

Medical word elements:
• Radiculo: nerve root (radiculopathy)
• Theco: sheath (intrathecal)
• Tono: tension (tonometry, dystonic)

Medical Word Elements
• Others are from anatomic structure names
• Ventriculo: ventricles
• Thalamo: thalamus
• Myelo: spinal cord or bone marrow
• Meningo: meninges
• Glio: neuroglial tissue
• Dentro: treee-like

Suffixes: Neuro
• -algia or algesia: pain
• -asthenia or –paresis: weakness, disability
• -esthesia: feeling
• -kinesia: movement
• -lepsy: seizure (epilepsy, narcolepsy)
• -phasia: speech
• -plegia: paralysis

Suffixes: Neuro
• -plexy: stroke
• -taxia: coordination (ataxia)
• -trophy: development

Prefixes: Neuro
• Contra- = against/opposite
• Pachy- = thick
• Para- = near
• Syn- = together, joined

Neurological Pathology
• Common symptoms:– Pain (head, neck, back, periphery)
– Abnormal movements
– Gait abnormalities
– Disturbances of special senses
– Speech abnormalities
– Altered level of consciousness
– Focal weakness
– seizures

Bell’s Palsy
• Facial paralysis (unilateral usually))
• Involves CN VII
• Herpes viral infection
• Usually transient
• Facial weakness and numbness, problems with blink reflex and speech

Cerebrovascular Disease
• Cerebrovascular accident (CVA) or stroke– Focal loss of function due to loss of blood
supply– Lasts more than 24 hours– Causes:
• Ischemic: due to thrombus or carotid emboli (75%)
• Hemorrhagic (25%)
• Extrinsic compression of blood vessel (rare)

Cerebrovascular Disease
• Typical CVA symptoms:
• Anterior stroke:– Hemiparesis or hemiplegia– Aphasia or dysphasia– Partial loss vision/ visual field
• Posterior stroke:– Balance problems, ataxia, vertigo

Cerebrovascular Disease
• Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)– Focal symptoms like a CVA, lasting less than
24 hours– Typical symptoms: weakness or clumsiness of
upper extremity, visual field loss, hemiparesis of the face, paresthesias of upper extremities
– Indicates risk of CVA within next year

Seizure Disorders
• Nerve conduction dysrhythmias
• Epilepsy = chronic seizure disorder
• Generalized Sz (gran mal, tonic clonic)– Movements of entire body– unconsciousness
• Partial Sz (focal) (Jacksonian)
• Petit mal (absence Sz)

Seizure Disorders: Causes
• Congenital anomalies
• Brain injury
• Metabolic disease
• Brain tumors
• Genetic disorders
• Vascular anomalies

Seizures:
• Are often the symptom of the disease
• Status epilepticus– Life-threatening– Lengthy or muliple Sz
• Electroencephalography
• Magnetoencephalography
• Rx: antiepileptic meds

Parkinson Disease
• Parkinsonism also
• A movement disorder
• Progressive neurological disease affected the movement control centers of the brain
• Deficiency of dopamine, a neurotransmitter in the brain
• Rx: L-dopa administration

Parkinson Disease
• Symptoms:
• Bradykinesia or hypokinesia
• Uncontrollable shaking of head
• Shuffling gait, pill rolling of fingers
• Tremors
• Some stiffness,
• Mask-like facial expressions

Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
• Progressive demyelinating disease of CNS
• Impeding nerve conduction
• Disease of young adults, usually females
• Autoimmune disease suspected, fatal
• Symptoms:– Tremors, bradykinesias– Visual disturbances, muscle weakness

Alzheimer Disease
• Progressive, fatal neurological degenerative disease of the elderly
• Memory loss, cognitive dysfunction, anxiety, decline in social skills and ADL
• Plaques develop in cerebral cortex
• Common cause of senile dementia in US
• Some medications slow progress of disease

Mental Illnesses
• Alterations in behavior, mood, thought
• Some general terminology:– Phobia– Delusion– Hallucinations– Obsessive compulsive disorders (OCD)– Psychiatrist or clinical psychologist

Categories of Mental Illnesses
• Affective (mood) disorders– Mania– Depression– Manic-depressive disorder (bipolar disorder)
• Eating disorders– Anorexia nervosa– Bulimia nervosa

Categories of Mental Illnesses
• Anxiety disorders
• Panic attacks
• Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
• Schizophrenia (thought disorder)

Neuro Oncology
• Most intracranial neoplasms are primary brain tumors
• Papilledema = classic sign of intracranial tumor, slowly rising ICP
• Metastatic tumors to brain– Fairly common, slower growing than their
primary tumors, more easily resected than primary CNS tumors

Neuro Infections
• Meningitis– Bacterial = most rapid, meningococcal– Viral or fungal
• Encephalitis– Usually viral
• Brain or Spinal Cord abscesses– Usually bacterial– Parasitic also possible

Intracranial Hemorrhages
• Epidural hemorrhage
• Subdural hemorrhage
• Subarachnoid hemorrhage
• Intracerebral hemorrhage

Epidural Hemorrhage
• Arterial bleeding
• Often involves parietal skull fracture
• Disrupts the middle meningeal artery
• Famous “lucid interval” symptoms
• Usual symptoms: headache, unconsciousness, unilateral weakness or abnormal reflexes

Subdural Hemorrhage
• Venous bleeding from the bridging veins
• Slower bleed
• Symptoms: similar to EDH but no lucid interval

Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
• Thin filmy layer of blood around the brain and cord
• May be spontaneous or due to trauma• Symptoms and Signs:
– “the worst headache of my life”– Sudden onset– Nuchal rigidity– Photophobia, nausea, vomiting

Intracerebral Hemorrhage
• May also be spontaneous or traumatic
• Hemorrhage is deep in the CNS tissue
• Creates raised intracranial pressure (ICP) due to space-occupying mass
• Like all of these bleeds, may cause herniation.

Diagnostic & Symptomatic Terms
• Agnosia = inability to process sensory input
• Aura
• Autism = withdrawal, inability to communicate
• Cerebral palsy = developmental defects in brain or birth trauma to brain
• Closed head injury

Diagnostic & Symptomatic Terms
• Coma• Concussion• Dementia• Dyslexia: inability to learn/process written
language• Guillain-Barre Syndrome• Huntington Chorea: inherited movement
disorder (also speech & mental symptoms)

Diagnostic & Symptomatic Terms
• Hydrocephalus
• Lethargy
• Neurosis
• Psychosis
• Spina bifida/ occulta
• Meningocele
• myelomeningocele

Diagnostic & Symptomatic Terms
• Paraplegia / quadriplegia
• Paresthesia
• Poliomyelitis
• Reye Syndrome
• Sciatica
• Syncope

Diagnostic Procedures
• Electroencephalography (EEG)• Electromyography (EMG)• Lumbar puncture (LP)• Nerve conduction velocity (NVC)• CSF analysis
– Glucose concentration– Types of blood or other cells present– Culture to grow bacteria

Diagnostic Procedures
• Cerebral angiography
• Myelography
• Scans: CT, MRI, PET

Pharmacology
• Analgesics
• Anesthetics– Local & general
• Anticonvulsants– Tegretol, Depakote, Lamictal
• Antiparkinsonian drugs– Levodopa, Sinemet

Pharmacology
• Hypnotics (sedate)– Barbiturates and valium derivatives
• Antipsychotics– Haldol, Zyprexia, etc
• Antidepressants– Paxil, Prozac, TCA’s
• Psychostimulants– Ritalin