Neck pain after trauma
-
Upload
radrounds-radiology-network -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Neck pain after trauma
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
1/18
Neck pain after trauma
Laura Avery, MDMassachusetts General Hospital
Harvard Medical School
Boston, MA, USA
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
2/18
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
3/18
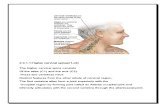
What is wrong?
Did you look at your lines?
Which lines you ask?
anterior spinal line
posterior spinal line
spinolaminar line
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
4/18
Anterior listhesis
Of C2 on C3
Posterior displacement of
Posterior elements of C2,
Note disruption of spinolaminar
line
Spinolaminar line
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
5/18
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
6/18
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
7/18
pars interarticularis
Superior articular facet
Of C2
Inferior articular facet of C2
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
8/18
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
9/18
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
10/18
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
11/18
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
12/18
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
13/18
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
14/18
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
15/18
Hangman's frx / Traumatic
Spondylolisthesis of the Axis frx ofpars interarticularis ofC2 & disruption of C2-C3 junction
- type of traumatic spondylolisthesis - "Hangman's frx"- term "hangman's fracture" is not accurate for the majority of cases,
because mechanism of injury for clinically encountered frxs often lacks largetraction force present in judicial hangings;
- in cases in which there is neurologic injury, there will usually besignificant horizontal translation w/ accompanying damage to the posteriorlongitudinal ligament w/ or w/o damage of the C2-C3 interspace; - mechanism of injury in adults:
- judical lesion: hyperextension and distraction;- hyperextension w/ vertical compression ofposterior column, &
translation ofC2 and C3;- forceful extension of already extended neck is most commonly
described mech of injury, but other causes include
flexion of flexed neck & compression of an extended neck;- a blow on the forehead forcing the neck into extension is a classicmechanism of injury producing fractures thru the pedicles
ofC2 known as traumatic spondyloslisthesis ofC2;
http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/anatomy_of_the_axishttp://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/posterior_columnhttp://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/anatomy_of_the_axishttp://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/anatomy_of_the_axishttp://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/anatomy_of_the_axishttp://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/anatomy_of_the_axishttp://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/anatomy_of_the_axishttp://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/anatomy_of_the_axishttp://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/posterior_columnhttp://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/anatomy_of_the_axis -
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
16/18
Schematic lateral view of the cervical spine.
Note the odontoid (dens), the predental space and the
spinal canal. (A=anterior spinal line; B=posterior spinal line;C=spinolaminar line; D=clivus base line)
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
17/18
-
8/14/2019 Neck pain after trauma
18/18
http://www.wheelessonline.com/image4/dens1.jpg