Ncm103 6th Cv II
-
Upload
kamx-mohammed -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of Ncm103 6th Cv II
-
7/30/2019 Ncm103 6th Cv II
1/6
jcmendiola_Achievers2013
Care of Clients with Problems In Oxygenation,
Fluids and Electrolytes, Metabolism and Endocrine
(NCM103)
Cardiovascular System: Coronary Vascular Disease
Coronary Atherosclerosis
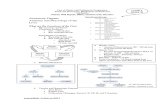
Definition: Abnormal accumulation of fatty substances Creates BLOCKAGE Repetitious inflammatory response
o Obstruction + Inflammation = Blood FlowMI or APAtherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis
1. Definition Lumen Lumen2. Cause Deposition of fatty substances Elasticity of blood vessels3. Age Toddlers Aging process4. Layer Tunica intima Tunica media
Risk Factors:
Blood lipid level Smoking lumen; vasoconstriction Hypertension Narrowing down of blood vessels Diabetes / Hyperlipidemia Obesity Metabolic Syndrome
o Hyperglycemia FBS, Glucose Tolerance Testo Hypertensiono Level of lipids in bloodo Presence of elevation CRP
Clinical Manifestations:
- Depends on1. Location and degree of
narrowing
2. Thrombus formation andobstruction of blood
CHEST PAIN~ Asymptomatic~
Prevention:
Control of cholesterol level Get lipid profile once ever 5 years (20
y/o and above)
a. Dietb. Physical Activityc. Medications Anti-lipid Drugsd. Promoting cessation of tobacco
Nicotine!! Viscosity
of blood
Vasoconstriction of Blood
Vessels
e. Managing Hypertension Religious intake of
DRUGS
Regular exercise Diet Alcohol intake
Topics Discussed Here Are:1. Coronary Atherosclerosis2. Angina Pectoris3. Myocardial Infarction
LOOKY
HERE
-
7/30/2019 Ncm103 6th Cv II
2/6
jcmendiola_Achievers2013
NUTRIENT CONTENT OF THE THERAPEUTIC LIFESTYLE CHANGES (TLC) DIET
Nutrient Recommended IntakeTotal calories Balance intake and expenditure to maintain desirable weight
Total fat
Saturated fat Polyunsaturated fat
Monounsaturated fat
25% - 35% of total calories
Less than 7% of total caloriesUp to 10% of total calories
Up to 20% of total calories
Carbohydrate 50% - 60% of total calories
Dietary fiber 20 30 g/day
Protein Approximately 15% of total calories
Cholesterol Less than 200 mg/day
Angina PectorisFactors: Blood Flow due to Lumen
Non-modifiable Factors
1. Age2. Sex3. Race4. Family History
Modifiable Factors
5. Diet ( Na, Fat, Nicotine)6. Alcohol7. Obesity8. Sedentary activity9. Stress
Coronary
Insufficiency
Coronary occlusion
(Continuation of coronary insufficiency)
LumenCHEST
PAIN On and Off Bearable
Short Duration
Angina Pectoris
CONSTANTSEVERE
LONGER
Myocardial
Infarction
Ischemia
What is Angina Pectoris? Associated With:
Outside factors Mental / Emotional problems Relieved With: Rest Coronary vasodilators
Levines SignTypes of Angina Pectoris
1. Stable Angina Predictable and consistent pain Relieved by rest and / nitroglycerin
2. Unstable Angina / Preinfarction Angina / Crescendo Angina Symptoms increase in frequency May not be relieved by rest and nitroglycerin
3.
Variant Angina (Prinzmetals Angina) Pain at rest Reversible ST-segment elevation
4. Silent Ischemia Objective evidence of ischemia But NO PAIN :o
Management:1. Medical Management
a. Rest Minimum of 2 hours
-
7/30/2019 Ncm103 6th Cv II
3/6
jcmendiola_Achievers2013
b. Drugs1. Coronary Vasodilators
Dilates lumen of blood vessels in the myocardium Drugs:
o Nitroglycerin 1 Tab, SL q5 min PRN for chest pain Maximum of 3 Tablets; if not resolved considered
MI
Take the medications beforeany stressful event
Loses potency whenexposed in the sun; store in
dark colored bottles
If head gets big, warm, andflushing of face it is
NORMAL, not SIDE EFFECT or ADVERSE
EFFECT
2. Anti-platelet Drugs Aspirin (Produces GIT disturbance; Coated Aspirin New) Heparin
o Side Effect = Bleeding (Petechiae, Ecchymosis, Hematoma)o WOF: Tea colored urine for HEMATURIAo
WOF: BLACK STOOLS NO PARENTERAL ADMINISTRATION OF DRUGS; if needed,apply pressure after!!
Dont use dental floss3. Beta Blockers To reduce O2 demand of myocardium4. Ca+ Channel Blocking Agent Relaxes the Blood Vessel to BP
c. Take 30 60 cc of BRANDY/WHISKY To reduce chest pain by vasodilation Amount = Vasoconstriction Amount = Vasodilation
2. Prevention of Succeeding Attacks to Angina Pectorisa. Diet
Fat Diet (THE FOLLOWING FOODS ARE NOT ALLOWED OR MODERATE) 4 Legged animals Foods with wings (Moderate) White meat Chicken (NO SKIN) Intake of food in WATER; but grows in SOIL
Na Diet (2 gm Na) AVOID THE FF FOODS 1. Na Nitrate Food colorings, cold cuts, preserved food2. Na Nitrite Tocino, Tapa3. Na HCO3 Baking Soda, bread, biscuit, pastries
8:00 1st
Tablet
8:05 2nd
Tablet
8:10 3rd Tablet
8:00 1st
Tablet
8:05 2nd
Tablet
3:30 1st
Tablet
-
7/30/2019 Ncm103 6th Cv II
4/6
jcmendiola_Achievers2013
4. NaCl Fish sauce, soy sauce, dried fish5. Na Saccharin
b. Must be with the patient all the time!! Coronary Vasodilators
DONT EXPOSE IN THE SUN!! DONT LEAVE IN THE CAR!!
Myocardial Infarction Brought about by lack of blood supply going to the myocardium A.k.a. Coronary occlusion or Heart Attack
Pain:
- CRUSHING- TIGHTNESS- Sudden onset- Substernal- Severe- Unrelieved by Nitroglycerin- May radiate to: Back, neck, jaw, shoulders, arm-
Dyspnea- Syncope ( BP)- Nausea / Vomiting- Extreme weakness- Diaphoresis- Denial is common- HR
Treatment:
- O2 IV Medications- Dietary restrictions- Na, Cholesterol, Caffeine- Surgery? Pacemaker?
Causes:
1. Atheroma Associated with body metabolism2. O2 / Blood demand Patients with hyperthyroidism3. O2 Supply (Anemia, BP)4. Vasospasm Sudden constriction / narrowing of coronary arteries
How to Diagnose Clients With MI1. Presenting Manifestations
Chief complaint Previous illnesses ECG: Done in 10 minutes PRIOR to admission
P
Q
R
S
T
ANG HIRAP MAG DROWING NG ECG PQRST SA PC XDComponents
1. P Wave Atrial Contraction / Depolarization (0.08 seconds)2. PR Interval Time for impulses to travel from Artery to Ventricle (0.16 seconds)3. QRS Complex Ventricular Contraction / Depolarization (0.08 seconds)4. ST Segment Length of time for the ventricle to relax (0.12 seconds)5. T Wave Ventricular relaxation / Repolarization (0.16 seconds)
0.08
seconds
2
seconds
-
7/30/2019 Ncm103 6th Cv II
5/6
jcmendiola_Achievers2013
Diagnosing Myocardial Infarction Inverted T Wave
Injury becomes ischemic, myocardial Repolarization is altered and delayed Which causes the T Wave to invert
Elevated ST-segment Injured myocardial cells depolarize normally, but repolarize more rapidly than normal
cells
Causing the ST-segment to rise at least 1 mm above the isoelectric line Laboratory Results
Creatinine Kinase (CK-MB) Lactic Dehydrogenase Myoglobin Troponin T and I
Management1. Minimize Myocardial damage
a. Cardiac overload Place patient on absolute bed rest
NO VISITORS ALLOWED (NEAREST RELATIVE ONLY) Health team should be calm
b. Get baseline Vital Signs TPR
Temperature = Due to cell death Pulse = Respiration = Blood Pressure =
Baseline ECG Basic serum electrolytes
c. Administration of Drugs Thrombolytic Drugs (Alteplase)
1st Drug To dissolve the blood clot The faster it is given, it is better
Analgesics To relieve chest pain Morphine - Pain and Anxiety related to MI
ACE Inhibitors To prevent BP
2. Cardiac Rehabilitation Main objective: To extend the life of the patient and improve the quality of life of
patients
Consists of different activities3 Phases of Cardiac Rehabilitation
1. Phase I Time of diagnosis of atherosclerosis Found out by lipid profile Management:
Preventive measures1. Level of activities (Walking)2. Initial education of patient and family (For self care)3. Quit Smoking!4. DIET > NO FATTY FOODS
If patient is not compliant, there
would be repeated attacks of
angina pectoris and myocardialinfarction.
-
7/30/2019 Ncm103 6th Cv II
6/6
jcmendiola_Achievers2013
2. Phase II Time the patient has been discharged from the hospital All activities are supervised; support from an outside person Based on the stress test of the client Dietitian would make a list of foods to be eaten and not eaten
3. Phase III Maintain cardiovascular stability Patient can still be on diet and exercise, but no longer supervised
Reperfusion Therapy- Procedures wherein to further improve the blood flow to the myocardium such as:
o Angioplasty: Repair of blood vessel PTA (Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty) PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty) It is the inflation of a balloon pushing atheromas to the side, done not to attain
100%
o Coronary Stent Inserted through the femur Placement of a spring Can cause thrombus formation But eventually becomes part of the endothelial tissue
o Atherectomy Removal of atheromas Hollow cylinder Diamond chip-blade Rotation: Scrape atheromas Not full scraping of atheromas
o Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) They cannot perform not until there are still very minimal amount of blood to
the myocardium
Harvest a Graft Artery Vein
o Common blood vessel used Internal mammary artery Saphenous vein
Nursing Care Patient should be VERY compliant
Drugs be taken religiously Thrombolytics Beta blockers Digitalis
Compliance to diet FAT Na
Ambulation Gradually increasing
Sexual Intercourse Patient should be able to make 5 7 steps in the stairs without fatigability