Nationalism vs sectionalism ppt
Transcript of Nationalism vs sectionalism ppt

EERA OF RA OF GGOOD OOD
FFEELINGSEELINGS??::Nationalism & Sectionalism Nationalism & Sectionalism
after the War of 1812after the War of 1812

Results of the War of 1812Results of the War of 1812 Draw militarilyDraw militarily
Small war and insignificant in military terms. Small war and insignificant in military terms.
Important consequences for the U.S.:Important consequences for the U.S.: Winners: War HawksWinners: War Hawks; ; Republicans, Andrew JacksonRepublicans, Andrew Jackson Losers: Indians, FederalistsLosers: Indians, Federalists New spirit of nationalismNew spirit of nationalism Paranoia about Britain died awayParanoia about Britain died away (“Second War for Independence”)(“Second War for Independence”)
Rush-Bagot Agreement Rush-Bagot Agreement & Convention of 1818 & Convention of 1818
No U.S. involvement withNo U.S. involvement with Europe Europe for 100 years.for 100 years.
America looks inwardAmerica looks inward

Guiding QuestionGuiding Question
Historians have traditionally labeled Historians have traditionally labeled the period after the War of 1812 the period after the War of 1812 (1815-1825) the “Era of Good (1815-1825) the “Era of Good Feelings.” How accurate was this Feelings.” How accurate was this label, considering the emergence of label, considering the emergence of nationalism and sectionalism during nationalism and sectionalism during the period? the period?

Presidential Election of 1816Presidential Election of 1816

Politics: “ERA OF GOOD FEELINGSPolitics: “ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS””
““Era of Good Feelings” Era of Good Feelings” James Monroe - President (1817-1825) James Monroe - President (1817-1825) John Quincy Adams John Quincy Adams John Calhoun John Calhoun
NationalismNationalism SectionalismSectionalism
President James Monroe Sec. of State J.Q. Adams

1820 Presidential Election1820 Presidential Election

ECONOMIC & DEMOGRAPHIC EXPANSIONECONOMIC & DEMOGRAPHIC EXPANSION
Great Migration WestwardGreat Migration Westward
Old NorthwestOld Northwest Old SouthwestOld Southwest
Spread of Settlement: Spread of Settlement: Westward Surge, Westward Surge, 1800–18201800–1820
Concentration of Slavery, 1820Concentration of Slavery, 1820

ECONOMIC & DEMOGRAPHIC EXPANSIONECONOMIC & DEMOGRAPHIC EXPANSION
““internal improvements”internal improvements” Henry Clay – “American System” Henry Clay – “American System”
Tariff of 1816 - protective Second Bank of the U. S. Internal improvements
at federal expense.
National Road
SECTIONAL IMPLICATIONS?SECTIONAL IMPLICATIONS?•WEST WEST got roads, canals, and federal aid got roads, canals, and federal aid•EAST EAST protective tariffs protective tariffs (w/ support from the (w/ support from the West)West)
•SOUTH SOUTH ?? ?? Major Migration Major Migration Routes, 1800–1820Routes, 1800–1820

ECONOMIC & DEMOGRAPHIC EXPANSIONECONOMIC & DEMOGRAPHIC EXPANSION
Panic of 1819Panic of 1819 boom & bust cyclesboom & bust cycles About every 20 yrs. in 19About every 20 yrs. in 19thth C. C.
Causes of the PanicCauses of the Panic Deflation Deflation – falling crop prices– falling crop prices
Esp. cotton: British demand drops - find cheaper sourcesEsp. cotton: British demand drops - find cheaper sources Competition from Europe increases - end of Napoleanic WarsCompetition from Europe increases - end of Napoleanic Wars
Overspeculation on land Overspeculation on land – easy credit from banks– easy credit from banks Western farmers unable to pay loansWestern farmers unable to pay loans
Trade deficit – drained U.S. of specieTrade deficit – drained U.S. of specie Bank of the U.S. tightens credit Bank of the U.S. tightens credit
Tougher loan requirements, requires specie from state banksTougher loan requirements, requires specie from state banks
Who/What Who/What is is blamed?blamed?

MISSOURI MISSOURI Missouri statehood controversy Missouri statehood controversy (1819)(1819)
Tallmadge Amendment Tallmadge Amendment (1819)(1819) – – gradual abolition (passed HR, failed in Senate)gradual abolition (passed HR, failed in Senate)
Missouri Compromise Missouri Compromise (1820)(1820) ((Maine-Missouri Bill) Maine-Missouri Bill)

MISSOURI COMPROMISEMISSOURI COMPROMISEREACTIONSREACTIONS ““like a fire-bell in the night . . . the [death] knell like a fire-bell in the night . . . the [death] knell
of the Union”of the Union” - Thomas Jefferson- Thomas Jefferson
““the title page to a great tragic volume” the title page to a great tragic volume” – J. Adams– J. Adams
Continued Existence of Slavery:Continued Existence of Slavery:a)a) Legal Status Legal Status
b)b) Political Power Political Power
c)c) Geographic/Economic NecessityGeographic/Economic Necessity
Nationalism vs. Sectionalism??Nationalism vs. Sectionalism??

THETHE SUPREME SUPREME COURT COURT && NATIONALISMNATIONALISM Marbury v. MadisonMarbury v. Madison (1803)(1803)
judicial reviewjudicial review Fletcher v. PeckFletcher v. Peck (1810) (1810)
Constitution forbids state laws “impairing” contractsConstitution forbids state laws “impairing” contracts Dartmouth v. WoodwardDartmouth v. Woodward
(Dartmouth College Case)(Dartmouth College Case) (1819)(1819) McCulloch v. MarylandMcCulloch v. Maryland (1819)(1819)
Elastic (“necessary & proper”) clauseElastic (“necessary & proper”) clause Gibbons v. OgdenGibbons v. Ogden (1824) (1824)
“Steamboat Case”“Steamboat Case” Commerce Clause Commerce Clause
Old Supreme Court ChamberOld Supreme Court Chamber

NATIONALISM IN FOREIGN AFFAIRSNATIONALISM IN FOREIGN AFFAIRS Florida (1819)Florida (1819)

NATIONALISM IN FOREIGN AFFAIRSNATIONALISM IN FOREIGN AFFAIRS
Adams-OnAdams-Oníís Treaty s Treaty of 1819of 1819 ( Transcontinental Treaty)( Transcontinental Treaty)

North America in 1824North America in 1824

NATIONALISM IN FOREIGN AFFAIRSNATIONALISM IN FOREIGN AFFAIRS
The Monroe Doctrine (1823)
The US to declare the Americas
off-limits to Europe.
A continuation of the neutrality and isolationist policies established by Washington.
Monroe Doctrine
US will protect the Americas---new countries which formed in Central and South America
No European Colonization in the Americas
US will recognize existing European Colonies
US will not meddle in European affairs

END OF END OF THE “ERA”THE “ERA” Election of 1824 - Election of 1824 -
Era Breaks DownEra Breaks Down
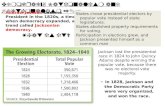
electoral changes - electoral changes - elections based elections based much more on much more on popular supportpopular support
““Corrupt Bargain” Corrupt Bargain” (according to whom???)(according to whom???)

Election of 1824: A “Corrupt Bargain”?Election of 1824: A “Corrupt Bargain”?

John Quincy John Quincy AdamsAdams
President, President, 1825-18291825-1829
John Quincy Adams
(Library of Congress)

The The Election Election of 1828of 1828 Andrew JacksonAndrew Jackson
(Library of Congress)(Library of Congress)

Review of PresidentsReview of Presidents1.1. George WashingtonGeorge Washington (1789-1797) (1789-1797) no partyno party VirginiaVirginia2.2. John AdamsJohn Adams (1797-1801) (1797-1801) FederalistFederalist Mass.Mass.3.3. Thomas JeffersonThomas Jefferson (1801-1809)(1801-1809) RepublicanRepublican VirginiaVirginia4.4. James MadisonJames Madison (1809-1817)(1809-1817) RepublicanRepublican VirginiaVirginia5.5. James MonroeJames Monroe (1817-1825)(1817-1825) Republican Republican VirginiaVirginia6.6. John Quincy AdamsJohn Quincy Adams (1825-1829) (1825-1829) RepublicanRepublican Mass.Mass.7.7. Andrew JacksonAndrew Jackson (1829-1837)(1829-1837) DemocratDemocrat Tenn.Tenn.