NAT and Stateful Inspection Firewall for Secure Router ...
Transcript of NAT and Stateful Inspection Firewall for Secure Router ...

Advanced Gateway 2330
Secure Router 2330
Secure Router 4134
Engineering
> NAT and Stateful Inspection Firewall for Secure Router Technical Configuration Guide
Avaya Data Solutions
Document Date: June 2011
Document Number: NN48500-627
Document Version: 1.0

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 2
avaya.com
June 2011
© 2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Notices While reasonable efforts have been made to ensure that the information in this document is complete and accurate at the time of printing, Avaya assumes no liability for any errors. Avaya reserves the right to make changes and corrections to the information in this document without the obligation to notify any person or organization of such changes.
Documentation disclaimer Avaya shall not be responsible for any modifications, additions, or deletions to the original published version of this documentation unless such modifications, additions, or deletions were performed by Avaya. End User agree to indemnify and hold harmless Avaya, Avaya’s agents, servants and employees against all claims, lawsuits, demands and judgments arising out of, or in connection with, subsequent modifications, additions or deletions to this documentation, to the extent made by End User.
Link disclaimer Avaya is not responsible for the contents or reliability of any linked Web sites referenced within this site or documentation(s) provided by Avaya. Avaya is not responsible for the accuracy of any information, statement or content provided on these sites and does not necessarily endorse the products, services, or information described or offered within them. Avaya does not guarantee that these links will work all the time and has no control over the availability of the linked pages.
Warranty Avaya provides a limited warranty on this product. Refer to your sales agreement to establish the terms of the limited warranty. In addition, Avaya’s standard warranty language, as well as information regarding support for this product, while under warranty, is available to Avaya customers and other parties through the Avaya Support Web site: http://www.avaya.com/support Please note that if you acquired the product from an authorized reseller, the warranty is provided to you by said reseller and not by Avaya.
Licenses
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE TERMS AVAILABLE ON THE AVAYA WEBSITE, HTTP://SUPPORT.AVAYA.COM/LICENSEINFO/ ARE APPLICABLE TO ANYONE WHO DOWNLOADS, USES AND/OR INSTALLS AVAYA SOFTWARE, PURCHASED FROM AVAYA INC., ANY AVAYA AFFILIATE, OR AN AUTHORIZED AVAYA RESELLER (AS APPLICABLE) UNDER A COMMERCIAL AGREEMENT WITH AVAYA OR AN AUTHORIZED AVAYA RESELLER. UNLESS OTHERWISE AGREED TO BY AVAYA IN WRITING, AVAYA DOES NOT EXTEND THIS LICENSE IF THE SOFTWARE WAS OBTAINED FROM ANYONE OTHER THAN AVAYA, AN AVAYA AFFILIATE OR AN AVAYA AUTHORIZED RESELLER, AND AVAYA RESERVES THE RIGHT TO TAKE LEGAL ACTION AGAINST YOU AND ANYONE ELSE USING OR SELLING THE SOFTWARE WITHOUT A LICENSE. BY INSTALLING, DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE, OR AUTHORIZING OTHERS TO DO SO, YOU, ON BEHALF OF YOURSELF AND THE ENTITY FOR WHOM YOU ARE INSTALLING, DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE (HEREINAFTER REFERRED TO INTERCHANGEABLY AS "YOU" AND "END USER"), AGREE TO THESE TERMS AND CONDITIONS AND CREATE A BINDING CONTRACT BETWEEN YOU AND AVAYA INC. OR THE APPLICABLE AVAYA AFFILIATE ("AVAYA").
Copyright Except where expressly stated otherwise, no use should be made of the Documentation(s) and Product(s) provided by Avaya. All content in this documentation(s) and the product(s) provided by Avaya including the selection, arrangement and design of the content is owned either by Avaya or its licensors and is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws including the sui generis rights relating to the protection of databases. You may not modify, copy, reproduce, republish, upload, post, transmit or distribute in any way any content, in whole or in part, including any code and software. Unauthorized reproduction, transmission, dissemination, storage, and or use without the express written consent of Avaya can be a criminal, as well as a civil offense under the applicable law.
Third Party Components Certain software programs or portions thereof included in the Product may contain software distributed under third party agreements ("Third Party Components"), which may contain terms that expand or limit rights to use certain portions of the Product ("Third Party Terms"). Information regarding distributed Linux OS source code (for those Products that have distributed the Linux OS source code), and identifying the copyright holders of the Third Party Components and the Third Party Terms that apply to them is available on the Avaya Support Web site: http://support.avaya.com/Copyright.
Trademarks The trademarks, logos and service marks ("Marks") displayed in this site, the documentation(s) and product(s) provided by Avaya are the registered or unregistered Marks of Avaya, its affiliates, or other third parties. Users are not permitted to use such Marks without prior written consent from Avaya or such third party which may own the Mark. Nothing contained in this site, the documentation(s) and product(s) should be construed as granting, by implication, estoppel, or otherwise, any license or right in and to the Marks without the express written permission of Avaya or the applicable third party. Avaya is a registered trademark of Avaya Inc. All non-Avaya trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Downloading documents For the most current versions of documentation, see the Avaya Support. Web site: http://www.avaya.com/support
Contact Avaya Support Avaya provides a telephone number for you to use to report problems or to ask questions about your product. The support telephone number is 1-800-242-2121 in the United States. For additional support telephone numbers, see the Avaya Web site: http:// www.avaya.com/support.

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 3
avaya.com
June 2011
Abstract This Technical Configuration Guide outlines the configuration steps required on an Avaya Secure Router to configure various NAT and firewall scenarios. The main components include the Avaya Secure Router 2330 or 4134.
The audience for this Technical Configuration Guide is intended to be Avaya Sales teams, Partner Sales teams and end-user customers.
Acronym Key
Throughout this guide the following acronyms will be used:
ALG: Application Layer Gateway
CLI: Command Line Interface
DMZ: Demilitarized Zone
ICMP: Internet Control Message Protocol
MIM: Medium Interface Module
NAT: Network Address Translation
PAT: Port Address Translation
SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol
SSH: Secure Shell
Revision Control
No Date Version Revised By Remarks
1 June 2011 1.0 PLM Initial Draft

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 4
avaya.com
June 2011
Table of Contents Figures .......................................................................................................................................................... 6
Tables ............................................................................................................................................................ 7
1. Overview ............................................................................................................................................... 9
1.1 Stateful Packet Inspection ........................................................................................................... 10
1.2 Application Layer Gateways (ALGs) ........................................................................................... 13
1.3 Network Address Translation ...................................................................................................... 15
2. Configuration Examples ...................................................................................................................... 17
2.1 Single Subnet with PAT .............................................................................................................. 17
2.2 Multiple Subnets with PAT and Guest ........................................................................................ 21
2.3 Multiple Subnets with PAT and DMZ .......................................................................................... 26
2.4 Single Subnet with Reverse NAT ................................................................................................ 31
2.5 Single Subnet with NAT Failover ................................................................................................ 35
3. Additional Firewall Features ................................................................................................................ 39
3.1 Bypass Trusted to Trusted Firewall Processing .......................................................................... 39
3.2 Enabling Application Layer Gateways (ALGs) ............................................................................ 39
3.3 Permitting Untrusted Traffic to Self ............................................................................................. 41
3.4 Maximum Firewall Connections .................................................................................................. 45
3.5 Stealth Mode ............................................................................................................................... 46
4. Firewall Debugging ............................................................................................................................. 47
4.1 Clearing Firewall Connections: ................................................................................................... 47
4.2 Disable Firewall Processing ........................................................................................................ 47
4.3 Enabling / Disabling Debug Modules .......................................................................................... 48
4.4 Viewing Debug Messages ........................................................................................................... 49
5. Verification .......................................................................................................................................... 50
5.1 Firewall Connections ................................................................................................................... 50
5.2 NAT Translations ........................................................................................................................ 51
5.3 Global Statistics........................................................................................................................... 53
6. Running Configuration Files ................................................................................................................ 54
6.1 Section 2.1 Running Configuration ............................................................................................. 54
6.2 Section 2.2 Running Configuration ............................................................................................. 57
6.3 Section 2.3 Running Configuration ............................................................................................. 61
6.4 Section 2.4 Running Configuration ............................................................................................. 65
6.5 Section 2.5 Running Configuration ............................................................................................. 68
7. Reference Documentation .................................................................................................................. 73

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 5
avaya.com
June 2011

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 6
avaya.com
June 2011
Figures
Figure 1.0 – Firewall Deployment Example .................................................................................................. 9 Figure 1.1 – Virtual Firewall Zones ............................................................................................................. 11 Figure 1.2 – Untrusted Zone ....................................................................................................................... 11 Figure 1.1.2-1 – Trusted to Untrusted Connections .................................................................................... 12 Figure 1.1.2-2 – Trusted to Trusted Connections ....................................................................................... 12 Figure 2.1 – Single Internal Subnet with PAT ............................................................................................. 17 Figure 2.2 – Multiple Internal Subnets with PAT ......................................................................................... 21 Figure 2.3 – Multiple Subnets with PAT and DMZ ...................................................................................... 26 Figure 2.4 – Single Subnet with Reverse NAT ........................................................................................... 31 Figure 2.5 – Single Internal Subnet with NAT Failover ............................................................................... 35

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 7
avaya.com
June 2011
Tables
Table 1.0 – Secure Router Firewall Features ............................................................................................. 10 Table 1.2 – Application Layer Gateways .................................................................................................... 14 Table 1.3 – Network Address Translation ................................................................................................... 15 Table 3.4 – Default Maximum Firewall Connections .................................................................................. 45 Table 4.3 – Firewall Debug Modules .......................................................................................................... 48

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 8
avaya.com
June 2011
Conventions This section describes the text, image, and command conventions used in this document.
Symbols
Tip – Highlights a configuration or technical tip.
Note – Highlights important information to the reader.
Warning – Highlights important information about an action that may result in equipment damage, configuration or data loss.
Text
Bold text indicates emphasis.
Italic text in a Courier New font indicates text the user must enter or select in a menu item, button or command:
sr2330-1# show running-config
Output examples from Avaya devices are displayed in a Lucida Console font:
sr2330-1# show ver
Runtime: 10.3.0.0
Created: Nov 1 2010, 13:37:35
Boot: 0.0.0.46 (NORMAL Boot)
NorBoot: 0.0.0.46
GolBoot: 0.0.0.46
Slot/SubSlot Card-Type Status FPGA-Rev FPGA-Eng-Rev CPLD-Rev CPLD-Eng-Rev
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
0/- MPU_A NORMAL --- --- --- 0x16
1/- ADSL_ANX_A NORMAL --- --- --- 0x3

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 9
avaya.com
June 2011
1. Overview
Firewalls perform a critical role in perimeter security by protecting network resources and determining who can access hosts and applications on the network as well as verify the integrity of the packets and protocols forwarded through the firewall. In addition a firewall may provide Network Address Translation services providing seamless communications between publically routable and private RFC-1918 IPv4 addresses.
To provide these services a firewall is commonly placed where trusted and untrusted networks intersect. For example a firewall will be placed between the public Internet and one or more internal networks. Firewalls may also be placed between trusted networks for regulatory compliance such as PCI or to restrict user access to specific applications and services in a data center.
Figure 1.0 – Firewall Deployment Example
A firewall is a set of programs restricting incoming and outgoing traffic between networks according to user defined security policies. As a general rule all network traffic flows through the firewall. The firewall screens all incoming IPv4 traffic and blocks the flows which do not meet the security policy. Most firewalls will by default deny all inbound flows received on untrusted interfaces providing protection for internal services.
There are three different types of firewall technologies available in the market which includes stateless packet filtering, application proxy and stateful packet inspection. The Avaya Secure Router implements a stateful packet inspection firewall. In a typical deployment outbound policies are defined to permit or deny certain types of traffic. When permitting traffic the stateful packet inspection firewall creates a unique session for the connection. Based on the application type and the corresponding protocol, an appropriate inbound policy for the connection is dynamically created. When a return packet is received, the packet is permitted as long as the state of connection permits the reception of the return packet.
The inbound policy is a temporary policy that expires upon the expiry of the connection. Since the inbound policy does not keep ports open indefinitely, network vulnerability is drastically reduced in contrast to packet filtering where the inbound policy is permanent and the port is always permitted.

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 10
avaya.com
June 2011
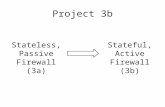
The Avaya Advanced Gateway 2330 (with Full Routing License), Avaya Secure Router 2330 and Avaya Secure Router 4134 support the following firewall features:
Advanced Gateway 2330 Secure Router 2330 Secure Router 4134
Firewall Features:
Application Layer Gateways
Cone NAT
Denial of Service (DoS) Protection
Logging
Stateful Packet Inspection
Stealth Mode
Network Address Translations (NAT)
Network Address Translations (NAT) Failover
Proxy Network Address Translation (NAT)
Scheduling
URL Filtering
Scaling:
75,000 Concurrent Firewall Connections (System Wide)
29,912 Concurrent Firewall Connections (Per Zone)
25 Virtual Firewall Zones
1,024 Policies per Virtual Firewall Zone
75,000 Entries in NAT translation table
Table 1.0 – Secure Router Firewall Features
1.1 Stateful Packet Inspection
A Stateful Inspection firewall keeps track of the state information associated with all network connections. All traffic passing through stateful inspection firewall is analyzed against the state of these connections in order to determine if the connection is permitted through the firewall. Typically a firewall connection is identified by 5 basic elements (below). Additional elements may also be included in the firewall connection for some special protocols:
Source IPv4 Address
Destination IPv4 Address
Source Port
Destination Port
Protocol
Application Specific Elements
Most stateful packet inspection firewalls apply rules to individual interfaces, however the Secure Router places interfaces into rule sets called virtual firewalls or zones. The advantage of configuring common rule sets is that you can perform the most complex task (editing policies) once, and apply the configuration across multiple interfaces. You no longer need to repeat policy definitions on multiple interfaces. Once a policy is defined for a zone, you can place any number of interfaces into that zone. As a result, the Secure Router can accommodate complex policy configurations with less duplication of rule entries. Each Secure Router can support one untrusted zone and up to 25 trusted virtual firewall zones.

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 11
avaya.com
June 2011
Figure 1.1 – Virtual Firewall Zones
Note – On the Secure Router 4134, layer 3 Ethernet ports on a Medium Interface Module (MIM) cannot be assigned to an untrusted zone. In addition traffic forwarded between MIM switch ports are forwarded in hardware and will bypass firewall processing.
1.1.1 Untrusted Zone
The Secure Router provides a default untrusted zone named internet. Only one untrusted zone is supported on the Secure Router and all untrusted interfaces must be assigned to the internet zone. The Secure Router will not trust inbound connections received on interfaces assigned to the internet zone and these connections are blocked by default. This includes packets destined to a trusted zone as well as traffic destined to the Secure Router ( or self).
Figure 1.2 – Untrusted Zone
To permit inbound sessions destined to the Secure Router policies must be added to the internet zone. It’s important to note that policies in the internet zone should only be used to permit traffic destined to the Secure Router (self). To permit traffic received on the internet zone destined to a trusted zone, inbound policies must be created in the corresponding trusted zone.

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 12
avaya.com
June 2011
1.1.2 Trusted Zones
The Secure Router provides a default trusted zone named corp and all other zones created on the Secure Router are trusted zones. No return traffic is allowed into a trusted zone unless the session is first initiated from within that zone. By default all outbound connections from the trusted zone are permitted and all inbound connections are denied. All additional zones that you create on the Secure Router are trusted zones.
Figure 1.1.2-1 – Trusted to Untrusted Connections
For trusted to trusted connections, by default the Secure Router will permit the outbound connection but will deny the inbound transient connection. To permit trusted to trusted connections an outbound permit policy must be created to permit the outbound connection while an inbound policy must be created to permit the return traffic. Each permitted traffic type will require an outbound and inbound policy.
Alternatively administrators can globally disable the inspection of trusted to trusted traffic if desired. When the bypassing of trusted to trusted traffic is globally enabled, all firewall processing of trusted to trusted connections are disabled. However firewall processing of untrusted to trusted, untrusted to self or trusted to untrusted connections will remain.
Figure 1.1.2-2 – Trusted to Trusted Connections

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 13
avaya.com
June 2011
1.2 Application Layer Gateways (ALGs)
It is common for the stateful inspection firewall to have one or more outbound policies but not inbound policies. When traffic is forwarded out a firewall there will naturally be inbound traffic as a response to the outgoing traffic. In order to permit the passing of the inbound traffic a stateful firewall creates a temporary inbound policy which is removed upon the expiry of the session.
For some applications the dynamic creation of the inbound policy requires intimate knowledge of the applications generating the traffic and Application Layer Gateways (ALGs) are used to create these policies. For example for the firewall to be able to dynamically open an inbound port for SIP voice traffic, a SIP ALG can be enabled to monitor the application layer information exchanged over the SIP control traffic to determine the dynamic media path ports negotiated by the SIP end-points. The SIP ALG can then dynamically open the necessary ports to permit the voice media path. Without a SIP ALG the administrator would have to permanently open a large number of ports providing a potential security risk.
In addition to dynamically opening inbound ports for specific applications, ALGs can also be used to recognize specific commands or fields for certain applications and protocols. For example the web ALG can be enabled on the firewall to filter out specific keywords or URLs for web filtering. Finally an ALG can be used to convert network layer information found inside an application payload for applications such as Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) when specific traffic types need to be supported.
The Secure Router version 10.3 supports various ALGs which are disabled by default but may be individually enabled to provide enhanced firewall support for specific applications:
ALG Name Description
aim ALG for AOL Instant Messenger/ICQ Messenger (TCP port 5190).
aimudp ALG for AOL Instant Messenger (UDP port 5190).
cuseeme ALG for CU-SeeMe (TCP port 7648).
dns ALG for Domain Name System (UDP port 53).
ftp ALG for File Transfer Protocol (TCP port 21).
gatekeeper ALG for H323-Gatekeeper (server to server) (UDP port 1719).
h323 ALG for H323 protocol (client to server) (UDP port 1720).
ike ALG for Internet Key Exchange protocol (UDP port 500).
ils ALG for Internet Location Server (netmeeting over LDAP protocol) (TCP port 389).
ils2 ALG for Internet Location Server (netmeeting over LDAP protocol) (TCP port 1002).
irc ALG for Internet Relay Chat (daemon running with user-privilege) (TCP port 6667).
msgtcp ALG for Microsoft Gaming Zone (TCP port 47624).
msgudp ALG for Microsoft Gaming Zone (UDP port 47624).
msn ALG for Microsoft Network Messenger (MSNP) (TCP port 1863).

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 14
avaya.com
June 2011
mszone ALG for Microsoft Gaming Zone (TCP port 28801).
n2p ALG for Net2Phone private protocol (UDP port 6801).
n2pe Net2Phone private protocol (TCP port 81).
nntp ALG for Network News Transfer Protocol (TCP port 119).
pcanywhere ALG for Norton/Symantec's pcanywhere protocol (UDP port 5632).
pptp Point to Point Tunneling Protocol (management session) (TCP port 1723).
rpc ALG for Remote Procedure Call (UDP port 111).
rtsp554 ALG for Real Time Streaming Protocol (UDP port 554).
rtsp7070 ALG for Real Time Streaming Protocol (Apple Quicktime port), (UDP port 7070).
sip ALG for Session Initiation Protocol (UDP port 5060).
sip-p2p-media Peer-to-Peer Media b/w trusted clients
sip-tcp ALG for Session Initiation Protocol (TCP port 5060).
smtp Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (TCP port 25).
sql ALG for Structured Query Language, Oracle's port (UDP port 1521).
tftp ALG for Trivial File Transfer Protocol (UDP port 69).
web ALG for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (TCP port 80).
Table 1.2 – Application Layer Gateways

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 15
avaya.com
June 2011
1.3 Network Address Translation
The Secure Router supports various Network Address Translation (NAT) modes which can be applied to firewall zones on a per policy basis. This is referred to as Policy based NAT as traffic is translated only when it matches a firewall policy as opposed to being applied to all traffic on an interface. In addition policies may be defined to ignore certain traffic so that traffic destined to an IPsec VPN tunnel will not be translated.
The following table highlights the various NAT modes supported by the Secure Router version 10.3:
NAT Mode Description
Forward NAT With Forward NAT translation occurs on traffic from an inside (trusted) interface to an outside (untrusted) interface. NAT is applied to an outgoing firewall policy and the source IP address of the packet gets translated.
Reverse NAT With Reverse NAT translation occurs on traffic from an outside (untrusted) interface to an inside (trusted) interface. NAT is applied to an incoming firewall policy and the destination IP address of the packet gets translated.
Static NAT This is a direct mapping of traffic from an unregistered address to a registered address on a one-to-one basis. This can be used to translate traffic going from trusted side to untrusted side or vice versa. It is particularly useful when a device on the inside needs to be accessible from the outside.
Dynamic NAT Dynamic NAT dynamically maps an unregistered address to a registered address from a configured group of IP addresses. The range of IP addresses could be lesser than the number of hosts on the trusted side to which it provides the translation service. It picks IP addresses on a round robin fashion.
Port Address Translation This is a form of Dynamic NAT. It maps multiple unregistered IP addresses to a single registered IP address by using different port numbers. With PAT multiple hosts on the inside can share the same public IP address and the Firewall will keep a list of assigned port numbers to track, which sessions belong to which host. With PAT enabled, theoretically up to 64K hosts can share a single IP address.
Cone NAT The type of PAT supported is port restricted cone NAT. Here all requests from the same internal IP address and port is mapped to the same external IP address and port number. Specifically, an external host can send a packet, with source IP address X and source port P, to the internal host only if the internal host had previously sent a packet to IP address X and port P. In the nomenclature of draft-ietf-behave-nat-udp-07.txt, a Port Restricted Cone NAT is one with both Endpoint Independent Mapping and Address and Port Dependent Filtering
Table 1.3 – Network Address Translation
Note – This guide focuses on common NAT implementations and includes examples for Port Address Translation and Reverse NAT.

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 16
avaya.com
June 2011
1.3.1 NAT Failover
When you specify the external address for the NAT translation, you can either specify an IP address or an interface name. If you specify an interface name, packets going out through the interface are translated using the IP address bound to that interface. However, firewall policies do not change when an interface goes up or down or the ISPs router is unreachable. If the NAT interface goes down, NAT continues to perform the translation of internal IP addresses to the public IP address of this interface. Therefore traffic is blackholed.
The Secure Router supports NAT failover by allowing a primary interface using PAT to failover to a backup interface if the primary interface goes down. When the primary interface is up, packets egressing the interface are translated using the IP address assigned to the interface. If the primary interface fails, the IP address assigned to the backup interface is used for the translations and the stale firewall connections are flushed.
NAT failover is supported on any Secure Router interface allowing the Secure Router to maintain Internet connectivity to users regardless of how the primary and secondary Internet service is being delivered to the premises. For NAT failover to function it is recommended that the primary public interface be assigned a static IP address while the secondary public interface can support either a static or dynamic IP address.
1.3.1.1 Static IP Addresses
When connecting to two ISPs the Secure Router can only support one active default gateway at a time. When static IP addresses are being used on the primary and secondary public interfaces, two default static routes must be defined on the Secure Router (one for each ISP). The static default route to the secondary ISP must have a higher cost than the static default route to the primary ISP. The default route to the primary ISP will be placed into the routing table until the interface fails at which point the default route to the secondary ISP will be utilized:
sr2330-1/configure# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 <primary-isp-router-ip> 1
sr2330-1/configure# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 <secondary-isp-router-ip> 10
1.3.1.2 Static & Dynamic IP Addresses
When both a static and dynamic IP addresses are assigned to the public interfaces, one static default route to the primary ISP will need to be defined with a lower cost than the default route learned by DHCP or PPPoE.
1) If the primary interface uses static IP addressing and the secondary interface uses a dynamic IP addressing, a static default route to the primary ISP will need to be defined with a lower cost than the dynamically assigned default gateway learned from the secondary public IP interface:
sr2330-1/configure# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 <primary-isp-router-ip> 1
Note – At this time NAT failover cannot be utilized with two public interfaces with dynamically assigned IP addresses. In addition NAT failover cannot be utilized when a dynamic IP address is assigned to the primary public interface and a static IP address is assigned to the secondary public interface.

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 17
avaya.com
June 2011
2. Configuration Examples
2.1 Single Subnet with PAT
The following scenario provides a step-by-step configuration example for how to configure a Secure Router to provide Port Address Translation (PAT) services for a single internal subnet and translate the internal traffic to a single public interface with a static or dynamically assigned IPv4 address.
Figure 2.1 – Single Internal Subnet with PAT
2.1.1 CLI Example
1 Access the global configuration context:
sr2330-1# configure terminal
sr2330-1/configure#
2 Access Fast Ethernet port 0/1 and name it Internet then assign the public IP address 76.7.100.25/24:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/1
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# description Internet
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# ip address 76.7.100.25 255.255.255.0
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# exit

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 18
avaya.com
June 2011
Tip – If the public IP address is dynamic, you can enable the DHCP client on the interface by issuing the dhcp-client enable command.
3 Access Gigabit Ethernet port 0/5 and name it Corp then assign the RFC 1918 private IP address 192.168.10.1/24:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/5
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# description Corp
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# exit
4 View IP interfaces:
sr2330-1/configure# show ip interface format brief
Interface Type IP-Address/Mask Status Method
ethernet0/1 ETHERNET (802.3) 76.7.100.25/24 Up MANUAL
ethernet0/5 ETHERNET (802.3) 192.168.10.1/24 Up MANUAL
ethernet0/2 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/3 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/4 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/6 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/7 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/8 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
5 Define a default route. In this example the default route will point to the service providers router interface 76.7.100.1 with a cost of 1:
sr2330-1/configure# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 76.7.100.1 1
Note – If the public IP address is being assigned from DHCP, the default route will be automatically learned from DHCP server and does not need to be statically defined.
6 Verify the default route has been correctly defined. Note that the default route will only be displayed in route table if the default gateway can be reached by the Secure Router:
sr2330-1/configure# show ip route

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 19
avaya.com
June 2011
Codes: C - connected, S - static,D - DHCP, R - RIP, B - BGP, M - MPLS
O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
* - candidate default
IP Load balancing policy is per_flow
Gateway of last resort is 76.7.100.1 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 76.7.100.1, ethernet0/1
C 76.7.100.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/1
C 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, lo0
C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/5
7 Access the firewall zone named internet and add the public interface ethernet0/1:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall internet
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# interface ethernet0/1
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# exit
8 View the internet zone interface mappings:
sr2330-1/configure# show firewall interface internet
Interface Map Name
--------- --------
ethernet0/1 internet
9 Access the firewall zone named corp and add the private interface ethernet0/5:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall corp
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# interface ethernet0/5
10 View the corp zone interface mappings:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# show firewall interface corp
Interface Map Name
--------- --------
ethernet0/5 corp
11 Create an outbound firewall policy 100 in the firewall zone corp that permits the source subnet 192.168.10.0/24 and NATs the traffic to the public interface ethernet0/1:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 100 out permit address 192.168.10.0 24 any
any nat-ip ethernet0/1
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 100 out# exit
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# exit

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 20
avaya.com
June 2011
12 View the modified firewall policy for the corp zone:
sr2330-1/configure# show firewall policy corp
Advanced: S - Self Traffic, F - Ftp-Filter, H - Http-Filter,
R - Rpc-Filter, N - Nat-Ip/Nat-Pool, L - Logging,
E - Policy Enabled, M - Smtp-Filter
Pri Dir Source Addr Destination Addr Sport Dport Proto Action Advanced
--- --- ----------- ---------------- ----------------- ------ --------
100 out 192.168.10.0/24 any any any any PERMIT NEL
1022 out any any any any any PERMIT SEL
1023 in any any any any any PERMIT SEL
1024 out any any any any any PERMIT EL
13 Save the changes to the startup configuration file:
sr2330-1/configure# save local

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 21
avaya.com
June 2011
2.2 Multiple Subnets with PAT and Guest
The following scenario provides a step-by-step configuration example for how to configure a Secure Router to provide Port Address Translation (PAT) services for multiple internal subnets and translate the internal traffic to a single public interface with a static or dynamically assigned IPv4 address. In additional firewall policies will be defined in the corp zone to deny communications between hosts in the Guest network and Corp1 / Corp2 networks.
Figure 2.2 – Multiple Internal Subnets with PAT
2.2.1 CLI Example
1 Access the global configuration context:
sr2330-1# configure terminal
sr2330-1/configure#
2 Access Fast Ethernet port 0/1 and name it Internet then assign the public IP address 76.7.100.25/24:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/1
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# description Internet
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# ip address 76.7.100.25 255.255.255.0
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# exit
Tip – If the public IP address is dynamic, you can enable the DHCP client on the interface by issuing the dhcp-client enable command.

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 22
avaya.com
June 2011
3 Access Fast Ethernet port 0/2 and name it Guest then assign the RFC 1918 private IP address 192.168.14.1/24:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/2
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/2)# description Guest
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/2)# ip address 192.168.14.1 255.255.255.0
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/2)# exit
4 Access Gigabit Ethernet port 0/5 and name it Corp1 then assign the RFC 1918 private IP address 192.168.10.1/24:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/5
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# description Corp1
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# exit
5 Access Gigabit Ethernet port 0/6 and name it Corp2 then assign the RFC 1918 private IP address 192.168.11.1/24:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/6
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/6)# description Corp2
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/6)# ip address 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/6)# exit
6 View IP interfaces:
sr2330-1/configure# show ip interface format brief
Interface Type IP-Address/Mask Status Method
ethernet0/1 ETHERNET (802.3) 76.7.100.25/24 Up MANUAL
ethernet0/2 ETHERNET (802.3) 192.168.14.1/24 Up MANUAL
ethernet0/5 ETHERNET (802.3) 192.168.10.1/24 Up MANUAL
ethernet0/6 ETHERNET (802.3) 192.168.11.1/24 Up MANUAL
ethernet0/3 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/4 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/7 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/8 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
7 Define a default route. In this example the default route will point to the service providers router interface 76.7.100.1 with a cost of 1:
sr2330-1/configure# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 76.7.100.1 1
Note – If the public IP address is being assigned from DHCP, the default route will be automatically learned from DHCP server and does not need to be statically defined.

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 23
avaya.com
June 2011
8 Verify the default route has been correctly defined. Note that the default route will only be displayed in route table if the default gateway can be reached by the Secure Router:
sr2330-1/configure# show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static,D - DHCP, R - RIP, B - BGP, M - MPLS
O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
* - candidate default
IP Load balancing policy is per_flow
Gateway of last resort is 76.7.100.1 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 76.7.100.1, ethernet0/1
C 76.7.100.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/1
C 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, lo0
C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/5
C 192.168.11.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/6
C 192.168.14.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/2
9 Access the firewall zone named internet and add the public interface ethernet0/1:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall internet
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# interface ethernet0/1
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# exit
10 View the internet zone interface mappings:
sr2330-1/configure# show firewall interface internet
Interface Map Name
--------- --------
ethernet0/1 internet
11 Access the trusted firewall zone named corp and add the private interfaces ethernet0/2, ethernet0/5 and ethernet0/6:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall corp
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# interface ethernet0/2
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# interface ethernet0/5
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# interface ethernet0/6

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 24
avaya.com
June 2011
12 View the corp zone interface mappings:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# show firewall interface corp
Interface Map Name
--------- --------
ethernet0/2 corp
ethernet0/5 corp
ethernet0/6 corp
13 Create outbound firewall policy 10 in the corp zone that denies all Guest Corp1 and Guest Corp2 inter-subnet communications:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 10 out deny address 192.168.14.0 24
192.168.0.0 16
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 10 out# exit
14 Create outbound firewall policy 11 in the corp zone that denies all Corp1 Guest and Corp2 Guest inter-subnet communications:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 11 out deny address 192.168.0.0 16
192.168.14.0 24
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 11 out# exit
15 Create outbound and inbound firewall policies 20 and 21 in the corp zone to permit all Corp1 Corp2 inter-subnet communications:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 20 out permit address 192.168.0.0 16
192.168.0.0 16
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 20 out# exit
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 21 in permit address 192.168.0.0 16
192.168.0.0 16
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 21 in# exit
16 Create an outbound firewall policy 100 in the corp zone that permits the Corp1 subnet 192.168.10.0/24 and NATs the traffic to the public interface ethernet0/1:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 100 out permit address 192.168.10.0 24 any
any nat-ip ethernet0/1
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 100 out# exit
17 Create an outbound firewall policy 101 in the corp zone that permits the Corp2 subnet 192.168.11.0/24 and NATs the traffic to the public interface ethernet0/1:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 101 out permit address 192.168.11.0 24 any
any nat-ip ethernet0/1
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 101 out# exit

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 25
avaya.com
June 2011
18 Create an outbound firewall policy 102 in the corp zone that permits the Guest subnet 192.168.14.0/24 and NATs the traffic to the public interface ethernet0/1:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 102 out permit address 192.168.14.0 24 any
any nat-ip ethernet0/1
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 102 out# exit
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# exit
19 View the modified firewall policy for the corp zone:
sr2330-1/configure# show firewall policy corp
Advanced: S - Self Traffic, F - Ftp-Filter, H - Http-Filter,
R - Rpc-Filter, N - Nat-Ip/Nat-Pool, L - Logging,
E - Policy Enabled, M - Smtp-Filter
Pri Dir Source Addr Destination Addr Sport Dport Proto Action Advanced
--- --- ----------- ---------------- ----------------- ------ --------
10 out 192.168.14.0/24 192.168.0.0/16 any any any DENY EL
11 out 192.168.0.0/16 192.168.14.0/24 any any any DENY EL
20 out 192.168.0.0/16 192.168.0.0/16 any any any PERMIT EL
21 in 192.168.0.0/16 192.168.0.0/16 any any any PERMIT EL
100 out 192.168.10.0/24 any any any any PERMIT NEL
101 out 192.168.11.0/24 any any any any PERMIT NEL
102 out 192.168.14.0/24 any any any any PERMIT NEL
1022 out any any any any any PERMIT SEL
1023 in any any any any any PERMIT SEL
1024 out any any any any any PERMIT EL
20 Save the changes to the startup configuration file:
sr2330-1/configure# save local

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 26
avaya.com
June 2011
2.3 Multiple Subnets with PAT and DMZ
The following scenario provides a step-by-step configuration example for how to configure a Secure Router to provide Port Address Translation (PAT) services for multiple internal subnets and translate the internal traffic to a single public interface with a static or dynamically assigned IPv4 address. In additional firewall policies will be defined in the dmz zone to permit HTTP and DNS services to servers located in the DMZ.
Figure 2.3 – Multiple Subnets with PAT and DMZ
2.3.1 CLI Example:
1 Access the global configuration context:
sr2330-1# configure terminal
sr2330-1/configure#
2 Access Fast Ethernet port 0/1 and name it Internet then assign the public IP address 76.7.100.25/24:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/1
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# description Internet
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# ip address 76.7.100.25 255.255.255.0
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# exit

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 27
avaya.com
June 2011
3 Access Fast Ethernet port 0/2 and name it DMZ then assign the public IP address 76.7.101.1/24:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/2
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/2)# description DMZ
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/2)# ip address 76.7.101.1 255.255.255.0
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/2)# exit
4 Access Gigabit Ethernet port 0/5 and name it Corp1 then assign the RFC 1918 private IP address 192.168.10.1/24:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/5
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# description Corp1
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# exit
5 Access Gigabit Ethernet port 0/6 and name it Corp2 then assign the RFC 1918 private IP address 192.168.11.1/24:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/6
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/6)# description Corp2
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/6)# ip address 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/6)# exit
6 View IP interfaces:
sr2330-1/configure# show ip interface format brief
Interface Type IP-Address/Mask Status Method
ethernet0/1 ETHERNET (802.3) 76.7.100.25/24 Up MANUAL
ethernet0/2 ETHERNET (802.3) 76.7.101.1/24 Up MANUAL
ethernet0/5 ETHERNET (802.3) 192.168.10.1/24 Up MANUAL
ethernet0/6 ETHERNET (802.3) 192.168.11.1/24 Up MANUAL
ethernet0/3 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/4 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/7 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/8 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
7 Define a default route. In this example the default route will point to the service providers router interface 76.7.100.1 with a cost of 1:
sr2330-1/configure# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 76.7.100.1 1
8 Verify the default route has been correctly defined. Note that the default route will only be displayed in route table if the default gateway can be reached by the Secure Router:
sr2330-1/configure# show ip route

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 28
avaya.com
June 2011
Codes: C - connected, S - static,D - DHCP, R - RIP, B - BGP, M - MPLS
O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
* - candidate default
IP Load balancing policy is per_flow
Gateway of last resort is 76.7.100.1 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 76.7.100.1, ethernet0/1
C 76.7.100.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/1
C 76.7.101.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/2
C 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, lo0
C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/5
C 192.168.11.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/6
9 Access the untrusted firewall zone named internet and add the public interface ethernet0/1:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall internet
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# interface ethernet0/1
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# exit
10 View the internet zone interface mappings:
sr2330-1/configure# show firewall interface internet
Interface Map Name
--------- --------
ethernet0/1 internet
11 Access the trusted firewall zone named dmz and add the dmz interface ethernet0/2:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall dmz
sr2330-1/configure/firewall dmz# interface ethernet0/2
12 View the dmz zone interface mappings:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall dmz# show firewall interface dmz
Interface Map Name
--------- --------
ethernet0/2 dmz

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 29
avaya.com
June 2011
13 Create an inbound firewall policy 10 in the dmz zone that permits the HTTP protocol to the web server 76.7.101.10:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall dmz# policy 10 in permit protocol tcp port any 80 address
any 76.7.101.10 32
sr2330-1/configure/firewall dmz/policy 10 in# exit
14 Create an inbound firewall policy 11 in the dmz zone that permits the DNS protocol to the DNS server 76.7.101.5:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall dmz# policy 11 in permit protocol udp port any 53 address
any 76.7.101.5 32
sr2330-1/configure/firewall dmz/policy 11 in# exit
sr2330-1/configure/firewall dmz# exit
15 View the modified firewall policy for the dmz zone:
sr2330-1/configure# show firewall policy dmz
Advanced: S - Self Traffic, F - Ftp-Filter, H - Http-Filter,
R - Rpc-Filter, N - Nat-Ip/Nat-Pool, L - Logging,
E - Policy Enabled, M - Smtp-Filter
Pri Dir Source Addr Destination Addr Sport Dport Proto Action Advanced
--- --- ----------- ---------------- ----------------- ------ --------
10 in any 76.7.101.10/32 any 80 tcp PERMIT EL
11 in any 76.7.101.5/32 any 53 udp PERMIT EL
1022 out any any any any any PERMIT SEL
1023 in any any any any any PERMIT SEL
1024 out any any any any any PERMIT EL
16 Access the trusted firewall zone named corp and add the private interfaces ethernet0/5 and ethernet0/6:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall corp
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# interface ethernet0/5
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# interface ethernet0/6
17 View the corp zone interface mappings:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# show firewall interface corp
Interface Map Name
--------- --------
ethernet0/5 corp
ethernet0/6 corp

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 30
avaya.com
June 2011
18 Create outbound and inbound firewall policies 20 and 21 in the corp zone to permit all Corp1 Corp2 inter-subnet communications:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 20 out permit address 192.168.0.0 16
192.168.0.0 16
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 20 out# exit
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 21 in permit address 192.168.0.0 16
192.168.0.0 16
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 21 in# exit
19 Create an outbound firewall policy 100 in the corp zone that permits the Corp1 subnet 192.168.10.0/24 and NATs the traffic to the public interface ethernet0/1:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 100 out permit address 192.168.10.0 24 any
any nat-ip ethernet0/1
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 100 out# exit
20 Create an outbound firewall policy 101 in the corp zone that permits the Corp2 subnet 192.168.11.0/24 and NATs the traffic to the public interface ethernet0/1:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 101 out permit address 192.168.11.0 24 any
any nat-ip ethernet0/1
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 101 out# exit
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# exit
21 View the modified firewall policy for the corp zone:
sr2330-1/configure# show firewall policy corp
Advanced: S - Self Traffic, F - Ftp-Filter, H - Http-Filter,
R - Rpc-Filter, N - Nat-Ip/Nat-Pool, L - Logging,
E - Policy Enabled, M - Smtp-Filter
Pri Dir Source Addr Destination Addr Sport Dport Proto Action Advanced
--- --- ----------- ---------------- ----------------- ------ --------
20 out 192.168.0.0/16 192.168.0.0/16 any any any PERMIT EL
21 in 192.168.0.0/16 192.168.0.0/16 any any any PERMIT EL
100 out 192.168.10.0/24 any any any any PERMIT NEL
101 out 192.168.11.0/24 any any any any PERMIT NEL
1022 out any any any any any PERMIT SEL
1023 in any any any any any PERMIT SEL
1024 out any any any any any PERMIT EL
22 Save the changes to the startup configuration file:
sr2330-1/configure# save local

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 31
avaya.com
June 2011
2.4 Single Subnet with Reverse NAT
The following scenario provides a step-by-step configuration example for how to configure a Secure Router to provide Port Address Translation (PAT) services for a single internal subnet and translate the internal traffic to a single public interface with a statically assigned IPv4 address. In addition the Secure Router will be configured to provide reverse NAT for HTTP and FTP protocols from the public interface to an internal server located in the corp zone.
Figure 2.4 – Single Subnet with Reverse NAT
2.4.1 CLI Example
1 Access the global configuration context:
sr2330-1# configure terminal
sr2330-1/configure#
2 Access Fast Ethernet port 0/1 and name it Internet then assign the public IP address 76.7.100.25/24:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/1
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# description Internet
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# ip address 76.7.100.25 255.255.255.0
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# exit

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 32
avaya.com
June 2011
3 Access Gigabit Ethernet port 0/5 and name it Corp then assign the RFC 1918 private IP address 192.168.10.1/24:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/5
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# description Corp
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# exit
4 View IP interfaces:
sr2330-1/configure# show ip interface format brief
Interface Type IP-Address/Mask Status Method
ethernet0/1 ETHERNET (802.3) 76.7.100.25/24 Up MANUAL
ethernet0/5 ETHERNET (802.3) 192.168.10.1/24 Up MANUAL
ethernet0/2 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/3 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/4 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/6 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/7 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/8 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
5 Define a default route. In this example the default route will point to the service providers router interface 76.7.100.1 with a cost of 1:
sr2330-1/configure# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 76.7.100.1 1
6 Verify the default route has been correctly defined. Note that the default route will only be displayed in route table if the default gateway can be reached by the Secure Router:
sr2330-1/configure# show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static,D - DHCP, R - RIP, B - BGP, M - MPLS
O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
* - candidate default
IP Load balancing policy is per_flow
Gateway of last resort is 76.7.100.1 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 76.7.100.1, ethernet0/1
C 76.7.100.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/1
C 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, lo0
C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/5

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 33
avaya.com
June 2011
7 Access the firewall zone named internet and add the public interface ethernet0/1:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall internet
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# interface ethernet0/1
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# exit
8 View the internet zone interface mappings:
sr2330-1/configure# show firewall interface internet
Interface Map Name
--------- --------
ethernet0/1 internet
9 Access the firewall zone named corp and add the private interface ethernet0/5:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall corp
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# interface ethernet0/5
10 View the corp zone interface mappings:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# show firewall interface corp
Interface Map Name
--------- --------
ethernet0/5 corp
11 Create an inbound firewall policy 10 in the corp zone that permits the HTTP protocol on the public interface 76.7.100.25 and NATs the traffic to the internal server 192.168.10.10:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 10 in address any 76.7.100.25 32 protocol tcp
port any 80 nat-ip 192.168.10.10
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 10 in# exit
12 Create inbound firewall policies 11 and 12 in the corp zone that permits both FTP Data and FTP File Transfer protocols on the public interface 76.7.100.25 and NATs the traffic to the internal server 192.168.10.10:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 11 in address any 76.7.100.25 32 protocol tcp
port any 20 nat-ip 192.168.10.10
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 11 in# exit
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 12 in address any 76.7.100.25 32 protocol tcp
port any 21 nat-ip 192.168.10.10
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 12 in# exit

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 34
avaya.com
June 2011
13 Create an outbound firewall policy 100 in the firewall zone corp that permits the source subnet 192.168.10.0/24 and NATs the traffic to the public interface ethernet0/1:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 100 out permit address 192.168.10.0 24 any
any nat-ip ethernet0/1
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 100 out# exit
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# exit
14 View the modified firewall policy for the corp zone:
sr2330-1/configure# show firewall policy corp
Advanced: S - Self Traffic, F - Ftp-Filter, H - Http-Filter,
R - Rpc-Filter, N - Nat-Ip/Nat-Pool, L - Logging,
E - Policy Enabled, M - Smtp-Filter
Pri Dir Source Addr Destination Addr Sport Dport Proto Action Advanced
--- --- ----------- ---------------- ----------------- ------ --------
10 in any 76.7.100.25/32 any 80 tcp PERMIT NEL
11 in any 76.7.100.25/32 any 20 tcp PERMIT NEL
12 in any 76.7.100.25/32 any 21 tcp PERMIT NEL
100 out 192.168.10.0/24 any any any any PERMIT NEL
1022 out any any any any any PERMIT SEL
1023 in any any any any any PERMIT SEL
1024 out any any any any any PERMIT EL
15 Save the changes to the startup configuration file:
sr2330-1/configure# save local

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 35
avaya.com
June 2011
2.5 Single Subnet with NAT Failover
The following scenario provides a step-by-step configuration example for how to configure a Secure Router to provide Port Address Translation (PAT) services for a single internal subnet and translate the internal traffic to a single public interface with a statically assigned IPv4 address. In addition the Secure Router will be configured to provide NAT failover to a secondary ISP providing user connectivity in the event of primary ISP link failure.
Figure 2.5 – Single Internal Subnet with NAT Failover
2.5.1 CLI Example
1 Access the global configuration context:
sr2330-1# configure terminal
sr2330-1/configure#
2 Access Fast Ethernet port 0/1 and name it ISP1 then assign the public IP address 76.7.100.25/24:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/1
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# description ISP1
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# ip address 76.7.100.25 255.255.255.0
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/1)# exit

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 36
avaya.com
June 2011
3 Access Fast Ethernet port 0/2 and name it ISP2 then enable the DHCP client:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/2
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/2)# description ISP2
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/2)# dhcp-client enable
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/2)# exit
4 Access Gigabit Ethernet port 0/5 and name it Corp then assign the RFC 1918 private IP address 192.168.10.1/24:
sr2330-1/configure# interface ethernet 0/5
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# description Corp
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
sr2330-1/configure/interface/ethernet (0/5)# exit
5 View IP interfaces:
sr2330-1/configure# show ip interface format brief
Interface Type IP-Address/Mask Status Method
ethernet0/1 ETHERNET (802.3) 76.7.100.25/24 Up MANUAL
ethernet0/2 ETHERNET (802.3) 76.7.10.2/24 Up DHCP
ethernet0/5 ETHERNET (802.3) 192.168.10.1/24 Up MANUAL
ethernet0/3 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/4 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/6 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/7 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
ethernet0/8 ETHERNET (802.3) unassigned Down -
6 Define a default route. In this example the default route will point to the service providers router interface 76.7.100.1 with a cost of 1:
sr2330-1/configure# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 76.7.100.1 1
Note – In this example the Secure Router will prefer the static default route to ISP1 until the primary interface fails at which point the default route learned from DHCP for the secondary ISP2 will be used.
7 Verify the default route has been correctly defined. Note that the default route will only be displayed in route table if the default gateway can be reached by the Secure Router:
sr2330-1/configure# show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static,D - DHCP, R - RIP, B - BGP, M - MPLS
O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
* - candidate default

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 37
avaya.com
June 2011
IP Load balancing policy is per_flow
Gateway of last resort is 76.7.100.1 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 76.7.100.1, ethernet0/1
C 76.7.10.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/2
C 76.7.100.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/1
C 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, lo0
C 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, ethernet0/5
Note – You can view all the routes in the routing table database by issuing the show ip route database command.
8 Access the firewall zone named internet and add the public interfaces ethernet0/1 and ethernet0/2:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall internet
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# interface ethernet0/1
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# interface ethernet0/2
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# exit
9 View the internet zone interface mappings:
sr2330-1/configure# show firewall interface internet
Interface Map Name
--------- --------
ethernet0/1 internet
ethernet0/2 internet
10 Access the firewall zone named corp and add the private interface ethernet0/5:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall corp
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# interface ethernet0/5
11 View the corp zone interface mappings:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# show firewall interface corp
Interface Map Name
--------- --------
ethernet0/5 corp

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 38
avaya.com
June 2011
12 Create an outbound firewall policy 100 in the firewall zone corp that permits the source subnet 192.168.10.0/24 and NATs the traffic to the public interface ethernet0/1:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# policy 100 out permit address 192.168.10.0 24 any
any nat-ip ethernet0/1
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp/policy 100 out# exit
sr2330-1/configure/firewall corp# exit
13 View the modified firewall policy for the corp zone:
sr2330-1/configure# show firewall policy corp
Advanced: S - Self Traffic, F - Ftp-Filter, H - Http-Filter,
R - Rpc-Filter, N - Nat-Ip/Nat-Pool, L - Logging,
E - Policy Enabled, M - Smtp-Filter
Pri Dir Source Addr Destination Addr Sport Dport Proto Action Advanced
--- --- ----------- ---------------- ----------------- ------ --------
100 out 192.168.10.0/24 any any any any PERMIT NEL
1022 out any any any any any PERMIT SEL
1023 in any any any any any PERMIT SEL
1024 out any any any any any PERMIT EL
14 Access the global firewall configuration and enable NAT failover using ethernet0/1 as the primary NAT interface and ethernet0/2 as the secondary NAT interface:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall global
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global# nat-failover ethernet0/1 ethernet0/2
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global# exit
15 View the NAT failover configuration:
sr2330-1/configure# show firewall nat-failover
Primary Interface Backup Interface
----------------- ----------------
ethernet0/1 ethernet0/2
16 Save the changes to the startup configuration file:
sr2330-1/configure# save local

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 39
avaya.com
June 2011
3. Additional Firewall Features
3.1 Bypass Trusted to Trusted Firewall Processing
You can optionally globally disable the firewall processing of traffic forwarded between trusted interfaces by issuing the global firewall bypass-trusted command. Once enabled the Secure Router will cease the inspection of traffic forwarded between trusted interfaces but will maintain inspection for untrusted trusted traffic as well as traffic forwarded from an untrusted interface destined to the Secure Router (self):
1 Access the global configuration context:
sr2330-1# configure terminal
sr2330-1/configure#
2 Access the firewall global parameters and disable the processing of trusted to trusted traffic:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall global
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global# bypass-trusted
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global# exit
3 Verify that the firewall processing of trusted to trusted traffic is bypassed:
sr2330-1/configure # show firewall bypass-trusted
bypass_trusted is enabled
4 Save the changes to the startup configuration file:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# save local
3.2 Enabling Application Layer Gateways (ALGs)
By default all Application Layer Gateways (ALGs) are disabled on the Secure Router. Using the CLI an administrator can enable or disable an individual ALG for a specific application or bulk enable common or all ALGs using a single command:
1 Access the global configuration context:
sr2330-1# configure terminal
sr2330-1/configure#
2 Access the firewall global ALG parameters:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall global
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global# algs
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global/algs#

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 40
avaya.com
June 2011
3a Enable an individual ALG. In this example the FTP ALG will be enabled:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global/algs# ftp
Firewall FTP Alg enabled
3b Enable typical ALGs (aim, aimudp, ftp, ike, msn, pptp, rpc, rtsp544, rtsp7070, stmp, tftp and web):
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global/algs# enable-typical
3c Enable all ALGs:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global/algs# enable-all
4 View enabled ALGs:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global/algs# show firewall algs
Firewall Algs Status
--------------- ---------
aim Enabled
aimudp Enabled
cuseeme Disabled
dns Disabled
ftp Enabled
gatekeeper Disabled
h323 Disabled
ike Enabled
ils Disabled
ils2 Disabled
..
..
pptp Enabled
rpc Enabled
rtsp554 Enabled
rtsp7070 Enabled
sip Disabled on port 5060
sip-tcp Disabled
sip-p2p-media Disabled
smtp Enabled
sql Disabled
tftp Enabled
web Enabled
6 Save the changes to the startup configuration file:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global/algs# save local

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 41
avaya.com
June 2011
3.3 Permitting Untrusted Traffic to Self
By default all inbound traffic received on an untrusted interface destined to the Secure Router (self) will be denied by the firewall. The following scenarios provide step-by-step configuration examples for how to permit ICMP, Telnet, SSH and SNMP management traffic destined to the Secure Router on an untrusted interface:
3.3.1 Permit ICMP
The following configuration example will permit ICMP traffic destined to the untrusted interface which will allow the Secure Router to respond to ICMP requests:
3.3.1.1 CLI Example
1 Access the global configuration context:
sr2330-1# configure terminal
sr2330-1/configure#
2 Access the firewall zone named internet and add policy 1000 that permits the ICMP protocol for inbound traffic destined to the public IPv4 interface:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall internet
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# policy 1000 in protocol icmp self
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet/policy 1000 in# exit
3 View the modified firewall policy for the internet zone:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# show firewall policy internet
Advanced: S - Self Traffic, F - Ftp-Filter, H - Http-Filter,
R - Rpc-Filter, N - Nat-Ip/Nat-Pool, L - Logging,
E - Policy Enabled, M - Smtp-Filter
Pri Dir Source Addr Destination Addr Sport Dport Proto Action Advanced
--- --- ----------- ---------------- ----------------- ------ --------
1000 in any any any any icmp PERMIT SEL
1024 out any any any any any PERMIT SEL
4 Save the changes to the startup configuration file:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# save local

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 42
avaya.com
June 2011
3.3.2 Permit Telnet
The following configuration example will permit telnet traffic destined to the untrusted interface which will allow the Secure Router to be managed over the public Internet using the telnet protocol:
3.3.2.1 CLI Example
1 Access the global configuration context:
sr2330-1# configure terminal
sr2330-1/configure#
2 Access the firewall zone named internet and add policy 1001 that permits the Telnet remote access from the source host 135.11.22.75 to the Secure Routers public IPv4 interface 76.7.100.25:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall internet
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# policy 1001 in address 135.11.22.75 32
76.7.100.25 32 service telnet self
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet/policy 1001 in# exit
3 View the modified firewall policy for the internet zone:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# show firewall policy internet
Advanced: S - Self Traffic, F - Ftp-Filter, H - Http-Filter,
R - Rpc-Filter, N - Nat-Ip/Nat-Pool, L - Logging,
E - Policy Enabled, M - Smtp-Filter
Pri Dir Source Addr Destination Addr Sport Dport Proto Action Advanced
--- --- ----------- ---------------- ----------------- ------ --------
1001 in 135.11.22.75/32 76.7.100.25/32 - telnet - PERMIT SEL
1024 out any any any any any PERMIT SEL
Note – The telnet service must be enabled on the Secure Router before telnet remote access will be permitted on the public IPv4 interface.
4 Save the changes to the startup configuration file:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# save local

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 43
avaya.com
June 2011
3.3.3 Permit SSH
The following configuration example will permit ssh traffic destined to the untrusted interface which will allow the Secure Router to be managed over the public Internet using the ssh protocol:
3.3.3.1 CLI Example
1 Access the global configuration context:
sr2330-1# configure terminal
sr2330-1/configure#
2 Access the firewall zone named internet and add policy 1002 that permits the SSH remote access from the source host 135.11.22.75 to the Secure Routers public IPv4 interface 76.7.100.25:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall internet
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# policy 1002 in address 135.11.22.75 32
76.7.100.25 32 service ssh self
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet/policy 1002 in# exit
3 View the modified firewall policy for the internet zone:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# show firewall policy internet
Advanced: S - Self Traffic, F - Ftp-Filter, H - Http-Filter,
R - Rpc-Filter, N - Nat-Ip/Nat-Pool, L - Logging,
E - Policy Enabled, M - Smtp-Filter
Pri Dir Source Addr Destination Addr Sport Dport Proto Action Advanced
--- --- ----------- ---------------- ----------------- ------ --------
1002 in 135.11.22.75/32 76.7.100.25/32 - ssh - PERMIT SEL
1024 out any any any any any PERMIT SEL
Note – The ssh service must be correctly configured and enabled on the Secure Router before ssh remote access will be permitted on the public IPv4 interface.
4 Save the changes to the startup configuration file:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# save local

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 44
avaya.com
June 2011
3.3.4 Permit SNMP
The following configuration example will permit snmp traffic destined to the untrusted interface which will allow the Secure Router to be managed over the public Internet using the snmp protocol:
3.3.4.1 CLI Example
1 Access the global configuration context:
sr2330-1# configure terminal
sr2330-1/configure#
2 Access the firewall zone named internet and add policy 1003 that permits the SNMP remote access from the source host 135.11.22.75 to the Secure Routers public IPv4 interface 76.7.100.25:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall internet
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# policy 1003 in address 135.11.22.75 32
76.7.100.25 32 service snmp self
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet/policy 1003 in# exit
3 View the modified firewall policy for the internet zone:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# show firewall policy internet
Advanced: S - Self Traffic, F - Ftp-Filter, H - Http-Filter,
R - Rpc-Filter, N - Nat-Ip/Nat-Pool, L - Logging,
E - Policy Enabled, M - Smtp-Filter
Pri Dir Source Addr Destination Addr Sport Dport Proto Action Advanced
--- --- ----------- ---------------- ----------------- ------ --------
1003 in 135.11.22.75/32 76.7.100.25/32 - snmp - PERMIT SEL
1024 out any any any any any PERMIT SEL
Note – The snmp service must be correctly configured and enabled on the Secure Router before snmp remote access will be permitted on the public IPv4 interface.
4 Save the changes to the startup configuration file:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall internet# save local

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 45
avaya.com
June 2011
3.4 Maximum Firewall Connections
Each trusted and untrusted zone supports a specific number of connections which can be increased or decreased as required. In addition the maximum number of connections can also be defined for traffic destined to the Secure Router (self). The following table highlights the default maximum connections for each virtual firewall zone supported by the Secure Router:
Zone Default Maximum Connections
Default Trusted Zone (corp) 2,500
User Defined Trusted Zones 2,500
Default Untrusted Zone (internet) 7,500
Internet Secure Router (self) 2,048
Table 3.4 – Default Maximum Firewall Connections
The following configuration example demonstrates how to increase the maximum connections for the default corp zone:
1 Access the global configuration context:
sr2330-1# configure terminal
sr2330-1/configure#
2 Access the global firewall configuration and set the maximum connections for the corp zone to 5000:
sr2330-1/configure# firewall global
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global# max-connection-limit corp 5000
3 View the summary for the corp zone:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global# show firewall connections corp summary
TCP UDP ICMP HTTP(S) Max Conn Active Conn
--- --- ---- ------- -------- -----------
1 13 0 0 5000 14
4 Save the changes to the startup configuration file:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global# save local
Note – Connection limits are only applied to new policies added to the zone. Existing policies will not inherit the new value. You can modify the max-connection-limit by defining the value in the zone.

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 46
avaya.com
June 2011
3.5 Stealth Mode
Stealth mode is disabled by default and maybe optionally enabled to hide the firewall and make it undetectable. When enabled the firewall will not send reset packets for TCP traffic when there is no corresponding matching policy for an incoming packet.
Stealth mode can be enabled for individual firewall zones as well as for traffic destined to the Secure Router (self) from an untrusted interface. The following configuration example demonstrates how to enable stealth mode for the untrusted internet zone and traffic destined to the Secure Router (self):
1 Access the global configuration context:
sr2330-1# configure terminal
sr2330-1/configure#
2 Access the global firewall configuration and enable stealth-mode for the internet zone as well as traffic destined to the Secure Router (self):
sr2330-1/configure# firewall global
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global# stealth-mode internet
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global# stealth-mode self
3 Verify stealth-mode configuration:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global# show firewall stealth-mode
Map Name Stealth-mode
-------- ------------
self enable
internet enable
corp disable
4 Save the changes to the startup configuration file:
sr2330-1/configure/firewall global# save local

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 47
avaya.com
June 2011
4. Firewall Debugging
4.1 Clearing Firewall Connections:
For troubleshooting and debugging active firewall connections can be cleared. Connections can be cleared for individual host IP addresses as well as all active connections.
Command Syntax:
sr2330-1# clear firewall connection [<ip-address> <all>]
Clearing connections to a specific host IP address:
sr2330-1# clear firewall connection 192.168.10.100
Clearing all connections:
sr2330-1# clear firewall connection all
Warning – Clearing firewall connections should only be performed for troubleshooting purposes. In production environments this command should only be invoked during a scheduled maintenance window.
4.2 Disable Firewall Processing
For troubleshooting and debugging firewall processing can be globally disabled using a debug command. This command is meant for debugging and troubleshooting purposes only and will be disruptive to all traffic using the firewall module.
Command Syntax:
sr2330-1# [no] debug disable-firewall
Disable Firewall:
sr2330-1# debug disable-firewall
WARNING! Enabling this command would temporarily disable firewall on this box.
Do you want to continue?(Y/N) Y
firewall feature on this box is disabled
Re-Enable Firewall:
sr2330-1# no debug disable-firewall
firewall feature on this box is enabled
Warning – Disabling the firewall should only be performed for troubleshooting purposes. In production environments this command should only be invoked during a scheduled maintenance window.

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 48
avaya.com
June 2011
4.3 Enabling / Disabling Debug Modules
The Secure Router supports various firewall debug modules which can be individually enabled or disabled to assist in troubleshooting firewall related issues. The following table highlights the supported firewall debug modules:
Debug Option Description
alg Enables or disables the firewall ALG debug module.
all Enables or disables all firewall debug modules except the firewall packet trace module.
attack Enables or disables the firewall attack (DoS Protect) debug module.
connections Enables or disables the firewall connections debug module
ip-reassembly Enables or disables the firewall ip-reassembly debug module
packet Enables or disables the firewall packet trace debug module
Table 4.3 – Firewall Debug Modules
Command Syntax:
sr2330-1# [no] debug firewall <debug-module>
Enable Firewall Debug Module(s):
sr2330-1# debug firewall all
Disable Firewall Debug Module(s):
sr2330-1# no debug firewall all
View Enabled Firewall Debug Modules:
sr2330-1# show debug firewall
Debug level Status
==================================================
Debug Firewall All levels Enabled
Debug Firewall Ip-Reassembly Enabled
Debug Firewall ALGs Enabled
Debug Firewall Attack Enabled
Debug Firewall Connection Enabled
Debug Firewall Packet Disabled
Warning – The debug modules should be used cautiously as excessive debug messages can overwhelm the CPU and impact the performance or console access into the Secure Router.

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 49
avaya.com
June 2011
4.4 Viewing Debug Messages
Firewall debug messages can be viewed locally on the router serial console or over a remote telnet / ssh session. By default the system console is configured to display critical events and will need to be modified to display any debug level events captured by the enabled firewall debug modules:
1 Access the system logging console configuration context:
sr2330-1# configure terminal
sr2330-1/configure# system logging
sr2330-1/configure/system/logging# console
2 Change the console priority to debug:
sr2330-1/configure/system/logging/console# priority debug
3 Debug events from the firewall debug modules will now be displayed on the console:
06/14/2011-14:42:06 FWL-CONN debug: [corp 100: src: 192.168.10.100:56768 -> dst: 208.67.222.222:53 udp protocol: domain] Connection timed out.Bytes transferred : 327
06/14/2011-14:42:06 FWL-CONN debug: [corp 100: src: 192.168.10.100:63544 -> dst: 208.67.222.222:53 udp protocol: domain] Connection timed out.Bytes transferred : 310
06/14/2011-14:42:06 FWL-CONN debug: [corp 100: src: 192.168.10.100:58217 -> dst: 208.67.222.222:53 udp protocol: domain] Connection timed out.Bytes transferred : 92
06/14/2011-14:42:06 FWL-CONN debug: [corp 100: src: 192.168.10.100:55192 -> dst: 66.220.151.76:443 tcp protocol: https] Connection closed.Bytes transferred : 6536
06/14/2011-14:42:12 FWL-CONN info: [corp 100: src: 192.168.10.100:55194 -> dst: 24.29.138.75:443 tcp protocol: https] RST packet with out of range SEQ number detected
06/14/2011-14:42:12 FWL-CONN info: [corp 100: src: 192.168.10.100:55194 -> dst: 24.29.138.75:443 tcp protocol: https] RST packet with out of range SEQ number detected
4 When debugging has been completed, change the console priority back to critical:
sr2330-1/configure/system/logging/console# priority critic
Tip – When remotely accessing the Secure Router using Telnet or SSH, terminal monitoring can be enabled by issuing the terminal monitor command in the global configuration context.

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 50
avaya.com
June 2011
5. Verification
5.1 Firewall Connections
The Secure Router maintains connection tables for each trusted and untrusted zone. Details can be viewed for all active connections within a zone as well as for specific connections based on host IP address, protocols and ports:
Example displaying all active connections for the trusted firewall zone corp:
sr2330-1# show firewall connections corp
P: Protocol. T - TCP, U - UDP, I - ICMP, A - AH, E - ESP, G - GRE, H - HTTP(S), O - Other
Life: Specified in Seconds
...
P Source Dest Life Bytes
- ------ ---- ---- -----
U 192.168.10.100:51770 208.67.222.222:53 120 43
208.67.222.222:53 192.168.10.100:51770 120 229
U 192.168.10.100:52821 208.67.222.222:53 93 31
208.67.222.222:53 192.168.10.100:52821 93 166
T 192.168.10.100:54958 17.172.236.156:5223 600 1196
17.172.236.156:5223 192.168.10.100:54958 600 2475
Tip – A summary of all the firewall connections can be viewed by issuing the show firewall connections summary command.
Example displaying all active HTTP connections for the trusted firewall zone corp:
sr2330-1# show firewall connections corp port 80
sr2330-1# show firewall connections corp protocol http
P: Protocol. T - TCP, U - UDP, I - ICMP, A - AH, E - ESP, G - GRE, H - HTTP(S), O - Other
Life: Specified in Seconds
...
P Source Dest Life Bytes
- ------ ---- ---- -----
H 192.168.10.100:55258 74.125.95.120:80 600 685
74.125.95.120:80 192.168.10.100:55258 600 13583
H 192.168.10.100:55255 74.125.93.99:80 600 3750
74.125.93.99:80 192.168.10.100:55255 600 21420
H 192.168.10.100:55257 74.125.93.99:80 600 1530

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 51
avaya.com
June 2011
74.125.93.99:80 192.168.10.100:55257 600 58364
H 192.168.10.100:55256 74.125.93.99:80 600 2734
74.125.93.99:80 192.168.10.100:55256 600 36089
Example displaying all active connections for the host IP address 192.168.10.100 in the trusted firewall zone corp:
sr2330-1# show firewall connections corp address 192.168.10.100
P: Protocol. T - TCP, U - UDP, I - ICMP, A - AH, E - ESP, G - GRE, H - HTTP(S), O - Other
Life: Specified in Seconds
...
P Source Dest Life Bytes
- ------ ---- ---- -----
T 192.168.10.100:55241 17.172.236.8:5223 114 1621
17.172.236.8:5223 192.168.10.100:55241 114 2677
Tip – Firewall connections can be cleared by issuing the clear firewall connection all command.
5.2 NAT Translations
The Secure Router maintains NAT translation tables for each trusted and untrusted zone. Details can be viewed for all active translations within a zone as well as for specific translations based on host IP address, protocols and ports:
Example displaying all active NAT translations for the trusted firewall zone corp:
sr2330-1# show firewall nat-translations corp
P: Protocol. T - TCP, U - UDP, I - ICMP, A - AH, E - ESP, G - GRE, H - HTTP(S), O - Other
P Source Dest NatAddr Bytes
- ----- ---- ------- -----
U 192.168.10.100:59536 208.67.222.222:53 76.7.100.25:30173 31
208.67.222.222:53 192.168.10.100:59536 76.7.100.25:30173 166
U 192.168.10.100:52412 208.67.222.222:53 76.7.100.25:30169 76
208.67.222.222:53 192.168.10.100:52412 76.7.100.25:30169 64
U 192.168.10.100:62510 208.67.222.222:53 76.7.100.25:30166 31
208.67.222.222:53 192.168.10.100:62510 76.7.100.25:30166 166
U 192.168.10.100:65331 208.67.222.222:53 76.7.100.25:30165 31
208.67.222.222:53 192.168.10.100:65331 76.7.100.25:30165 166
U 192.168.10.100:53535 208.67.222.222:53 76.7.100.25:30168 31
208.67.222.222:53 192.168.10.100:53535 76.7.100.25:30168 166
U 192.168.10.100:51459 208.67.222.222:53 76.7.100.25:30164 31

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 52
avaya.com
June 2011
208.67.222.222:53 192.168.10.100:51459 76.7.100.25:30164 166
T 192.168.10.100:54958 17.172.236.156:5223 76.7.100.25:30102 1621
17.172.236.156:5223 192.168.10.100:54958 76.7.100.25:30102 2677
Example displaying all active HTTP translations for the trusted firewall zone corp:
sr2330-1# show firewall nat-translations corp port 80
sr2330-1# show firewall nat-translations corp protocol http
P: Protocol. T - TCP, U - UDP, I - ICMP, A - AH, E - ESP, G - GRE, H - HTTP(S), O - Other
P Source Dest NatAddr Bytes
- ----- ---- ------- -----
H 192.168.10.100:55282 74.125.91.147:80 76.7.100.25:30409 1284
74.125.91.147:80 192.168.10.100:55282 76.7.100.25:30409 371
Example displaying all active translations for the host IP address 192.168.10.100 in the trusted firewall zone corp:
sr2330-1# show firewall nat-translations corp address 192.168.10.100
P: Protocol. T - TCP, U - UDP, I - ICMP, A - AH, E - ESP, G - GRE, H - HTTP(S), O - Other
P Source Dest NatAddr Bytes
- ----- ---- ------- -----
U 192.168.10.100:55971 208.67.222.222:53 76.7.100.25:30963 34
208.67.222.222:53 192.168.10.100:55971 76.7.100.25:30963 58
U 192.168.10.100:63650 208.67.222.222:53 76.7.100.25:30966 44
208.67.222.222:53 192.168.10.100:63650 76.7.100.25:30966 68
T 192.168.10.100:55262 17.172.237.53:5223 76.7.100.25:30389 1621
17.172.237.53:5223 192.168.10.100:55262 76.7.100.25:30389 2677
U 192.168.10.100:55004 208.67.222.222:53 76.7.100.25:30961 32
208.67.222.222:53 192.168.10.100:55004 76.7.100.25:30961 156
U 192.168.10.100:59518 208.67.222.222:53 76.7.100.25:30964 46
208.67.222.222:53 192.168.10.100:59518 76.7.100.25:30964 200
U 192.168.10.100:53222 208.67.222.222:53 76.7.100.25:30965 45
208.67.222.222:53 192.168.10.100:53222 76.7.100.25:30965 199
U 192.168.10.100:50534 208.67.222.222:53 76.7.100.25:30962 33
208.67.222.222:53 192.168.10.100:50534 76.7.100.25:30962 132

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 53
avaya.com
June 2011
5.3 Global Statistics
The Secure Router maintains global firewall statistics which can be viewed to determine how many packets have been forwarded or dropped by the firewall as well as how many packets have been forwarded between zones. Statistics can be displayed in a summary view (shown below) as well as in a more detailed verbose view:
Example displaying the firewall statistics summary:
sr2330-1# show firewall statistics [verbose]
Global packet statistics
------------------------
Received 1187
Transmitted 1187
Local delivery 0
Global packet discard statistics
--------------------------------
Inbound policy not found 0 , Outbound policy not found 0
Spoofed packets 0 , Data without connection 0
Invalid tcp request 0 , Invalid udp echo reply 0
Invalid icmp error msg 0 , Invalid icmp echo reply 0
Invalid ack value 0 , Access deleted policy 0
Src addr broadcast 0 , Dest addr broadcast 0
No route for dest 0 , Local delivery failed 0
Map-Name To Internet From Internet
-------- ----------- -------------
self 2 0
corp 530 474
Total 535 474
Tip – Firewall statistics can be cleared by issuing the clear firewall statistics command.

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 54
avaya.com
June 2011
6. Running Configuration Files
6.1 Section 2.1 Running Configuration
system logging
console
priority crit
exit console
syslog
module alarms local0 none
module dos local0 none
module forwarding local0 none
module voip-ssm-cdr local0 none
module voip-cdr local0 none
exit syslog
exit logging
hostname sr2330-1
log utc
event
exit event
terminal
exit terminal
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
module xdsl 1/1
exit xdsl
aaa
tacacs
exit tacacs
radius
primary_server
exit primary_server
secondary_server
exit secondary_server
exit radius
exit aaa
vlan database

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 55
avaya.com
June 2011
exit database
vlan classification
exit classification
bridge
mstp
exit mstp
exit bridge
lacp
exit lacp
interface ethernet 0/1
description Internet
ip address 76.7.100.25 255.255.255.0
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface ethernet 0/5
description Corp
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface console
aaa
exit aaa
exit console
gvrp
exit gvrp
snmp-server
chassis-id sr2330-1

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 56
avaya.com
June 2011
enable traps
exit traps
exit snmp-server
rmon
exit rmon
oam
cfm
enable
ethtype 88e6
exit cfm
exit oam
icmp_timestamp
telnet_banner
exit telnet_banner
sntp
exit sntp
ip proxy-dns
exit proxy-dns
ip host_add sr2330-1 192.168.24.10
ip load-balancing per-flow
ip icmp rate-limit 500
ip dhcps
exit dhcps
ip route 0.0.0.0/0 76.7.100.1
ipv6 icmp rate-limit 500
ipv6 unicast-routing
ipv6 load-balancing per-flow
mpls tunnel-mode uniform
firewall global
algs
dns
exit dns
exit algs
max-connection-limit self 2048
exit firewall
firewall internet
interface ethernet0/1
exit firewall
firewall corp
interface ethernet0/5
policy 100 out permit address 192.168.10.0 24 any any nat-ip ethernet0/1

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 57
avaya.com
June 2011
exit policy
policy 1024 out permit
exit policy
exit firewall
dst
no enable
exit dst
6.2 Section 2.2 Running Configuration
system logging
console
priority crit
exit console
syslog
module alarms local0 none
module dos local0 none
module forwarding local0 none
module voip-ssm-cdr local0 none
module voip-cdr local0 none
exit syslog
exit logging
hostname sr2330-1
log utc
event
exit event
terminal
exit terminal
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
module xdsl 1/1
exit xdsl
aaa
tacacs
exit tacacs
radius
primary_server

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 58
avaya.com
June 2011
exit primary_server
secondary_server
exit secondary_server
exit radius
exit aaa
vlan database
exit database
vlan classification
exit classification
bridge
mstp
exit mstp
exit bridge
lacp
exit lacp
interface ethernet 0/1
description Internet
ip address 76.7.100.25 255.255.255.0
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface ethernet 0/2
description Guest
ip address 192.168.14.1 255.255.255.0
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface ethernet 0/5
description Corp1

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 59
avaya.com
June 2011
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface ethernet 0/6
description Corp2
ip address 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface console
aaa
exit aaa
exit console
gvrp
exit gvrp
snmp-server
chassis-id sr2330-1
enable traps
exit traps
exit snmp-server
rmon
exit rmon
oam
cfm
enable
ethtype 88e6
exit cfm
exit oam

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 60
avaya.com
June 2011
icmp_timestamp
telnet_banner
exit telnet_banner
sntp
exit sntp
ip proxy-dns
exit proxy-dns
ip host_add sr2330-1 192.168.24.10
ip load-balancing per-flow
ip icmp rate-limit 500
ip dhcps
exit dhcps
ip route 0.0.0.0/0 76.7.100.1
ipv6 icmp rate-limit 500
ipv6 unicast-routing
ipv6 load-balancing per-flow
mpls tunnel-mode uniform
firewall global
algs
dns
exit dns
exit algs
max-connection-limit self 2048
exit firewall
firewall internet
interface ethernet0/1
exit firewall
firewall corp
interface ethernet0/2 ethernet0/5 ethernet0/6
policy 10 out deny address 192.168.14.0 24 192.168.0.0 16
exit policy
policy 11 out deny address 192.168.0.0 16 192.168.14.0 24
exit policy
policy 20 out permit address 192.168.0.0 16 192.168.0.0 16
exit policy
policy 21 in permit address 192.168.0.0 16 192.168.0.0 16
exit policy
policy 100 out permit address 192.168.10.0 24 any any nat-ip ethernet0/1
exit policy
policy 101 out permit address 192.168.11.0 24 any any nat-ip ethernet0/1
exit policy

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 61
avaya.com
June 2011
policy 102 out permit address 192.168.14.0 24 any any nat-ip ethernet0/1
exit policy
policy 1024 out permit
exit policy
exit firewall
dst
no enable
exit dst
6.3 Section 2.3 Running Configuration
system logging
console
priority crit
exit console
syslog
module alarms local0 none
module dos local0 none
module forwarding local0 none
module voip-ssm-cdr local0 none
module voip-cdr local0 none
exit syslog
exit logging
hostname sr2330-1
log utc
event
exit event
terminal
exit terminal
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
module xdsl 1/1
exit xdsl
aaa
tacacs
exit tacacs
radius

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 62
avaya.com
June 2011
primary_server
exit primary_server
secondary_server
exit secondary_server
exit radius
exit aaa
vlan database
exit database
vlan classification
exit classification
bridge
mstp
exit mstp
exit bridge
lacp
exit lacp
interface ethernet 0/1
description Internet
ip address 76.7.100.25 255.255.255.0
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface ethernet 0/2
description DMZ
ip address 76.7.101.1 255.255.255.0
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface ethernet 0/5

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 63
avaya.com
June 2011
description Corp1
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface ethernet 0/6
description Corp2
ip address 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface console
aaa
exit aaa
exit console
gvrp
exit gvrp
snmp-server
chassis-id sr2330-1
enable traps
exit traps
exit snmp-server
rmon
exit rmon
oam
cfm
enable
ethtype 88e6
exit cfm

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 64
avaya.com
June 2011
exit oam
icmp_timestamp
telnet_banner
exit telnet_banner
sntp
exit sntp
ip proxy-dns
exit proxy-dns
ip host_add sr2330-1 192.168.24.10
ip load-balancing per-flow
ip icmp rate-limit 500
ip dhcps
exit dhcps
ip route 0.0.0.0/0 76.7.100.1
ipv6 icmp rate-limit 500
ipv6 unicast-routing
ipv6 load-balancing per-flow
mpls tunnel-mode uniform
firewall global
algs
dns
exit dns
exit algs
max-connection-limit self 2048
exit firewall
firewall internet
interface ethernet0/1
exit firewall
firewall corp
interface ethernet0/5 ethernet0/6
policy 20 out permit address 192.168.0.0 16 192.168.0.0 16
exit policy
policy 21 in permit address 192.168.0.0 16 192.168.0.0 16
exit policy
policy 100 out permit address 192.168.10.0 24 any any nat-ip ethernet0/1
exit policy
policy 101 out permit address 192.168.11.0 24 any any nat-ip ethernet0/1
exit policy
policy 1024 out permit
exit policy
exit firewall

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 65
avaya.com
June 2011
firewall dmz
interface ethernet0/2
policy 10 in permit address any any 76.7.101.10 32 protocol tcp port any 80
exit policy
policy 11 in permit address any any 76.7.101.10 32 protocol udp port any 53
exit policy
policy 1024 out permit
exit policy
exit firewall
dst
no enable
exit dst
6.4 Section 2.4 Running Configuration
system logging
console
priority crit
exit console
syslog
module alarms local0 none
module dos local0 none
module forwarding local0 none
module voip-ssm-cdr local0 none
module voip-cdr local0 none
exit syslog
exit logging
hostname sr2330-1
log utc
event
exit event
terminal
exit terminal
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
module xdsl 1/1
exit xdsl

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 66
avaya.com
June 2011
aaa
tacacs
exit tacacs
radius
primary_server
exit primary_server
secondary_server
exit secondary_server
exit radius
exit aaa
vlan database
exit database
vlan classification
exit classification
bridge
mstp
exit mstp
exit bridge
lacp
exit lacp
interface ethernet 0/1
description Internet
ip address 76.7.100.25 255.255.255.0
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface ethernet 0/5
description Corp
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module
exit module
chassis

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 67
avaya.com
June 2011
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface console
aaa
exit aaa
exit console
gvrp
exit gvrp
snmp-server
chassis-id sr2330-1
enable traps
exit traps
exit snmp-server
rmon
exit rmon
oam
cfm
enable
ethtype 88e6
exit cfm
exit oam
icmp_timestamp
telnet_banner
exit telnet_banner
sntp
exit sntp
ip proxy-dns
exit proxy-dns
ip host_add sr2330-1 192.168.24.10
ip load-balancing per-flow
ip icmp rate-limit 500
ip dhcps
exit dhcps
ip route 0.0.0.0/0 76.7.100.1
ipv6 icmp rate-limit 500
ipv6 unicast-routing
ipv6 load-balancing per-flow
mpls tunnel-mode uniform
firewall global
algs

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 68
avaya.com
June 2011
dns
exit dns
exit algs
max-connection-limit self 2048
exit firewall
firewall internet
interface ethernet0/1
exit firewall
firewall corp
interface ethernet0/5
policy 10 in permit address any any 76.7.100.25 32 protocol tcp port any 80 nat-ip
192.168.10.10
exit policy
policy 11 in permit address any any 76.7.100.25 32 protocol tcp port any 20 nat-ip
192.168.10.10
exit policy
policy 12 in permit address any any 76.7.100.25 32 protocol tcp port any 21 nat-ip
192.168.10.10
exit policy
policy 100 out permit address 192.168.10.0 24 any any nat-ip ethernet0/1
exit policy
policy 1024 out permit
exit policy
exit firewall
dst
no enable
exit dst
6.5 Section 2.5 Running Configuration
system logging
console
priority crit
exit console
syslog
module alarms local0 none
module dos local0 none
module forwarding local0 none
module voip-ssm-cdr local0 none
module voip-cdr local0 none
exit syslog
exit logging

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 69
avaya.com
June 2011
hostname sr2330-1
log utc
event
exit event
terminal
exit terminal
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
module xdsl 1/1
exit xdsl
aaa
tacacs
exit tacacs
radius
primary_server
exit primary_server
secondary_server
exit secondary_server
exit radius
exit aaa
vlan database
exit database
vlan classification
exit classification
bridge
mstp
exit mstp
exit bridge
lacp
exit lacp
interface ethernet 0/1
description ISP1
ip address 76.7.100.25 255.255.255.0
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 70
avaya.com
June 2011
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface ethernet 0/2
description ISP2
dhcp-client request-default-router
dhcp-client enable
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface ethernet 0/5
description Corp
ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
aaa
exit aaa
qos
module
exit module
chassis
exit chassis
exit qos
exit ethernet
interface console
aaa
exit aaa
exit console
gvrp
exit gvrp
snmp-server
chassis-id sr2330-1
enable traps
exit traps
exit snmp-server

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 71
avaya.com
June 2011
rmon
exit rmon
oam
cfm
enable
ethtype 88e6
exit cfm
exit oam
icmp_timestamp
telnet_banner
exit telnet_banner
sntp
exit sntp
ip proxy-dns
exit proxy-dns
ip host_add sr2330-1 192.168.24.10
ip pname_server 208.67.222.222
ip name_server 208.67.220.220
ip load-balancing per-flow
ip icmp rate-limit 500
ip route 0.0.0.0/0 76.7.100.1
ipv6 icmp rate-limit 500
ipv6 unicast-routing
ipv6 load-balancing per-flow
mpls tunnel-mode uniform
firewall global
algs
dns
exit dns
exit algs
max-connection-limit self 2048
nat-failover ethernet0/1 ethernet0/2
exit firewall
firewall internet
interface ethernet0/1 ethernet0/2
exit firewall
firewall corp
interface ethernet0/5
policy 100 out permit address 192.168.10.0 24 any any nat-ip ethernet0/1
exit policy
policy 1024 out permit

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 72
avaya.com
June 2011
exit policy
exit firewall
dst
no enable
exit dst

Avaya Inc. – External Distribution 73
avaya.com
June 2011
7. Reference Documentation
Publication Number Document Title
NN47263-600 Avaya Secure Router 2330 / 4134 Security Configuration and Management
NN47263-507 Avaya Secure Router 2330 / 4134 Command Line Reference
© 2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Avaya and the Avaya Logo are trademarks of Avaya Inc. and are registered in the United States and other countries. All trademarks identified by ®, TM or SM are registered marks, trademarks, and service marks, respectively, of Avaya Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Avaya may also have trademark rights in other terms used herein. References to Avaya include the Nortel Enterprise business, which was acquired as of December 18, 2009.