Name: Date: Period: - Edl and On the sketch below, label the following: outside cell, inside cell....
Transcript of Name: Date: Period: - Edl and On the sketch below, label the following: outside cell, inside cell....
Name: _____________________________________________ Date: __________________ Period: ___________
Chapter 48: Nervous Systems
1) Define
a) Nerve net
b) Nerve
c) Cephalization
d) Ganglia
2) For the animals sketched below, give the common name of the organism and its phylum. Also note the important
features of its nervous system.
3) Review from taxonomy:
a) Which phylum has a nerve net?
b) Which phylum showed cephalization?
c) Which phylum has a ventral nerve cord?
d) Which phylum has a dorsal nerve cord?
4) The CNS is made up of a ________________________ and _____________________________________
5) Label the following: stimulus, receptors
(sensors), sensory neuron, interneuron, spinal
cord, gray matter, white matter, motor
neuron, effector (muscle).
6) What is a neuron?
7) Neurons can be placed into three groups, based on their location and function. Fill in the table below
Type of Neuron Function
Sensory
Interneuron
Motor
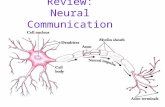
8) Label the following elements of this figure: cell body, dendrites, axon, synapse, presynaptic cell, postsynaptic
cell, synaptic vesicles, synaptic terminal, and neurotransmitter.
9) What are glial cells?
a) List the types below with a brief description of each
10) What is the typical resting potential of a neuron?
11) On the sketch below, label the following: outside cell, inside cell. Show where the concentrations of Na+ and
K+ are highest.
12) In a resting neuron, the outside of the membrane is positively charged relative to the inside of the
membrane. If positively charged ions flow out, the difference in charge between the two sides of the
membrane becomes greater. What is the increase in the magnitude of the membrane potential called?
13) When a stimulus is applied, ion channels will open. If positively charged ions flow in, the membrane is said
to depolarize. If depolarization causes the membrane potential to drop to a critical value, a wave of
depolarization will follow. What is this critical value called?
14) What is an action potential? What is meant by an “all or none” response to a stimulus?
15) What are the two types of glial cells that produce myelin sheaths?
16) How does a myelin sheath speed impulse transmission?
17) In the disease multiple sclerosis, the myelin sheaths harden and deteriorate. How would this affect nervous
system function?
18) Figure 48.13 contains almost all you need to know about nerve impulse transmission, so it is worth some careful study time. Let’s approach it in steps.
a. Label Na+, K+, and their respective ion channels. b. Label the Resting state figure. Are the Na+ and K+ channels open, or closed? ________________ c. Label Depolarization. What triggers depolarization? ____________________ What channels open?
______________ What occurs if the depolarization threshold is reached? _______________ d. Label Stage 4 in the figure Repolarization. How is the charge on the membrane reestablished?
_______________________________________________________________ e. Label these regions of the graph: x- and y-axes, threshold, resting potential, depolarization, action
potential, and repolarization.
19) When the wave of depolarization arrives at the synaptic terminal, calcium ion channels open. What occurs to the synaptic vesicles as the Ca2+ level increases?
20) What is contained within the synaptic vesicles? 21) Label the figure below: synaptic vesicle, neurotransmitter, calcium ion channel, presynaptic membrane,
postsynaptic membrane, and synapse.
22) Explain how an action potential is transmitted from one cell to another across a synapse by summarizing
what is shown above in six steps
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
23) There are many different types of neurotransmitters. Each neuron secretes only ONE type of neurotransmitter. Some neurotransmitters hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane. Are these excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitters?
24) Define and explain summation.
25) A single postsynaptic neuron can be affected by neurotransmitter molecules released by many other neurons, some releasing excitatory and some releasing inhibitory neurotransmitters. What will determine whether an action potential is generated in the postsynaptic neuron?
26) Fill in the table below
Neurotransmitter Overall Effect/Function Functional Class
Acetylcholine
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
dopamine
Serotonin
GABA
Glutamate
glycine
Substance P
Endorphins
Nitric oxide (NO)
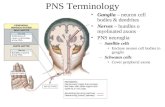
27) What is the general function of the peripheral nervous system?
28) Figure 48.21 shows the branches of the peripheral nervous system. Label these branches. Which branch is
sometimes called the “voluntary nervous system”? Which one is often termed “involuntary?” Include these
terms on the diagram below.
29) When the sympathetic nervous system is stimulated, what effect does it have on heart rate?
When the parasympathetic nervous system is stimulated, what effect does it have on peristalsis?
30) Which division of your autonomic nervous system would likely be activated if you learned that an exam you
had forgotten about would start in 5 minutes? Explain your answer.
a. Describe the physiological responses that would occur.
31) Label the following structures on the figure of the brain, and give a primary function of each labeled structure.
brainstem (includes pons, medulla)
cerebrum
cerebellum
thalamus
hypothalamus
32) Fill in the table below
Lobe of cerebral cortex General functions
33) What is the limbic system? What parts of the brain make up the limbic system? What kinds of behaviors are
connected to this part of the brain?
34) Briefly describe each of the following:
a) Schizophrenia
b) Depression
c) Alzheimer’s disease
d) Parkinson’s disease
Chapter 49: Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
1) What are the types of sensory receptors? What do they each detect?
2) Label the parts of the ear:
3) Describe how sound “travels” within the ear to the auditory nerve.
4) Describe how smell is interpreted by the brain by labeling the diagram below:
5) Label the parts of the eye:
6) What are the photoreceptors of the eye? What does each detect?
Nervous System Questions
1. Match the structure with the correct letter from the
diagram below.
______ Dendrites
______ Schwann cell nucleus
______ Axon
______ Node of Ranvier
______ Cell body
______ Myelin sheath
______ Nucleus
______ Axon terminals
______ Neurilemma
______ End bulbs
2. Identify each of the following as true of the sensory neuron (SN) or the motor neuron (MN)
______ anterior root
______ posterior root
______ has a ganglion
______ lacks a ganglion
______ carriers impulses from receptor to
spinal cord
______ carriers impulses from spinal cord to
effector
______ has a relatively long dendrite &
short axon
______ has relatively short dendrites & a
long axon
______ enters spinal cord
______ exits spinal cord
3. Match the following parts with the correct
letter from the diagram.
______ Dorsal Root
______ Dorsal Root Ganglion
______ Effector
______ Interneuron
______ Receptor
______ Ventral Root
4. Match the following parts with the correct
letter from the diagram.
______ Motor neuron axon
______ Sensory neuron axon
______ Sensory neuron cell body
______ Sensory neuron dendrite
5. Match the description with the correct event.
A. Depolarization
B. Hyperpolarization
C. Refractory Period
D. Repolarization
E. Resting potential
______ More Na+ outside cell; more K+ inside cell
______ Na+ ion gates open and Na+ rush into cell
______ K+ gates open & Na+ gates close; K+ rush out of cell
______ More K+ moved out of cell than necessary to reestablish charge across membrane
______ Na+ pumped out of cell & K+ pumped into cell
6. How is the resting potential different from repolarization?
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
7. Answer the following questions regarding the transmission of a nerve impulse.
a) What maintains the excess of Na+ outside the cell and an excess of K+ inside the cell during the resting
potential stage?
___________________________________________________________________________________
b) The resting potential of a neuron (-70mV) indicates that the inside of the cell is more negative than the
outside. What two factors cause this negative charge?
___________________________________________________________________________________
c) What causes Na+ channels (gates) to open?
___________________________________________________________________________________
d) What causes Na+ to rush into the neuron during depolarization?
___________________________________________________________________________________
e) What causes K+ to rush out of the neuron during repolarization?
___________________________________________________________________________________
f) What causes the neuron to be hyperpolarized?
___________________________________________________________________________________
g) What reestablishes the original distribution of K+ and Na+ during the refractory period?
___________________________________________________________________________________
8. Listed below is the distribution / movement of Na+ and K+ during the transmission of a nerve impulse. Put
the following in the correct order.
___1__ More Na+ outside the neuron; more K+ inside the neuron
______ Na+ gates open
______ Na+ gates close & K+ gates open
______ Na+ rushes into the neuron
______ K+ rushes out of the neuron
______ More K+ is outside the neuron; more Na+ is inside the neuron
______ Na+ is pumped out of the cell & K+ is pumped into the cell
9. Match the structure with the correct
letter from the diagram below.
______ Neurotransmitter
______ Postsynaptic membrane
______ Presynaptic membrane
______ Receptor site (protein)
______ Synaptic cleft
______ Synaptic end bulb
______ Synaptic vesicle
10. Why was cephalization important in the evolution of the animal kingdom?
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________
11. Use Figure 48.22 to identify the autonomic nervous system division (Parasympathetic or Sympathetic)
described in each of the following.
______ Long preganglionic fibers
______ Short preganglionic fibers
______ Long postganglionic fibers
______ Short postganglionic fibers
______ Ganglia near the CNS
______ Ganglia near the effector
______ Originate from the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spine
______ Originate from the brain and sacrum
______ Constricts the pupil
______ Dilates the pupil
______ Increases activity of the digestive system
______ Decreases the activity of the digestive system
______ Stimulates defecation and urination
______ Constricts respiratory passageways
______ Dilates respiratory passageways
______ Reduces heart rate and the force of cardiac contractions
______ Increases heart rate and the force of cardiac contractions
______ Centers on relaxation, food processing, and energy absorption
______ Prepares the body for emergencies; triggers the fight or flight response
12. Match the structure with the correct function.
A) Brainstem
B) Epithalamus
C) Cerebellum
D) Thalamus
E) Hypothalamus
F) Cerebral hemispheres
______ Contains centers that control breathing, heart and blood vessel activity, swallowing, vomiting, digesting
______ Helps coordinate large-scale body movements such as walking
______ Contains centers for receipt and integration of several types of sensory information
______ Most of descending axons cross from one side to CNS to the other; results in right side of brain controlling left side of body
______ Medulla, pons, midbrain
______ Coordination of movement
______ Receives information about position of joints, length of muscles, information from auditory and visual systems, and information from motor pathways; uses information to provide automatic coordination of movements and balance
______ Contains the pineal body and choroid plexus
______ Major integration center; major input center for sensory information going to cerebrum; main output center for motor information leaving cerebrum
______ Produces hormones; contains centers that regulate body temperature, hunger, thirst, fight-or-flight response, sexual responses, pleasure
______ Center for higher thought processes; thinking, speech, vision, hearing