Muscular System Study Guide
-
Upload
james-dauray -
Category
Documents
-
view
112 -
download
4
description
Transcript of Muscular System Study Guide

Name: __________________________ Class: _____________________ Date: _____________________
Muscular System Study Guide
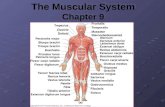
Be able to label each of the following muscles: Frontalis, temporalis, orbicularis oculi, zygomaticus, orbicularis oris, masseter, sternocleidomastoid, pectoralis major, deltoid, biceps brachii, rectus abdominis, external oblique, serratus anterior, adductor longus, gracilis, sartorius, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, fibularis longus, soleus, tibialis anterior.
Biology Teaching Resources http://www.aurumscience.com Page 1

Name: ___________________________ Class: ______________________ Date: ____________________
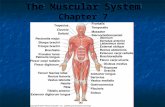
Be able to label each of the following muscles: Trapezius, deltoid, triceps brachii, latissimus dorsi, external oblique, gluteus medius, gluteus maximus, biceps femoris, semtendinosus, gastrocnemius, soleus.
Page 2

Name: ___________________________ Class: ______________________ Date: ____________________
Be able to label each of the following muscles: Frontalis, temporalis, orbicularis oculi, orbicularis oris, zygomaticus, masseter, buccinators, sternocleidomastoid, trapezius
Be able to label each of the following muscles: Trapezius, infraspinatus, deltoid, triceps brachii, teres major, serratus anterior
Page 3

Name: ___________________________ Class: ______________________ Date: ____________________
Be able to label each of the following muscles: Deltoid, pectoralis major, biceps brachii, triceps brachii, rectus abdominis, external oblique, internal oblique, serratus anterior, brachioradialis, extensor digitorum, extensor carpi ulnaris.
Be able to label each of the following muscles: Gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris, sartorius, gracilis, tensor fascia latae, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, gastrocnemius, soleus.
Page 4

Name: ___________________________ Class: ______________________ Date: ____________________
Vocabulary1. Motor Neuron –
2. Sarcolemma –
3. T-Tubules –
4. Sarcoplasmic Reticulum -
5. Acetylcholine –
6. Hypertrophy –
7. Atrophy –
8. Origin –
9. Insertion –
10. Flexion –
11. Extension –
12. Hyperextension –
13. Adduction –
14. Abduction –
15. Elevation –
16. Depression -
Page 5

Name: ___________________________ Class: ______________________ Date: ____________________
Short AnswerBe able to answer questions similar to these.
17. Which of the three types of muscle tissue is voluntary?
18. Motor neurons release acetylcholine to stimulate muscles to contract. What happens to the acetylcholine when the nerve signal stops and the muscle needs to relax?
19. How is the nerve signal sent to every muscle fiber simultaneously?
20. Which electrolyte is especially important in muscle contractions?
21. The diagram below illustrates a muscle fiber before contraction:
Page 6

Name: ___________________________ Class: ______________________ Date: ____________________
…and after contraction:
Explain what happens with the actin (thin filaments) and myosin (thick filaments) to cause this change.
Page 7

Name: ___________________________ Class: ______________________ Date: ____________________
22. Label the myofibril, muscle, muscle fiber, and fascicle on the diagram below.
23. Name the connective tissue covering each of these structures:
Muscle –
Fascicle –
Muscle Fiber (cell) -
24. Describe all of the steps required in a muscle contraction, beginning with the motor neuron.
25. Why do muscles appear to bulge and become physically larger when contracted?
26. What three factors influence how long a muscle can contract?
27. What is the difference between ATP and ADP?
28. Explain what the muscle is doing in terms of ATP, glucose, mitochondria, creatine, glycogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
a. Resting
b. Moderate Activity
c. Intense Activity
Page 8

Name: ___________________________ Class: ______________________ Date: ____________________
29. Why is relying on glycolysis not a desirable way to produce ATP in muscles?
30. For each of the types of muscle fiber, explain what type of activity it is best suited for, and how specifically it is designed differently to do this.
31. Fill out the chart of muscle disorders below:
Disorder Cause Symptoms / Effects
Polio Virus Destroys motor neurons, causing paralysis.
Muscular Dystrophy
Curare
Tetanus
Botulism
32. Why are muscle cells unable to divide by mitosis?
33. What is the relationship between a muscle twitch, summation, incomplete tetanus, and complete tetanus?
Page 9

Name: ___________________________ Class: ______________________ Date: ____________________
Muscle Movement
Frontalis
Eyelid movement – blinking, etc.
Buccinator
Zygomaticus
Chewing and elevating the mandible.
Opening and closing the lips
Sternocleidomastoid
Pectoralis major
Flexes the trunk; Aids in childbirth and defecation.
External oblique
Internal oblique
Transversus abdominis
Raises and lowers the scapula, such as in shrugging.
Flexes the arm at the elbow.
Extends the arm at the elbow.
Deltoid
Latissimus dorsi
Infraspinatus
Adducts the humerus with t he latissimus dorsi.
Extends the wrist (2 muscles)
Extends the fingers.
Flexes the forearm.
Page 10

Name: ___________________________ Class: ______________________ Date: ____________________
Muscle Movement
Gluteus maximus
Gluteus medius
Flexes the leg at the knee.
Flexes the leg at the knee.
Flexes the leg at the knee.
Gastrocnemius
Soleus
Extends the leg at the knee.
Extends the leg at the knee.
Extends the leg at the knee.
Extends the leg at the knee.
Used while checking your shoe to see if you stepped in something.
Flexes the foot.
Fibularis muscles
Page 11