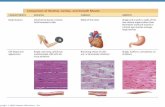
Muscle Function and Anatomy. Function of Muscle Motion of joints Movement of body fluids - pump...
-
date post
21-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
3
Transcript of Muscle Function and Anatomy. Function of Muscle Motion of joints Movement of body fluids - pump...

Muscle Function and Anatomy

Function of Muscle
Motion of joints Movement of body fluids - pump blood,
peristalsis Regulation of body fluids - bladder Body stability Heat production - 85%

Muscle Architecture

How Are Muscles Built?
In circular sections Deepest section
contains two proteins Myosin Actin
Myosin is surrounded by actin

Myofibrils
Bundles of actin and myosin


Muscle Fiber
Among others things, a muscle fiber contains many groups of myofibrils



Fascicle A group of muscle fibers bundled
together.

The Whole Muscle

The Whole Muscle

Muscle Membranes

Tendons All 3 membranes converge to form a tendon
which connects the muscle to the bone

Muscle Fiber Arrangement p. 25
Pennate muscles Greater cross sectional area – greater force
(strength) production
Parallel muscles Longer muscles – greater range of motion

Parallel muscles1. Flat (rectus abdominus)2. Fusiform (biceps)3. Strap (sartorius)4. Radiate (trapezius)5. Spincter Pennate1. Unipennate (biceps
femoris)2. Bipennate (rectus femoris)3. Multipennate (deltoid)
Muscle Fiber Arrangement
Strap

Types of Muscle Contraction p. 28
Isometric (Static) Isotonic (Dynamic)
Concentric Eccentric

Types of Muscle Contraction
Concentric contraction - If muscle force is greater than the resistance
Static or Isometric contraction - If muscle force is equal to the resistance
Eccentric contraction - If muscle force is less than the resistance

Lengthens Lengthens

Eccentric Contraction
Used to control agonist and prevent over lengthening of the antagonist.
Example: triceps lowers dumbbell while biceps ’controls’ the triceps activity (action).
Causes more damage than other types
Greater repair required… …producing a stronger
muscle Also, results in more muscle
soreness.

TABLE 2.1 Type of Contraction
Isometric
Isotonic
Concentric Eccentric
Agonist muscle No change Shortening Lengthening
Antagonist No change Lengthening Shortening
Joint angle No change In direction of force In direction of external resistance
Direction of body part Against immovable object
Against gravity or external force
Consistent with gravity or external force
Motion Pressure but no motion Causes motion Causes motion
Description Static Dynamic shortening Dynamic lengthening
Muscle force v. Resistance
F = R F > R F < R
Speed Equal to resistance Faster than the inertia of the resistance
Slower than the speed of gravity or applied inertial forces
Acceleration or Deceleration
Zero A D
Symbol = + -

ROLE OF MUSCLES
Agonist – prime mover Antagonist – have an action opposite to
the agonist Stabilizers – fixate or stabilize the joint Synergists – assist or guiding Neutralizers – counteract or neutralize
movements

Agonist and Antagonist

Types of Muscle Fibers
Fast twitch Slow twitch

Questions?